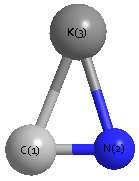Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at HSEh1PBE/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.544120 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.543510 |
| HF Energy | -692.544120 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 61.349663 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at HSEh1PBE/6-311G*
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.300 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.274 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.438 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.5742 | 3.7385 |
C2 | 2.5742 | | 1.1643 | N3 | 3.7385 | 1.1643 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
180.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HSEh1PBE/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.757 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.429 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.328 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.920 |
11.920 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-22.936 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-22.936 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-30.405 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
3.735 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.735 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-7.470 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -14.939 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.105 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.105 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.429 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
99.356 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.968 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at HSEh1PBE/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.546812 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -692.546812 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.873885 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at HSEh1PBE/6-311G*
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.202 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.388 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.215 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 3.5897 | 2.4164 |
C2 | 3.5897 | | 1.1734 | N3 | 2.4164 | 1.1734 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
180.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HSEh1PBE/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.764 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.220 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.545 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.868 |
11.868 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-22.827 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-22.827 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-32.733 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.953 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
4.953 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-9.905 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -19.811 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.053 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.053 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.275 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
88.301 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.397 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at HSEh1PBE/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.551116 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.550990 |
| HF Energy | -692.551116 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 69.035876 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at HSEh1PBE/6-311G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
1.036 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.623 |
-1.616 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-0.534 |
-1.425 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.7242 | 2.5182 |
C2 | 2.7242 | | 1.1733 | N3 | 2.5182 | 1.1733 | |
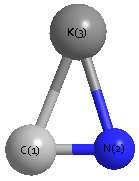 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
67.403 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
87.120 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
25.477 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HSEh1PBE/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.702 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.265 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.438 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.435 |
9.952 |
0.000 |
9.961 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.161 |
1.040 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.040 |
-26.258 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-23.075 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.494 |
1.040 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.040 |
-1.140 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.635 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 7.269 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.903 |
|---|
| xy | 1.040 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.395 |
-0.241 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.241 |
4.575 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.241 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
70.528 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.398 |