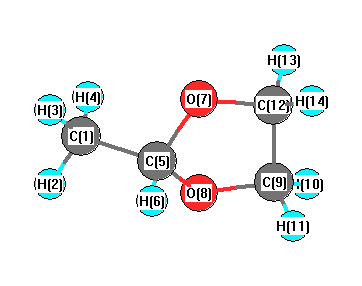
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at M06-2X/3-21G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3194 |
3026 |
14.19 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3173 |
3005 |
6.71 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3167 |
3000 |
16.61 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3150 |
2984 |
13.99 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3098 |
2934 |
36.77 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3091 |
2928 |
3.36 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3076 |
2913 |
35.62 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3044 |
2884 |
22.52 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1575 |
1492 |
0.35 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1563 |
1480 |
5.99 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1555 |
1473 |
2.43 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1548 |
1467 |
4.30 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1465 |
1387 |
23.48 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1429 |
1354 |
36.08 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1398 |
1324 |
0.61 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1386 |
1313 |
13.91 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1320 |
1250 |
7.81 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1256 |
1190 |
12.17 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1225 |
1161 |
3.18 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1181 |
1118 |
71.51 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1162 |
1101 |
60.64 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1145 |
1084 |
37.97 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1125 |
1065 |
52.86 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1066 |
1009 |
11.21 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1026 |
972 |
25.70 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
946 |
896 |
5.99 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
929 |
880 |
1.10 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
872 |
826 |
37.39 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
846 |
801 |
2.57 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
714 |
676 |
2.30 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
634 |
600 |
5.93 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
464 |
440 |
19.36 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
359 |
340 |
1.74 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
252 |
239 |
0.65 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
237 |
225 |
0.87 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
82 |
78 |
12.84 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 26876.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9472) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25457.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at M06-2X/3-21G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.569 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.211 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.207 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.206 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
0.246 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.219 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
O |
-0.510 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
O |
-0.516 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
C |
-0.167 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.219 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.210 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
C |
-0.186 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.206 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.224 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.054 |
0.189 |
-0.778 |
1.324 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-30.806 |
0.394 |
-1.495 |
| y |
0.394 |
-41.842 |
-1.363 |
| z |
-1.495 |
-1.363 |
-35.764 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
7.997 |
0.394 |
-1.495 |
| y |
0.394 |
-8.557 |
-1.363 |
| z |
-1.495 |
-1.363 |
0.560 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 1.120 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 11.036 |
|---|
| xy | 0.394 |
|---|
| xz | -1.495 |
|---|
| yz | -1.363 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.693 |
0.077 |
-0.361 |
| y |
0.077 |
5.693 |
-0.074 |
| z |
-0.361 |
-0.074 |
5.786 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
147.308 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
12.137 |