Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCD/6-31+G**
Geometric Data calculated at CCD/6-31+G**
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at CCD/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -350.999873 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -350.577411 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 81.744796 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCD/6-31+G**
Geometric Data calculated at CCD/6-31+G**
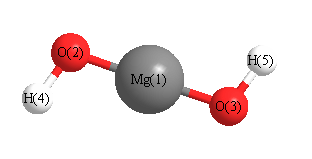
Point Group is C2
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Mg1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.008 |
| O2 |
0.000 |
1.791 |
-0.023 |
| O3 |
0.000 |
-1.791 |
-0.023 |
| H4 |
0.241 |
2.697 |
0.131 |
| H5 |
-0.241 |
-2.697 |
0.131 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Mg1 |
O2 |
O3 |
H4 |
H5 |
| Mg1 | | 1.7917 | 1.7917 | 2.7102 | 2.7102 |
O2 | 1.7917 | | 3.5828 | 0.9494 | 4.4972 | O3 | 1.7917 | 3.5828 | | 4.4972 | 0.9494 | H4 | 2.7102 | 0.9494 | 4.4972 | | 5.4149 | H5 | 2.7102 | 4.4972 | 0.9494 | 5.4149 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Mg1 |
O2 |
H4 |
161.907 |
|
Mg1 |
O3 |
H5 |
161.907 |
| O2 |
Mg1 |
O3 |
178.003 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at CCD/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -350.999830 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -350.577763 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 81.969390 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCD/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σg |
4157 |
3917 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Σg |
603 |
568 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Σu |
4156 |
3917 |
208.74 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Σu |
903 |
851 |
223.90 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Πg |
102i |
96i |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Πg |
102i |
96i |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Πu |
165 |
156 |
14.88 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Πu |
165 |
156 |
14.88 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
Πu |
42i |
40i |
377.67 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
Πu |
42i |
40i |
377.67 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4930.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9423) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4646.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at CCD/6-31+G**
Point Group is D∞h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Mg1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.785 |
| O3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.785 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.733 |
| H5 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.733 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Mg1 |
O2 |
O3 |
H4 |
H5 |
| Mg1 | | 1.7846 | 1.7846 | 2.7328 | 2.7328 |
O2 | 1.7846 | | 3.5692 | 0.9482 | 4.5174 | O3 | 1.7846 | 3.5692 | | 4.5174 | 0.9482 | H4 | 2.7328 | 0.9482 | 4.5174 | | 5.4656 | H5 | 2.7328 | 4.5174 | 0.9482 | 5.4656 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Mg1 |
O2 |
H4 |
180.000 |
|
Mg1 |
O3 |
H5 |
180.000 |
| O2 |
Mg1 |
O3 |
180.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
