Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -268.278814 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -268.278814 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 194.745610 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3155 |
3004 |
22.01 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3044 |
2899 |
2.82 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3037 |
2892 |
134.39 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
1557 |
1483 |
2.07 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1529 |
1456 |
0.80 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1398 |
1331 |
4.85 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1268 |
1208 |
15.28 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1238 |
1179 |
79.81 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1186 |
1130 |
134.35 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1155 |
1100 |
26.27 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
995 |
947 |
4.04 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
966 |
920 |
3.66 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
743 |
707 |
0.38 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
264 |
252 |
0.59 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
B |
3160 |
3009 |
31.72 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
B |
3088 |
2941 |
58.85 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
B |
3051 |
2905 |
76.47 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
B |
1523 |
1450 |
4.36 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
B |
1448 |
1379 |
9.27 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B |
1360 |
1295 |
0.39 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
1247 |
1188 |
4.89 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B |
1160 |
1104 |
21.96 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B |
1111 |
1058 |
36.25 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B |
983 |
936 |
78.48 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B |
916 |
872 |
20.04 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B |
650 |
619 |
5.08 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B |
81i |
77i |
20.93 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20574.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9523) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 19592.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Point Group is C2
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.206 |
| C2 |
-0.299 |
0.698 |
-0.945 |
| C3 |
0.299 |
-0.698 |
-0.945 |
| O4 |
0.000 |
1.142 |
0.372 |
| O5 |
0.000 |
-1.142 |
0.372 |
| H6 |
0.902 |
0.040 |
1.829 |
| H7 |
-0.902 |
-0.040 |
1.829 |
| H8 |
-1.385 |
0.666 |
-1.106 |
| H9 |
1.385 |
-0.666 |
-1.106 |
| H10 |
-0.162 |
-1.390 |
-1.651 |
| H11 |
0.162 |
1.390 |
-1.651 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
| C1 | | 2.2807 | 2.2807 | 1.4142 | 1.4142 | 1.0968 | 1.0968 | 2.7762 | 2.7762 | 3.1817 | 3.1817 |
C2 | 2.2807 | | 1.5183 | 1.4218 | 2.2825 | 3.0930 | 2.9325 | 1.0981 | 2.1728 | 2.2084 | 1.0914 | C3 | 2.2807 | 1.5183 | | 2.2825 | 1.4218 | 2.9325 | 3.0930 | 2.1728 | 1.0981 | 1.0914 | 2.2084 | O4 | 1.4142 | 1.4218 | 2.2825 | | 2.2846 | 2.0371 | 2.0816 | 2.0809 | 2.7154 | 3.2457 | 2.0453 | O5 | 1.4142 | 2.2825 | 1.4218 | 2.2846 | | 2.0816 | 2.0371 | 2.7154 | 2.0809 | 2.0453 | 3.2457 | H6 | 1.0968 | 3.0930 | 2.9325 | 2.0371 | 2.0816 | | 1.8059 | 3.7729 | 3.0570 | 3.9101 | 3.8055 | H7 | 1.0968 | 2.9325 | 3.0930 | 2.0816 | 2.0371 | 1.8059 | | 3.0570 | 3.7729 | 3.8055 | 3.9101 | H8 | 2.7762 | 1.0981 | 2.1728 | 2.0809 | 2.7154 | 3.7729 | 3.0570 | | 3.0731 | 2.4535 | 1.7926 | H9 | 2.7762 | 2.1728 | 1.0981 | 2.7154 | 2.0809 | 3.0570 | 3.7729 | 3.0731 | | 1.7926 | 2.4535 | H10 | 3.1817 | 2.2084 | 1.0914 | 3.2457 | 2.0453 | 3.9101 | 3.8055 | 2.4535 | 1.7926 | | 2.7987 | H11 | 3.1817 | 1.0914 | 2.2084 | 2.0453 | 3.2457 | 3.8055 | 3.9101 | 1.7926 | 2.4535 | 2.7987 | |
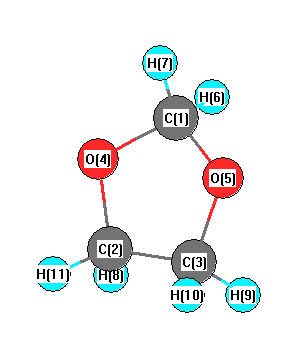 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O4 |
C2 |
107.068 |
|
C1 |
O5 |
C3 |
107.068 |
| C2 |
C3 |
O5 |
101.804 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
111.274 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
114.620 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
O4 |
101.804 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
111.274 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H11 |
114.620 |
| O4 |
C1 |
O5 |
107.754 |
|
O4 |
C1 |
H6 |
107.767 |
| O4 |
C1 |
H7 |
111.360 |
|
O4 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.685 |
| O4 |
C2 |
H11 |
108.228 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.360 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.767 |
|
O5 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.685 |
| O5 |
C3 |
H10 |
