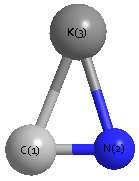Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.716754 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.716143 |
| HF Energy | -692.716754 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.329 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.311 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.484 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.6405 | 3.8129 |
C2 | 2.6405 | | 1.1724 | N3 | 3.8129 | 1.1724 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
180.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
1.022 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.602 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.420 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
13.048 |
13.048 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.351 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-23.351 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-31.972 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.311 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
4.311 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-8.621 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -17.243 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.336 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.336 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.313 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
103.445 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.171 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.720520 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.719866 |
| HF Energy | -692.720520 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.230 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.433 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.252 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 3.6629 | 2.4820 |
C2 | 3.6629 | | 1.1810 | N3 | 2.4820 | 1.1810 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
180.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.937 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.226 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.710 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
12.738 |
12.738 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.303 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-23.303 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-33.591 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.144 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
5.144 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-10.288 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -20.576 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.376 |
0.000 |
-0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.376 |
0.000 |
| z |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
6.196 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
91.928 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.588 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.721741 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.721588 |
| HF Energy | -692.721741 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 67.596805 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
1.066 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.624 |
-1.678 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-0.535 |
-1.454 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.8136 | 2.5761 |
C2 | 2.8136 | | 1.1800 | N3 | 2.5761 | 1.1800 | |
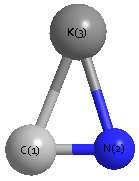 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
66.265 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
88.944 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
24.791 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.928 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.398 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.530 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.318 |
10.924 |
0.000 |
10.928 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.629 |
1.048 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.048 |
-27.348 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-23.355 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.277 |
1.048 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.048 |
-1.856 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.134 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 8.267 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.281 |
|---|
| xy | 1.048 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.105 |
-0.314 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.314 |
4.481 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.658 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
73.920 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.598 |