Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -551.362215 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -551.362215 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
1782 |
1691 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Ag |
1466 |
1390 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Ag |
672 |
638 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Ag |
583 |
553 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
B1g |
669 |
635 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
B1u |
1731 |
1642 |
0.94 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
B1u |
993 |
941 |
318.71 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
B1u |
294 |
279 |
1.70 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
B2g |
681i |
646i |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
B2u |
1548 |
1468 |
857.09 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
B2u |
997 |
946 |
28.82 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
B2u |
249 |
236 |
3.93 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
B3g |
3074 |
2915 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
B3g |
760 |
721 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
B3g |
218 |
207 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
B3u |
580 |
550 |
88.59 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
B3u |
130 |
123 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
B3u |
286i |
271i |
32.58 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7389.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9485) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7009.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-31G*
Point Group is D2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.055 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.957 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.055 |
| C4 |
0.000 |
-0.957 |
0.000 |
| F5 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.414 |
| F6 |
0.000 |
2.273 |
0.000 |
| F7 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.414 |
| F8 |
0.000 |
-2.273 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
F5 |
F6 |
F7 |
F8 |
| C1 | | 1.4242 | 2.1092 | 1.4242 | 1.3599 | 2.5056 | 3.4691 | 2.5056 |
C2 | 1.4242 | | 1.4242 | 1.9143 | 2.5973 | 1.3157 | 2.5973 | 3.2300 | C3 | 2.1092 | 1.4242 | | 1.4242 | 3.4691 | 2.5056 | 1.3599 | 2.5056 | C4 | 1.4242 | 1.9143 | 1.4242 | | 2.5973 | 3.2300 | 2.5973 | 1.3157 | F5 | 1.3599 | 2.5973 | 3.4691 | 2.5973 | | 3.3160 | 4.8290 | 3.3160 | F6 | 2.5056 | 1.3157 | 2.5056 | 3.2300 | 3.3160 | | 3.3160 | 4.5458 | F7 | 3.4691 | 2.5973 | 1.3599 | 2.5973 | 4.8290 | 3.3160 | | 3.3160 | F8 | 2.5056 | 3.2300 | 2.5056 | 1.3157 | 3.3160 | 4.5458 | 3.3160 | |
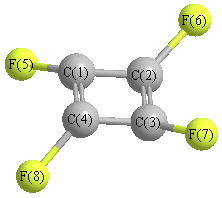 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
95.545 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
F6 |
132.227 |
| C1 |
C4 |
C3 |
95.545 |
|
C1 |
C4 |
F8 |
132.227 |
| C2 |
C1 |
C4 |
84.455 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
F5 |
137.773 |
| C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
84.455 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
F7 |
137.773 |
| C3 |
C2 |
F6 |
132.227 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
F8 |
132.227 |
| C4 |
C1 |
F5 |
137.773 |
|
C4 |
C3 |
F7 |
137.773 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.034 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.418 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.034 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
0.418 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
F |
-0.267 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
F |
-0.186 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
F |
-0.267 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
F |
-0.186 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-39.791 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-37.394 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-47.337 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.574 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
6.170 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-8.744 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -17.489 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.398 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.043 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
7.034 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
7.279 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
244.823 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
15.647 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -551.426844 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -551.426757 |
| HF Energy | -551.426844 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
1921 |
1822 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Ag |
1254 |
1190 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Ag |
700 |
664 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Ag |
275 |
261 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Ag |
169 |
160 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Au |
1362 |
1292 |
505.25 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
Au |
942 |
893 |
44.36 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
Au |
587 |
557 |
44.39 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
Au |
235 |
223 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
Au |
159 |
151 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
Bg |
1401 |
1328 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
Bg |
770 |
731 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
Bg |
489 |
464 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
Bg |
414 |
393 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
Bu |
1903 |
1805 |
155.83 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
Bu |
1013 |
961 |
184.64 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
Bu |
310 |
294 |
6.21 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
Bu |
192 |
183 |
1.69 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7048.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9485) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 6685.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-31G*
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.127 |
0.761 |
0.664 |
| C2 |
-0.127 |
-0.761 |
0.664 |
| C3 |
-0.127 |
-0.761 |
-0.664 |
| C4 |
0.127 |
0.761 |
-0.664 |
| F5 |
-0.127 |
1.669 |
1.586 |
| F6 |
0.127 |
-1.669 |
1.586 |
| F7 |
0.127 |
-1.669 |
-1.586 |
| F8 |
-0.127 |
1.669 |
-1.586 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
F5 |
F6 |
F7 |
F8 |
| C1 | | 1.5424 | 2.0359 | 1.3289 | 1.3188 | 2.5987 | 3.3119 | 2.4403 |
C2 | 1.5424 | | 1.3289 | 2.0359 | 2.5987 | 1.3188 | 2.4403 | 3.3119 | C3 | 2.0359 | 1.3289 | | 1.5424 | 3.3119 | 2.4403 | 1.3188 | 2.5987 | C4 | 1.3289 | 2.0359 | 1.5424 | | 2.4403 | 3.3119 | 2.5987 | 1.3188 | F5 | 1.3188 | 2.5987 | 3.3119 | 2.4403 | | 3.3478 | 4.6120 | 3.1723 | F6 | 2.5987 | 1.3188 | 2.4403 | 3.3119 | 3.3478 | | 3.1723 | 4.6120 | F7 | 3.3119 | 2.4403 | 1.3188 | 2.5987 | 4.6120 | 3.1723 | | 3.3478 | F8 | 2.4403 | 3.3119 | 2.5987 | 1.3188 | 3.1723 | 4.6120 | 3.3478 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
90.000 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
F6 |
130.370 |
| C1 |
C4 |
C3 |
90.000 |
|
C1 |
C4 |
F8 |
134.336 |
| C2 |
C1 |
C4 |
90.000 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
F5 |
130.370 |
| C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
90.000 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
F7 |
134.336 |
| C3 |
C2 |
F6 |
134.336 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
F8 |
130.370 |
| C4 |
C1 |
F5 |
134.336 |
|
C4 |
C3 |
F7 |
130.370 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.234 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.234 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.234 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
0.234 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
F |
-0.234 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
F |
-0.234 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
F |
-0.234 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
F |
-0.234 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-39.503 |
-0.015 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.015 |
-42.460 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-42.182 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.818 |
-0.015 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.015 |
-1.618 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.200 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -2.400 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 2.957 |
|---|
| xy | -0.015 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.978 |
-0.020 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.020 |
5.677 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
7.437 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
244.534 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
15.638 |
