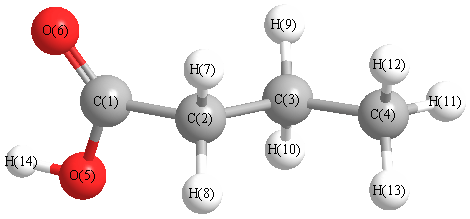Vibrational Frequencies calculated at M06-2X/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3766 |
3566 |
74.71 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3172 |
3004 |
22.39 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3168 |
3000 |
25.52 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3156 |
2988 |
22.59 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3130 |
2964 |
0.88 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3105 |
2940 |
15.92 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3089 |
2925 |
12.06 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3080 |
2916 |
16.72 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1911 |
1810 |
331.55 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1539 |
1458 |
5.28 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1533 |
1452 |
8.01 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1525 |
1444 |
1.90 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1505 |
1425 |
9.36 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1446 |
1369 |
5.60 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1424 |
1349 |
73.48 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1401 |
1326 |
15.67 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1340 |
1269 |
0.81 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1306 |
1237 |
0.62 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1280 |
1212 |
52.89 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1240 |
1174 |
130.90 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1135 |
1075 |
7.34 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1105 |
1046 |
58.01 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1077 |
1020 |
5.22 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
944 |
894 |
1.34 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
907 |
859 |
2.15 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
889 |
842 |
5.68 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
766 |
725 |
31.71 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
744 |
705 |
40.37 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
653 |
618 |
76.38 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
593 |
561 |
46.02 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
439 |
416 |
3.41 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
337 |
319 |
1.10 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
264 |
250 |
0.07 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
192 |
181 |
0.08 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
104 |
98 |
0.25 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
61 |
58 |
0.33 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 26660.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.947) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25247.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at M06-2X/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.576 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.361 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.311 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.481 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.599 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
O |
-0.469 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.189 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.185 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.169 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.180 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.169 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.162 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.161 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.432 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.117 |
1.286 |
0.278 |
1.726 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-35.695 |
5.424 |
0.264 |
| y |
5.424 |
-38.722 |
-1.510 |
| z |
0.264 |
-1.510 |
-35.960 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.646 |
5.424 |
0.264 |
| y |
5.424 |
-2.894 |
-1.510 |
| z |
0.264 |
-1.510 |
1.248 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.497 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.027 |
|---|
| xy | 5.424 |
|---|
| xz | 0.264 |
|---|
| yz | -1.510 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.239 |
-0.130 |
-0.313 |
| y |
-0.130 |
6.929 |
0.119 |
| z |
-0.313 |
0.119 |
5.765 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
206.953 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.386 |