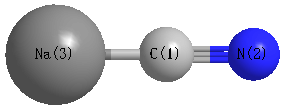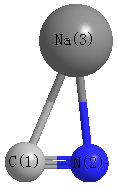Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -255.115854 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -255.115854 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 46.513004 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-311G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.698 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.858 |
| Na3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.563 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1605 | 2.2606 |
N2 | 1.1605 | | 3.4211 | Na3 | 2.2606 | 3.4211 | |
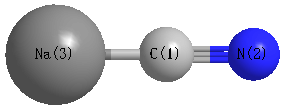 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
0.000 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
180.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.375 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.313 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Na |
0.689 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.860 |
10.860 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-17.004 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-17.004 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-13.053 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.975 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-1.975 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.950 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 7.901 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.516 |
0.000 |
-0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.516 |
-0.000 |
| z |
-0.000 |
-0.000 |
4.854 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
63.720 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.982 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -255.121026 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -255.120740 |
| HF Energy | -255.121026 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 51.514295 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-311G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.110 |
0.693 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
1.072 |
0.000 |
| Na3 |
-0.606 |
-1.061 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1732 | 2.4535 |
N2 | 1.1732 | | 2.2173 | Na3 | 2.4535 | 2.2173 | |
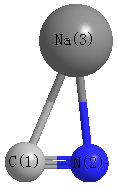 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
86.988 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
28.524 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
64.488 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.203 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.411 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Na |
0.613 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-4.716 |
-7.620 |
0.000 |
8.962 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-19.691 |
3.320 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.320 |
-13.854 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-17.157 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-4.185 |
3.320 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.320 |
4.570 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.385 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.770 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.837 |
|---|
| xy | 3.320 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.848 |
-0.096 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.096 |
3.277 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.705 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
45.333 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.733 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -255.117947 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -255.117947 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 48.759985 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-311G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.866 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.696 |
| Na3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.460 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1697 | 3.3259 |
N2 | 1.1697 | | 2.1562 | Na3 | 3.3259 | 2.1562 | |
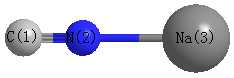 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
180.000 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.218 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.511 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Na |
0.729 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.931 |
10.931 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-16.924 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-16.924 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-15.753 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.585 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-0.585 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.171 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.341 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.432 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.432 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.738 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
57.029 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.552 |