Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at M06-2X/6-31G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -187.903177 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -187.907215 |
| HF Energy | -187.903177 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 101.947377 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at M06-2X/6-31G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3760 |
3760 |
30.93 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3642 |
3642 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
2428 |
2428 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
1703 |
1703 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1188 |
1188 |
7.43 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
862 |
862 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
513 |
513 |
2.22 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
511 |
511 |
147.09 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
408 |
408 |
319.09 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
218 |
218 |
34.89 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
B |
3760 |
3760 |
30.83 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
B |
3647 |
3647 |
30.89 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
B |
1711 |
1711 |
79.03 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
B |
1460 |
1460 |
131.41 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
B |
1188 |
1188 |
7.42 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
B |
511 |
511 |
149.73 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
B |
408 |
408 |
320.06 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
B |
218 |
218 |
34.72 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14066.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14066.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at M06-2X/6-31G
Point Group is C2
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.024 |
0.607 |
-0.035 |
| C2 |
-0.024 |
-0.607 |
-0.035 |
| N3 |
0.024 |
1.971 |
-0.016 |
| N4 |
-0.024 |
-1.971 |
-0.016 |
| H5 |
-0.393 |
2.451 |
0.773 |
| H6 |
0.792 |
2.465 |
-0.454 |
| H7 |
0.393 |
-2.451 |
0.773 |
| H8 |
-0.792 |
-2.465 |
-0.454 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
N3 |
N4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
| C1 | | 1.2140 | 1.3649 | 2.5783 | 2.0562 | 2.0543 | 3.1839 | 3.2055 |
C2 | 1.2140 | | 2.5783 | 1.3649 | 3.1839 | 3.2055 | 2.0562 | 2.0543 | N3 | 1.3649 | 2.5783 | | 3.9429 | 1.0128 | 1.0130 | 4.5072 | 4.5319 | N4 | 2.5783 | 1.3649 | 3.9429 | | 4.5072 | 4.5319 | 1.0128 | 1.0130 | H5 | 2.0562 | 3.1839 | 1.0128 | 4.5072 | | 1.7056 | 4.9644 | 5.0826 | H6 | 2.0543 | 3.2055 | 1.0130 | 4.5319 | 1.7056 | | 5.0826 | 5.1782 | H7 | 3.1839 | 2.0562 | 4.5072 | 1.0128 | 4.9644 | 5.0826 | | 1.7056 | H8 | 3.2055 | 2.0543 | 4.5319 | 1.0130 | 5.0826 | 5.1782 | 1.7056 | |
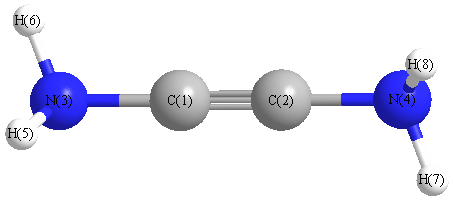 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
N4 |
177.638 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H5 |
118.974 |
| C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
118.773 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
N3 |
177.638 |
| C2 |
N4 |
H7 |
118.974 |
|
C2 |
N4 |
H8 |
118.773 |
| H5 |
N3 |
H6 |
114.698 |
|
H7 |
N4 |
H8 |
114.698 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at M06-2X/6-31G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.114 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.114 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.804 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
N |
-0.804 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.345 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.345 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.345 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.345 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.004 |
0.004 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.593 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-10.724 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-23.583 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.440 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
12.864 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-6.424 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -12.848 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -12.869 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.201 |
-0.001 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.001 |
8.684 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.203 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
97.280 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.863 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at M06-2X/6-31G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -187.903173 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -187.907242 |
| HF Energy | -187.903173 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 101.944807 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at M06-2X/6-31G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3646 |
3646 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
2428 |
2428 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
1705 |
1705 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A1 |
862 |
862 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
B1 |
518 |
518 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
B2 |
3651 |
3651 |
29.96 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
B2 |
1712 |
1712 |
79.70 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
B2 |
1459 |
1459 |
132.10 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
E |
3763 |
3763 |
30.75 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
E |
3763 |
3763 |
30.75 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
E |
1190 |
1190 |
7.41 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
E |
1190 |
1190 |
7.41 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
E |
514 |
514 |
184.55 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
E |
514 |
514 |
184.55 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
E |
422 |
422 |
286.49 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
E |
422 |
422 |
286.49 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
E |
216 |
216 |
32.08 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
E |
216 |
216 |
32.08 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14094.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14094.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at M06-2X/6-31G
Point Group is D2d
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.608 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.608 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.952 |
| N4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.952 |
| H5 |
0.000 |
0.859 |
2.474 |
| H6 |
0.000 |
-0.859 |
2.474 |
| H7 |
0.859 |
0.000 |
-2.474 |
| H8 |
-0.859 |
0.000 |
-2.474 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
N3 |
N4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
| C1 | | 1.2165 | 1.3438 | 2.5603 | 2.0543 | 2.0543 | 3.2000 | 3.2000 |
C2 | 1.2165 | | 2.5603 | 1.3438 | 3.2000 | 3.2000 | 2.0543 | 2.0543 | N3 | 1.3438 | 2.5603 | | 3.9041 | 1.0056 | 1.0056 | 4.5089 | 4.5089 | N4 | 2.5603 | 1.3438 | 3.9041 | | 4.5089 | 4.5089 | 1.0056 | 1.0056 | H5 | 2.0543 | 3.2000 | 1.0056 | 4.5089 | | 1.7188 | 5.0954 | 5.0954 | H6 | 2.0543 | 3.2000 | 1.0056 | 4.5089 | 1.7188 | | 5.0954 | 5.0954 | H7 | 3.2000 | 2.0543 | 4.5089 | 1.0056 | 5.0954 | 5.0954 | | 1.7188 | H8 | 3.2000 | 2.0543 | 4.5089 | 1.0056 | 5.0954 | 5.0954 | 1.7188 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
N4 |
180.000 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H5 |
121.281 |
| C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
121.281 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
N3 |
180.000 |
| C2 |
N4 |
H7 |
121.281 |
|
C2 |
N4 |
H8 |
121.281 |
| H5 |
N3 |
H6 |
117.437 |
|
H7 |
N4 |
H8 |
117.437 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at M06-2X/6-31G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.114 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.114 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.804 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
N |
-0.804 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.345 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.345 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.345 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.345 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.587 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-23.587 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-10.731 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.428 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-6.428 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
12.855 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 25.711 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.202 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.202 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.665 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
97.282 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.863 |
