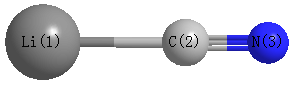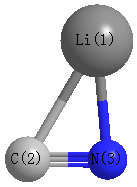Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -100.365601 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -100.364641 |
| HF Energy | -100.365601 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 27.801190 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Li1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.058 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.149 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.009 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| Li1 | | 1.9093 | 3.0675 |
C2 | 1.9093 | | 1.1582 | N3 | 3.0675 | 1.1582 | |
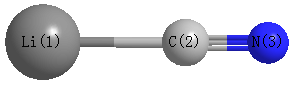 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
180.000 |
|
Li1 |
N3 |
C2 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
Li1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at M06-2X/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Li |
0.610 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.283 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.327 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-9.010 |
9.010 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-14.208 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-14.208 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.215 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-7.712 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-7.712 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
15.423 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 30.846 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.249 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.249 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.131 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
25.636 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
5.063 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -100.371838 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -100.371134 |
| HF Energy | -100.371838 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 29.498746 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Li1 |
1.432 |
-0.583 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
-0.716 |
-0.365 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.563 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| Li1 | | 2.1593 | 1.8343 |
C2 | 2.1593 | | 1.1721 | N3 | 1.8343 | 1.1721 | |
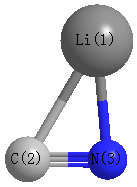 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
58.143 |
|
Li1 |
N3 |
C2 |
88.987 |
| C2 |
Li1 |
N3 |
32.870 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at M06-2X/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Li |
0.499 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.094 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.405 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
6.410 |
-2.539 |
0.000 |
6.895 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.191 |
-5.857 |
0.000 |
| y |
-5.857 |
-15.010 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-14.385 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
8.506 |
-5.857 |
0.000 |
| y |
-5.857 |
-4.722 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.784 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -7.568 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 8.819 |
|---|
| xy | -5.857 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.237 |
0.377 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.377 |
3.214 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.480 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
20.527 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
4.531 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -100.371814 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -100.370760 |
| HF Energy | -100.371814 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 28.518848 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
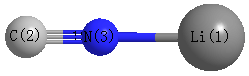
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Li1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.872 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.063 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.109 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| Li1 | | 2.9345 | 1.7629 |
C2 | 2.9345 | | 1.1717 | N3 | 1.7629 | 1.1717 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Li1 |
N3 |
C2 |
180.000 |
| C2 |
Li1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at M06-2X/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Li |
0.615 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.105 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.510 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.731 |
8.731 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-14.169 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-14.169 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.311 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-5.929 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-5.929 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.858 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 23.716 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.244 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.244 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.248 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
23.751 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
4.874 |