Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3550 |
3381 |
0.31 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3161 |
3010 |
23.39 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3132 |
2983 |
46.17 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3112 |
2963 |
53.92 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3106 |
2958 |
49.45 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3100 |
2952 |
59.59 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3096 |
2948 |
52.04 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3054 |
2908 |
40.21 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
3045 |
2900 |
51.54 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
3042 |
2897 |
36.96 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
3041 |
2896 |
28.28 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
3033 |
2888 |
32.80 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
3023 |
2879 |
9.57 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1519 |
1446 |
17.51 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1512 |
1440 |
4.55 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1509 |
1437 |
6.21 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1499 |
1427 |
7.81 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1494 |
1423 |
11.14 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1492 |
1421 |
2.80 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1481 |
1411 |
12.70 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1429 |
1361 |
12.76 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1407 |
1339 |
5.11 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1402 |
1335 |
4.25 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1393 |
1326 |
0.94 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1374 |
1308 |
2.00 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
1373 |
1307 |
0.39 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
1342 |
1278 |
1.20 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
1315 |
1252 |
3.48 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
1296 |
1234 |
4.85 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
1263 |
1203 |
9.66 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
1205 |
1148 |
6.55 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
1191 |
1134 |
12.66 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
1167 |
1111 |
17.75 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
1125 |
1071 |
3.16 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
1119 |
1065 |
4.77 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
1082 |
1031 |
3.18 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
1010 |
962 |
5.48 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
990 |
943 |
0.21 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
976 |
929 |
1.77 |
|
|
|
| 40 |
A |
930 |
885 |
11.03 |
|
|
|
| 41 |
A |
898 |
855 |
3.03 |
|
|
|
| 42 |
A |
868 |
826 |
2.69 |
|
|
|
| 43 |
A |
852 |
812 |
29.45 |
|
|
|
| 44 |
A |
817 |
778 |
14.26 |
|
|
|
| 45 |
A |
756 |
720 |
80.53 |
|
|
|
| 46 |
A |
571 |
544 |
1.56 |
|
|
|
| 47 |
A |
485 |
461 |
6.53 |
|
|
|
| 48 |
A |
466 |
443 |
1.12 |
|
|
|
| 49 |
A |
433 |
413 |
1.17 |
|
|
|
| 50 |
A |
338 |
322 |
1.22 |
|
|
|
| 51 |
A |
326 |
311 |
0.91 |
|
|
|
| 52 |
A |
254 |
242 |
3.22 |
|
|
|
| 53 |
A |
223 |
213 |
0.38 |
|
|
|
| 54 |
A |
153 |
146 |
0.92 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 41413.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9523) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 39437.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
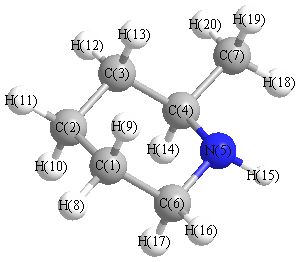
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.347 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.228 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.306 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.030 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
N |
-0.416 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.131 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
C |
-0.638 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.147 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.148 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.145 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.146 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.144 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.297 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
H |
0.147 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
H |
0.147 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
H |
0.176 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
H |
0.147 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
H |
0.152 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.564 |
0.950 |
0.530 |
1.225 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-45.759 |
1.948 |
0.349 |
| y |
1.948 |
-48.735 |
-1.607 |
| z |
0.349 |
-1.607 |
-44.396 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.806 |
1.948 |
0.349 |
| y |
1.948 |
-3.658 |
-1.607 |
| z |
0.349 |
-1.607 |
2.851 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 5.702 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 2.976 |
|---|
| xy | 1.948 |
|---|
| xz | 0.349 |
|---|
| yz | -1.607 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
12.424 |
0.085 |
0.070 |
| y |
0.085 |
11.242 |
-0.037 |
| z |
0.070 |
-0.037 |
10.146 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
231.242 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
15.207 |