Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -1592.619476 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -1592.619476 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 348.612535 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
532 |
504 |
0.00 |
53.93 |
0.07 |
0.14 |
| 2 |
A1 |
195 |
185 |
0.00 |
2.66 |
0.74 |
0.85 |
| 3 |
B1 |
478 |
453 |
0.00 |
35.49 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 4 |
B2 |
320 |
304 |
0.47 |
10.66 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
E |
457 |
433 |
0.00 |
7.33 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
E |
457 |
433 |
0.00 |
7.33 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 1219.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9485) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 1156.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-31G*
Point Group is D2d
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| S1 |
0.000 |
1.442 |
0.304 |
| S2 |
0.000 |
-1.442 |
0.304 |
| S3 |
-1.442 |
0.000 |
-0.304 |
| S4 |
1.442 |
0.000 |
-0.304 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
S1 |
S2 |
S3 |
S4 |
| S1 | | 2.8836 | 2.1279 | 2.1279 |
S2 | 2.8836 | | 2.1279 | 2.1279 | S3 | 2.1279 | 2.1279 | | 2.8836 | S4 | 2.1279 | 2.1279 | 2.8836 | |
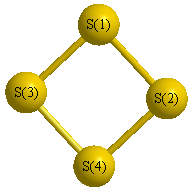 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| S1 |
S2 |
S4 |
47.345 |
|
S1 |
S3 |
S4 |
47.345 |
| S2 |
S1 |
S3 |
47.345 |
|
S2 |
S4 |
S3 |
47.345 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
S |
0.000 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
S |
0.000 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
S |
0.000 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
S |
0.000 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-49.709 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-49.709 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-54.977 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.634 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.634 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-5.267 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -10.534 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
10.366 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
10.366 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.256 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
171.114 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.081 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -1592.634942 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -1592.634942 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 331.745001 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
682 |
646 |
3.25 |
32.03 |
0.21 |
0.35 |
| 2 |
A1 |
423 |
401 |
7.50 |
45.16 |
0.23 |
0.37 |
| 3 |
A1 |
130 |
123 |
0.78 |
15.42 |
0.46 |
0.63 |
| 4 |
A2 |
217 |
206 |
0.00 |
0.32 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
B2 |
654 |
621 |
162.97 |
3.20 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 6 |
B2 |
345 |
327 |
0.32 |
15.33 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 1225.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9485) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 1161.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-31G*
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| S1 |
0.000 |
1.052 |
0.919 |
| S2 |
0.000 |
-1.052 |
0.919 |
| S3 |
0.000 |
1.603 |
-0.919 |
| S4 |
0.000 |
-1.603 |
-0.919 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
S1 |
S2 |
S3 |
S4 |
| S1 | | 2.1031 | 1.9191 | 3.2291 |
S2 | 2.1031 | | 3.2291 | 1.9191 | S3 | 1.9191 | 3.2291 | | 3.2065 | S4 | 3.2291 | 1.9191 | 3.2065 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| S1 |
S2 |
S4 |
106.706 |
|
S1 |
S3 |
S4 |
73.294 |
| S2 |
S1 |
S3 |
106.706 |
|
S2 |
S4 |
S3 |
73.294 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
S |
0.118 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
S |
0.118 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
S |
-0.118 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
S |
-0.118 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.800 |
1.800 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-51.346 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-54.432 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-49.899 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.819 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-3.809 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.990 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 5.980 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.086 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.321 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
18.411 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.069 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
204.110 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.287 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -1592.627368 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -1592.627368 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 335.287021 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
752 |
713 |
0.00 |
40.56 |
0.29 |
0.45 |
| 2 |
Ag |
300 |
285 |
0.00 |
44.21 |
0.29 |
0.45 |
| 3 |
Au |
256 |
242 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 4 |
B1u |
694 |
658 |
180.35 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 5 |
B2u |
166i |
158i |
26.28 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 6 |
B3g |
351 |
333 |
0.00 |
18.52 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 1093.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9485) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 1036.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-31G*
Point Group is D2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| S1 |
0.000 |
0.948 |
1.268 |
| S2 |
0.000 |
0.948 |
-1.268 |
| S3 |
0.000 |
-0.948 |
1.268 |
| S4 |
0.000 |
-0.948 |
-1.268 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
S1 |
S2 |
S3 |
S4 |
| S1 | | 2.5361 | 1.8961 | 3.1666 |
S2 | 2.5361 | | 3.1666 | 1.8961 | S3 | 1.8961 | 3.1666 | | 2.5361 | S4 | 3.1666 | 1.8961 | 2.5361 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| S1 |
S2 |
S4 |
90.000 |
|
S1 |
S3 |
S4 |
90.000 |
| S2 |
S1 |
S3 |
90.000 |
|
S2 |
S4 |
S3 |
90.000 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
S |
0.000 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
S |
0.000 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
S |
0.000 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
S |
0.000 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-51.737 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-49.220 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-53.904 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.175 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.601 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.426 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -6.852 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.517 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.274 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
11.687 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
17.202 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
192.675 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.881 |
