Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at M06-2X/6-31G(2df,p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -135.107248 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -135.115420 |
| HF Energy | -135.107248 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 82.928545 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at M06-2X/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3518 |
3350 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3134 |
2985 |
32.45 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3072 |
2926 |
33.06 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3052 |
2907 |
16.77 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1659 |
1580 |
20.78 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1508 |
1437 |
1.28 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1491 |
1420 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1413 |
1346 |
9.91 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1382 |
1316 |
12.33 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1171 |
1115 |
8.84 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1093 |
1041 |
28.05 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
906 |
863 |
27.77 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
880 |
838 |
134.96 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
405 |
386 |
5.62 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A" |
3599 |
3428 |
0.46 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A" |
3141 |
2991 |
47.80 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A" |
3109 |
2961 |
5.88 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A" |
1499 |
1428 |
6.42 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A" |
1392 |
1326 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A" |
1273 |
1213 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
1007 |
959 |
1.35 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
775 |
738 |
0.85 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
300 |
286 |
32.53 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
253 |
241 |
13.59 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20515.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9524) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 19539.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at M06-2X/6-31G(2df,p)
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| N1 |
-1.303 |
-0.088 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.575 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
1.207 |
-0.354 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
2.149 |
0.204 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
1.202 |
-1.000 |
0.883 |
| H6 |
1.202 |
-1.000 |
-0.883 |
| H7 |
0.036 |
1.232 |
-0.875 |
| H8 |
0.036 |
1.232 |
0.875 |
| H9 |
-1.374 |
-0.687 |
0.814 |
| H10 |
-1.374 |
-0.687 |
-0.814 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
N1 |
C2 |
C3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
| N1 | | 1.4616 | 2.5235 | 3.4638 | 2.8082 | 2.8082 | 2.0737 | 2.0737 | 1.0131 | 1.0131 |
C2 | 1.4616 | | 1.5229 | 2.1804 | 2.1693 | 2.1693 | 1.0945 | 1.0945 | 2.0356 | 2.0356 | C3 | 2.5235 | 1.5229 | | 1.0951 | 1.0944 | 1.0944 | 2.1564 | 2.1564 | 2.7267 | 2.7267 | H4 | 3.4638 | 2.1804 | 1.0951 | | 1.7684 | 1.7684 | 2.5066 | 2.5066 | 3.7241 | 3.7241 | H5 | 2.8082 | 2.1693 | 1.0944 | 1.7684 | | 1.7665 | 3.0711 | 2.5183 | 2.5962 | 3.1008 | H6 | 2.8082 | 2.1693 | 1.0944 | 1.7684 | 1.7665 | | 2.5183 | 3.0711 | 3.1008 | 2.5962 | H7 | 2.0737 | 1.0945 | 2.1564 | 2.5066 | 3.0711 | 2.5183 | | 1.7492 | 2.9195 | 2.3826 | H8 | 2.0737 | 1.0945 | 2.1564 | 2.5066 | 2.5183 | 3.0711 | 1.7492 | | 2.3826 | 2.9195 | H9 | 1.0131 | 2.0356 | 2.7267 | 3.7241 | 2.5962 | 3.1008 | 2.9195 | 2.3826 | | 1.6275 | H10 | 1.0131 | 2.0356 | 2.7267 | 3.7241 | 3.1008 | 2.5962 | 2.3826 | 2.9195 | 1.6275 | |
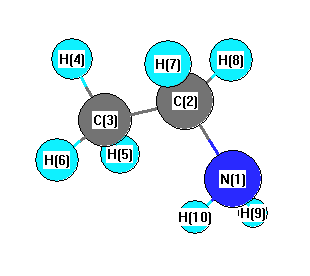 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| N1 |
C2 |
C3 |
115.443 |
|
N1 |
C2 |
H7 |
107.567 |
| N1 |
C2 |
H8 |
107.567 |
|
C2 |
N1 |
H9 |
109.344 |
| C2 |
N1 |
H10 |
109.344 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H4 |
111.753 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H5 |
110.902 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H6 |
110.902 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H7 |
109.871 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.871 |
| H4 |
C3 |
H5 |
107.743 |
|
H4 |
C3 |
H6 |
107.743 |
| H5 |
C3 |
H6 |
107.622 |
|
H7 |
C2 |
H8 |
106.080 |
| H9 |
N1 |
H10 |
106.870 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at M06-2X/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.549 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.142 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.405 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.128 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.122 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.122 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.122 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.122 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.241 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.241 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.890 |
-0.942 |
0.000 |
1.296 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.583 |
2.423 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.423 |
-20.035 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-18.966 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-4.083 |
2.423 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.423 |
1.239 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.844 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 5.687 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.548 |
|---|
| xy | 2.423 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.885 |
0.208 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.208 |
4.483 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.488 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
58.131 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.624 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at M06-2X/6-31G(2df,p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -135.106803 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at M06-2X/6-31G(2df,p)
Geometric Data calculated at M06-2X/6-31G(2df,p)
Point Group is Cs
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
