Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -697.532805 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -697.533957 |
| HF Energy | -697.532805 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 188.440158 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
851 |
811 |
117.78 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
581 |
553 |
13.63 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
346 |
329 |
16.57 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
159 |
152 |
10.05 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A" |
707 |
673 |
556.98 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
443 |
422 |
0.93 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 1542.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9526) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 1469.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| S1 |
-0.328 |
-0.194 |
0.000 |
| F2 |
1.240 |
0.059 |
0.000 |
| F3 |
-0.328 |
0.143 |
1.638 |
| F4 |
-0.328 |
0.143 |
-1.638 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
S1 |
F2 |
F3 |
F4 |
| S1 | | 1.5888 | 1.6723 | 1.6723 |
F2 | 1.5888 | | 2.2695 | 2.2695 | F3 | 1.6723 | 2.2695 | | 3.2761 | F4 | 1.6723 | 2.2695 | 3.2761 | |
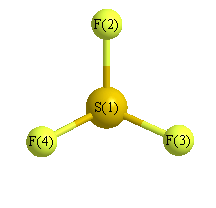 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| F2 |
S1 |
F3 |
88.166 |
|
F2 |
S1 |
F4 |
88.166 |
| F3 |
S1 |
F4 |
156.771 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
S |
1.095 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
F |
-0.301 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
F |
-0.397 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
F |
-0.397 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.763 |
-0.705 |
0.000 |
1.039 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-26.834 |
-0.038 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.038 |
-25.993 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-33.429 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.877 |
-0.038 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.038 |
4.139 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-7.016 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -14.031 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.841 |
|---|
| xy | -0.038 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.284 |
0.084 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.084 |
2.603 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.279 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
86.054 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.277 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -697.532009 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -697.532009 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 188.515299 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
858 |
817 |
118.94 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
571 |
544 |
4.53 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
350 |
334 |
16.60 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
B1 |
141i |
134i |
10.01 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
B2 |
725 |
691 |
627.18 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
B2 |
458 |
436 |
0.67 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 1410.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9526) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 1343.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| S1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.389 |
| F2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.204 |
| F3 |
0.000 |
1.683 |
0.256 |
| F4 |
0.000 |
-1.683 |
0.256 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
S1 |
F2 |
F3 |
F4 |
| S1 | | 1.5937 | 1.6878 | 1.6878 |
F2 | 1.5937 | | 2.2279 | 2.2279 | F3 | 1.6878 | 2.2279 | | 3.3651 | F4 | 1.6878 | 2.2279 | 3.3651 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| F2 |
S1 |
F3 |
85.467 |
|
F2 |
S1 |
F4 |
85.467 |
| F3 |
S1 |
F4 |
170.933 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
S |
1.153 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
F |
-0.291 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
F |
-0.431 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
F |
-0.431 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.887 |
0.887 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-25.741 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-34.109 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-26.767 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.697 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-7.856 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.159 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 6.317 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 8.368 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.571 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
5.380 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.291 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
86.455 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.298 |
