Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3791 |
3611 |
46.63 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3646 |
3473 |
43.82 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3145 |
2996 |
41.30 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3143 |
2994 |
42.53 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3118 |
2970 |
8.68 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3097 |
2950 |
16.43 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3079 |
2933 |
24.55 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3053 |
2909 |
34.89 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
3051 |
2907 |
16.24 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1815 |
1729 |
365.44 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1638 |
1560 |
140.14 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1528 |
1456 |
8.74 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1517 |
1446 |
9.70 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1515 |
1444 |
2.72 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1488 |
1418 |
8.98 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1444 |
1375 |
70.46 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1435 |
1367 |
10.88 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1380 |
1314 |
43.40 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1339 |
1276 |
21.43 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1285 |
1224 |
49.05 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1266 |
1206 |
6.87 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1149 |
1095 |
0.61 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1135 |
1081 |
2.34 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1088 |
1037 |
2.07 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1066 |
1016 |
2.67 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
945 |
901 |
2.95 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
906 |
863 |
0.63 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
864 |
823 |
2.44 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
773 |
737 |
4.99 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
677 |
644 |
5.88 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
613 |
584 |
12.50 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
525 |
500 |
7.71 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
437 |
416 |
2.65 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
349 |
332 |
2.34 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
281 |
268 |
0.21 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
216 |
206 |
221.50 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
192 |
183 |
8.12 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
107 |
102 |
2.47 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
82 |
78 |
4.15 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 29088.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9526) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27709.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
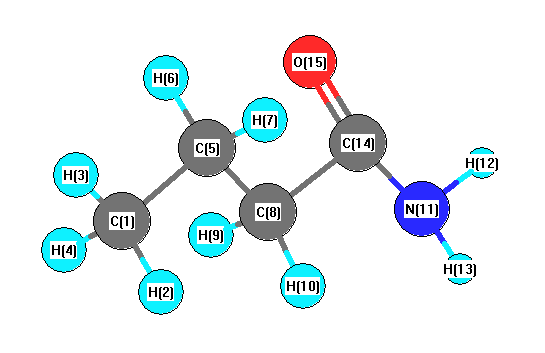
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.562 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.153 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.162 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.193 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.160 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.187 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.328 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.144 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.186 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
N |
-0.609 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.337 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.312 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
0.432 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
O |
-0.530 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.019 |
-3.800 |
-0.160 |
3.804 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-33.402 |
-6.747 |
-0.760 |
| y |
-6.747 |
-39.565 |
-0.014 |
| z |
-0.760 |
-0.014 |
-38.315 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.538 |
-6.747 |
-0.760 |
| y |
-6.747 |
-3.707 |
-0.014 |
| z |
-0.760 |
-0.014 |
-1.831 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -3.663 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 6.164 |
|---|
| xy | -6.747 |
|---|
| xz | -0.760 |
|---|
| yz | -0.014 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.976 |
-0.278 |
-0.187 |
| y |
-0.278 |
8.964 |
0.029 |
| z |
-0.187 |
0.029 |
7.015 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
217.601 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.751 |