Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -573.411680 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -573.411172 |
| HF Energy | -573.411680 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 78.740066 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Point Group is Cs
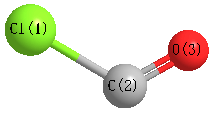
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Cl1 |
-0.500 |
-0.914 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.850 |
0.000 |
| O3 |
1.062 |
1.304 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Cl1 |
C2 |
O3 |
| Cl1 | | 1.8333 | 2.7123 |
C2 | 1.8333 | | 1.1547 | O3 | 2.7123 | 1.1547 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Cl1 |
C2 |
O3 |
128.956 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Cl |
0.106 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.068 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.173 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.531 |
-0.222 |
0.000 |
0.575 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-24.782 |
-0.958 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.958 |
-23.561 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-22.633 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.685 |
-0.958 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.958 |
0.146 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.539 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.077 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.221 |
|---|
| xy | -0.958 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.699 |
1.255 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.255 |
5.377 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.397 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
59.024 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.683 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -573.399673 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -573.399673 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 61.713367 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Cl1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.576 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.269 |
| O3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.397 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Cl1 |
C2 |
O3 |
| Cl1 | | 2.8454 | 3.9736 |
C2 | 2.8454 | | 1.1282 | O3 | 3.9736 | 1.1282 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Cl1 |
C2 |
O3 |
180.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Cl |
-0.014 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.193 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.179 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.107 |
1.107 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.350 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-23.350 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-23.437 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.043 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
0.043 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.087 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.173 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.546 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.546 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.344 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
102.943 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.146 |
