Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at M06-2X/aug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.869119 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.873154 |
| HF Energy | -169.869119 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 71.093827 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at M06-2X/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3905 |
3732 |
105.80 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3563 |
3406 |
22.05 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3091 |
2954 |
39.55 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1791 |
1712 |
242.38 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1426 |
1363 |
17.30 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1335 |
1276 |
187.80 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1201 |
1148 |
26.49 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1068 |
1020 |
211.86 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
626 |
599 |
1.41 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1059 |
1013 |
2.59 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
840 |
802 |
63.30 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
422 |
403 |
70.20 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10164.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9557) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9713.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at M06-2X/aug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.373 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-0.998 |
-0.535 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.193 |
-0.009 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.337 |
1.412 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-1.850 |
-0.093 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.819 |
0.789 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3488 | 1.2527 | 1.0931 | 1.9074 | 1.8660 |
O2 | 1.3488 | | 2.2532 | 2.0561 | 0.9597 | 3.1125 | N3 | 1.2527 | 2.2532 | | 2.0888 | 3.0440 | 1.0142 | H4 | 1.0931 | 2.0561 | 2.0888 | | 2.1336 | 2.2448 | H5 | 1.9074 | 0.9597 | 3.0440 | 2.1336 | | 3.7732 | H6 | 1.8660 | 3.1125 | 1.0142 | 2.2448 | 3.7732 | |
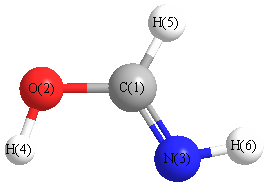 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
110.294 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
110.367 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
119.981 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
114.296 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
125.724 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at M06-2X/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.039 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.361 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.549 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.479 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.246 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.146 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-2.086 |
3.177 |
0.000 |
3.800 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-14.279 |
1.180 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.180 |
-18.138 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.159 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.370 |
1.180 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.180 |
-1.419 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.951 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -5.902 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.859 |
|---|
| xy | 1.180 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.466 |
0.021 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.021 |
3.755 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.920 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
41.261 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.423 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at M06-2X/aug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.877820 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.881982 |
| HF Energy | -169.877820 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 71.425209 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at M06-2X/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3799 |
3631 |
72.17 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3546 |
3389 |
21.61 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3168 |
3027 |
20.38 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1760 |
1682 |
314.87 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1411 |
1348 |
23.12 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1378 |
1317 |
3.08 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1202 |
1149 |
120.10 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1087 |
1039 |
173.22 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
605 |
578 |
47.92 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1077 |
1030 |
0.24 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
840 |
803 |
34.23 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
600 |
573 |
171.89 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10235.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9557) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9781.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at M06-2X/aug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.415 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.107 |
-0.341 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.152 |
-0.087 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.256 |
1.473 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.822 |
-1.265 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.867 |
0.632 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3403 | 1.2568 | 1.0886 | 1.8705 | 1.8798 |
O2 | 1.3403 | | 2.2733 | 2.0034 | 0.9672 | 3.1291 | N3 | 1.2568 | 2.2733 | | 2.1017 | 2.2991 | 1.0139 | H4 | 1.0886 | 2.0034 | 2.1017 | | 2.7960 | 2.2839 | H5 | 1.8705 | 0.9672 | 2.2991 | 2.7960 | | 3.2910 | H6 | 1.8798 | 3.1291 | 1.0139 | 2.2839 | 3.2910 | |
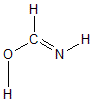 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
107.197 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
111.304 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
122.132 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
110.714 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
127.154 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at M06-2X/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.037 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.404 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.536 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.528 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.291 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.158 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.007 |
1.048 |
0.000 |
1.048 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-19.862 |
3.223 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.223 |
-14.320 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.156 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.124 |
3.223 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.223 |
5.189 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.065 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.130 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.543 |
|---|
| xy | 3.223 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.072 |
0.053 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.053 |
4.014 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.906 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
40.613 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.373 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at M06-2X/aug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.871986 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.876069 |
| HF Energy | -169.871986 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 71.082022 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at M06-2X/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3837 |
3667 |
54.23 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3473 |
3319 |
10.26 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3209 |
3066 |
8.63 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1769 |
1691 |
307.51 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1411 |
1348 |
2.78 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1353 |
1294 |
31.65 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1135 |
1085 |
282.27 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1087 |
1039 |
31.22 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
605 |
579 |
32.53 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1090 |
1041 |
55.59 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
864 |
826 |
62.27 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
483 |
462 |
74.28 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10158.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9557) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9708.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at M06-2X/aug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.442 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.092 |
-0.354 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.215 |
0.123 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.301 |
1.485 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.826 |
-1.281 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.361 |
-0.886 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3512 | 1.2557 | 1.0856 | 1.9102 | 1.9017 |
O2 | 1.3512 | | 2.3555 | 2.0016 | 0.9642 | 2.5103 | N3 | 1.2557 | 2.3555 | | 2.0374 | 2.4768 | 1.0200 | H4 | 1.0856 | 2.0016 | 2.0374 | | 2.8148 | 2.8956 | H5 | 1.9102 | 0.9642 | 2.4768 | 2.8148 | | 2.2224 | H6 | 1.9017 | 2.5103 | 1.0200 | 2.8956 | 2.2224 | |
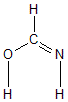 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
110.053 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
112.960 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
129.225 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
109.979 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
120.796 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at M06-2X/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.064 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.390 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.528 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.565 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.245 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.173 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.985 |
-1.729 |
0.000 |
1.990 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.236 |
-2.025 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.025 |
-13.205 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.102 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-7.082 |
-2.025 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.025 |
7.964 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.881 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.762 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -10.031 |
|---|
| xy | -2.025 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.953 |
-0.045 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.045 |
4.097 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.893 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
40.966 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.400 |