108.228 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.815 |
| H8 |
C2 |
H11 |
109.915 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.915 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.096 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.096 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.096 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.398 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.398 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.139 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.139 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.148 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.148 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.160 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.160 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.323 |
1.323 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-29.395 |
-0.426 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.426 |
-35.413 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-25.691 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.157 |
-0.426 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.426 |
-7.869 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.713 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 13.425 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 6.018 |
|---|
| xy | -0.426 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.635 |
-0.065 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.065 |
5.657 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.794 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
93.164 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.652 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -268.279160 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -268.287517 |
| HF Energy | -268.279160 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 194.713476 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3165 |
3014 |
25.03 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3161 |
3011 |
35.53 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3129 |
2980 |
26.15 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3074 |
2927 |
65.04 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3039 |
2894 |
50.39 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2974 |
2832 |
112.07 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1561 |
1486 |
1.80 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1545 |
1471 |
1.15 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1534 |
1461 |
3.26 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1436 |
1368 |
12.40 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1392 |
1326 |
0.18 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1363 |
1298 |
0.25 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1287 |
1226 |
6.34 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1246 |
1187 |
4.18 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1233 |
1175 |
1.85 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1210 |
1152 |
114.23 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1173 |
1117 |
17.31 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1142 |
1087 |
95.10 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1112 |
1059 |
44.00 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1018 |
969 |
34.26 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
979 |
932 |
71.01 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
962 |
917 |
22.23 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
873 |
832 |
6.96 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
748 |
713 |
1.30 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
710 |
676 |
6.67 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
298 |
284 |
14.62 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
59 |
56 |
4.29 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20711.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9523) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 19723.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.196 |
-0.054 |
0.077 |
| C2 |
-1.007 |
-0.678 |
-0.136 |
| C3 |
-0.874 |
0.803 |
0.197 |
| O4 |
0.315 |
-1.163 |
0.060 |
| O5 |
0.440 |
1.080 |
-0.253 |
| H6 |
1.627 |
0.037 |
1.087 |
| H7 |
1.991 |
-0.174 |
-0.666 |
| H8 |
-1.311 |
-0.825 |
-1.180 |
| H9 |
-0.958 |
0.977 |
1.281 |
| H10 |
-1.575 |
1.452 |
-0.330 |
| H11 |
-1.693 |
-1.220 |
0.520 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
| C1 | | 2.2998 | 2.2443 | 1.4166 | 1.4024 | 1.1022 | 1.0944 | 2.9088 | 2.6745 | 3.1804 | 3.1466 |
