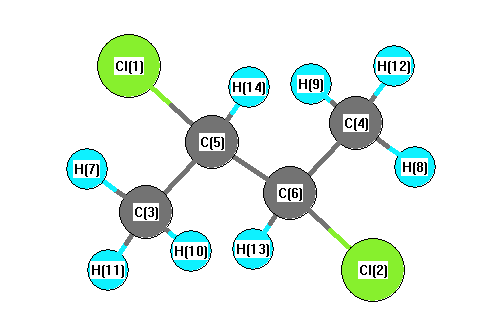
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HSEh1PBE/3-21G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
3181 |
3064 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Ag |
3172 |
3056 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Ag |
3160 |
3044 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Ag |
3087 |
2974 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Ag |
1552 |
1495 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Ag |
1551 |
1494 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
Ag |
1469 |
1415 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
Ag |
1422 |
1370 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
Ag |
1282 |
1235 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
Ag |
1218 |
1173 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
Ag |
1159 |
1117 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
Ag |
1053 |
1015 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
Ag |
875 |
843 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
Ag |
673 |
648 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
Ag |
487 |
469 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
Ag |
340 |
327 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
Ag |
280 |
270 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
Ag |
245 |
236 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
Au |
3193 |
3076 |
8.19 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
Au |
3176 |
3059 |
7.81 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
Au |
3163 |
3047 |
4.12 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
Au |
3087 |
2974 |
7.42 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
Au |
1553 |
1496 |
27.95 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
Au |
1547 |
1490 |
18.33 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
Au |
1469 |
1415 |
52.41 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
Au |
1359 |
1309 |
1.21 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
Au |
1221 |
1176 |
48.93 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
Au |
1123 |
1082 |
16.62 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
Au |
1064 |
1024 |
27.82 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
Au |
1012 |
975 |
28.31 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
Au |
628 |
605 |
92.87 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
Au |
357 |
343 |
4.07 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
Au |
328 |
316 |
3.59 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
Au |
255 |
245 |
3.03 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
Au |
206 |
198 |
6.20 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
Au |
76 |
74 |
5.04 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25510.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9633) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24574.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HSEh1PBE/3-21G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Cl |
-0.035 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Cl |
-0.035 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.603 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.603 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.407 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.407 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.247 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.247 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.261 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.261 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.240 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.240 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.298 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.298 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-50.289 |
2.770 |
-4.794 |
| y |
2.770 |
-53.863 |
4.840 |
| z |
-4.794 |
4.840 |
-56.866 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.076 |
2.770 |
-4.794 |
| y |
2.770 |
-0.285 |
4.840 |
| z |
-4.794 |
4.840 |
-4.790 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -9.581 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.574 |
|---|
| xy | 2.770 |
|---|
| xz | -4.794 |
|---|
| yz | 4.840 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.052 |
-0.555 |
0.899 |
| y |
-0.555 |
7.686 |
-2.602 |
| z |
0.899 |
-2.602 |
10.267 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
298.540 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
17.278 |