C2 | 2.2998 | | 1.5239 | 1.4219 | 2.2795 | 2.9910 | 3.0859 | 1.0978 | 2.1792 | 2.2128 | 1.0929 | C3 | 2.2443 | 1.5239 | | 2.3021 | 1.4163 | 2.7633 | 3.1478 | 2.1774 | 1.1009 | 1.0909 | 2.2065 | O4 | 1.4166 | 1.4219 | 2.3021 | | 2.2681 | 2.0535 | 2.0773 | 2.0729 | 2.7730 | 3.2502 | 2.0601 | O5 | 1.4024 | 2.2795 | 1.4163 | 2.2681 | | 2.0720 | 2.0366 | 2.7484 | 2.0777 | 2.0505 | 3.2302 | H6 | 1.1022 | 2.9910 | 2.7633 | 2.0535 | 2.0720 | | 1.8031 | 3.8102 | 2.7571 | 3.7769 | 3.5946 | H7 | 1.0944 | 3.0859 | 3.1478 | 2.0773 | 2.0366 | 1.8031 | | 3.4044 | 3.7161 | 3.9335 | 4.0086 | H8 | 2.9088 | 1.0978 | 2.1774 | 2.0729 | 2.7484 | 3.8102 | 3.4044 | | 3.0713 | 2.4452 | 1.7874 | H9 | 2.6745 | 2.1792 | 1.1009 | 2.7730 | 2.0777 | 2.7571 | 3.7161 | 3.0713 | | 1.7896 | 2.4385 | H10 | 3.1804 | 2.2128 | 1.0909 | 3.2502 | 2.0505 | 3.7769 | 3.9335 | 2.4452 | 1.7896 | | 2.8067 | H11 | 3.1466 | 1.0929 | 2.2065 | 2.0601 | 3.2302 | 3.5946 | 4.0086 | 1.7874 | 2.4385 | 2.8067 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O4 |
C2 |
108.234 |
|
C1 |
O5 |
C3 |
105.538 |
| C2 |
C3 |
O5 |
101.601 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
111.222 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
114.600 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
O4 |
102.736 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
111.264 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H11 |
113.938 |
| O4 |
C1 |
O5 |
107.132 |
|
O4 |
C1 |
H6 |
108.579 |
| O4 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.988 |
|
O4 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.045 |
| O4 |
C2 |
H11 |
109.310 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.071 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
108.687 |
|
O5 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.638 |
| O5 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.052 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.346 |
| H8 |
C2 |
H11 |
109.345 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.472 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.092 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.099 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.119 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.395 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.372 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.125 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.153 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.156 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.147 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.165 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.148 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.361 |
0.336 |
0.968 |
1.704 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-25.732 |
-0.767 |
0.695 |
| y |
-0.767 |
-34.988 |
0.438 |
| z |
0.695 |
0.438 |
-29.861 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
6.692 |
-0.767 |
0.695 |
| y |
-0.767 |
-7.192 |
0.438 |
| z |
0.695 |
0.438 |
0.499 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 0.999 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 9.256 |
|---|
| xy | -0.767 |
|---|
| xz | 0.695 |
|---|
| yz | 0.438 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.718 |
-0.057 |
0.051 |
| y |
-0.057 |
5.725 |
0.062 |
| z |
0.051 |
0.062 |
5.583 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
93.262 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.657 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -268.278841 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -268.278841 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 194.718375 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3160 |
3009 |
31.35 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3155 |
3005 |
22.35 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3088 |
2941 |
59.12 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3050 |
2905 |
76.04 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3044 |
2899 |
0.51 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3037 |
2893 |
136.96 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1555 |
1481 |
1.67 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1537 |
1464 |
0.97 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1530 |
1457 |
3.73 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1445 |
1376 |
10.01 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1409 |
1341 |
5.66 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1366 |
1301 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1268 |
1208 |
16.56 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1248 |
1188 |
5.07 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1233 |
1174 |
92.82 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1184 |
1128 |
104.35 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1162 |
1106 |
42.14 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1154 |
1098 |
23.57 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1113 |
1060 |
33.63 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
995 |
948 |
4.10 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
985 |
938 |
75.40 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
966 |
920 |
3.43 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
926 |
882 |
23.87 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
741 |
706 |
0.35 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
662 |
630 |
5.23 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
275 |
261 |
0.59 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
106i |
101i |
20.90 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20589.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9523) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 19607.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.206 |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
-0.944 |
0.733 |
0.195 |
| C3 |
-0.945 |
-0.733 |
-0.195 |
| O4 |
0.372 |
1.130 |
-0.172 |
| O5 |
0.372 |
-1.130 |
0.172 |
| H6 |
1.828 |
-0.094 |
-0.898 |
| H7 |
1.827 |
0.094 |
0.899 |
| H8 |
-1.098 |
0.858 |
1.275 |
| H9 |
-1.099 |
-0.858 |
-1.275 |
| H10 |
-1.652 |
-1.354 |
0.356 |
| H11 |
-1.652 |
1.354 |
-0.356 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
| C1 | | 2.2802 | 2.2802 | 1.4149 | 1.4149 | 1.0965 | 1.0965 | 2.7697 | 2.7700 | 3.1825 | 3.1825 |
C2 | 2.2802 | | 1.5176 | 1.4230 | 2.2813 | 3.0926 | 2.9301 | 1.0982 | 2.1721 | 2.2097 | 1.0910 | C3 | 2.2802 | 1.5176 | | 2.2813 | 1.4230 | 2.9304 | 3.0925 | 2.1722 | 1.0982 | 1.0910 | 2.2097 | O4 | 1.4149 | 1.4230 | 2.2813 | | 2.2859 | 2.0358 | 2.0827 | 2.0811 | 2.7074 | 3.2473 | 2.0447 | O5 | 1.4149 | 2.2813 | 1.4230 | 2.2859 | | 2.0827 | 2.0358 | 2.7074 | 2.0811 | 2.0447 | 3.2473 | H6 | 1.0965 | 3.0926 | 2.9304 | 2.0358 | 2.0827 | | 1.8065 | 3.7672 | 3.0477 | 3.9077 | 3.8079 | H7 | 1.0965 | 2.9301 | 3.0925 | 2.0827 | 2.0358 | 1.8065 | | 3.0471 | 3.7673 | 3.8076 | 3.9075 | H8 | 2.7697 | 1.0982 | 2.1722 | 2.0811 | 2.7074 | 3.7672 | 3.0471 | | 3.0742 | 2.4584 | 1.7931 | H9 | 2.7700 | 2.1721 | 1.0982 | 2.7074 | 2.0811 | 3.0477 | 3.7673 | 3.0742 | | 1.7931 | 2.4584 | H10 | 3.1825 | 2.2097 | 1.0910 | 3.2473 | 2.0447 | 3.9077 | 3.8076 | 2.4584 | 1.7931 | | 2.8000 | H11 | 3.1825 | 1.0910 | 2.2097 | 2.0447 | 3.2473 | 3.8079 | 3.9075 | 1.7931 | 2.4584 | 2.8000 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O4 |
C2 |
106.929 |
|
C1 |
O5 |
C3 |
106.932 |
| C2 |
C3 |
O5 |
101.710 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
111.272 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
114.812 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
O4 |
101.708 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
111.273 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H11 |
114.813 |
| O4 |
C1 |
O5 |
107.764 |
|
O4 |
C1 |
H6 |
107.641 |
| O4 |
C1 |
H7 |
111.428 |
|
O4 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.610 |
| O4 |
C2 |
H11 |
108.117 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.428 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.641 |
|
O5 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.609 |
| O5 |
C3 |
H10 |
108.117 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.922 |
| H8 |
C2 |
H11 |
109.979 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.979 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.097 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.096 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.096 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.399 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.399 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.139 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.139 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.148 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.148 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.160 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.160 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.324 |
0.000 |
0.001 |
1.324 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-25.704 |
-0.001 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.001 |
-35.164 |
1.264 |
| z |
0.000 |
1.264 |
-29.636 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
6.696 |
-0.001 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.001 |
-7.494 |
1.264 |
| z |
0.000 |
1.264 |
0.798 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 1.596 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 9.460 |
|---|
| xy | -0.001 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 1.264 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.794 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
5.681 |
0.059 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.059 |
5.610 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
93.201 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.654 |
