Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -323.554464 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -323.554464 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 234.924850 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3157 |
3007 |
27.63 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3087 |
2941 |
30.75 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3072 |
2927 |
26.12 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3064 |
2919 |
21.67 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1789 |
1704 |
242.05 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1535 |
1462 |
15.36 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1522 |
1450 |
3.33 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1511 |
1439 |
2.68 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1441 |
1372 |
18.62 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1432 |
1364 |
7.75 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1346 |
1282 |
6.17 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1175 |
1120 |
9.10 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1098 |
1046 |
37.76 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1061 |
1011 |
3.93 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
960 |
915 |
427.81 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
912 |
868 |
187.82 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
703 |
670 |
6.40 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
408 |
389 |
0.69 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
362 |
345 |
0.42 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
161 |
154 |
0.66 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
3152 |
3002 |
67.92 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
3134 |
2986 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
3120 |
2972 |
4.25 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
1508 |
1437 |
10.22 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
1333 |
1270 |
0.07 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
1284 |
1223 |
0.53 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
1196 |
1139 |
0.80 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
908 |
865 |
1.24 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
776 |
739 |
1.95 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
229 |
218 |
0.13 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
215 |
205 |
0.94 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
101 |
96 |
1.88 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
47i |
44i |
0.05 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 23352.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9526) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22245.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-1.956 |
2.172 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
-1.514 |
0.709 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
0.000 |
0.588 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
0.325 |
-0.813 |
0.000 |
| N5 |
1.675 |
-1.020 |
0.000 |
| O6 |
1.959 |
-2.165 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
-3.047 |
2.245 |
0.000 |
| H8 |
-1.587 |
2.700 |
0.886 |
| H9 |
-1.587 |
2.700 |
-0.886 |
| H10 |
-1.911 |
0.194 |
-0.880 |
| H11 |
-1.911 |
0.194 |
0.880 |
| H12 |
0.433 |
1.058 |
0.890 |
| H13 |
0.433 |
1.058 |
-0.890 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
N5 |
O6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
| C1 | | 1.5287 | 2.5177 | 3.7572 | 4.8350 | 5.8438 | 1.0930 | 1.0950 | 1.0950 | 2.1664 | 2.1664 | 2.7828 | 2.7828 |
C2 | 1.5287 | | 1.5185 | 2.3869 | 3.6270 | 4.5083 | 2.1700 | 2.1801 | 2.1801 | 1.0950 | 1.0950 | 2.1685 | 2.1685 | C3 | 2.5177 | 1.5185 | | 1.4377 | 2.3216 | 3.3792 | 3.4684 | 2.7865 | 2.7865 | 2.1406 | 2.1406 | 1.0955 | 1.0955 | O4 | 3.7572 | 2.3869 | 1.4377 | | 1.3652 | 2.1214 | 4.5518 | 4.0963 | 4.0963 | 2.6053 | 2.6053 | 2.0739 | 2.0739 | N5 | 4.8350 | 3.6270 | 2.3216 | 1.3652 | | 1.1801 | 5.7405 | 5.0261 | 5.0261 | 3.8863 | 3.8863 | 2.5789 | 2.5789 | O6 | 5.8438 | 4.5083 | 3.3792 | 2.1214 | 1.1801 | | 6.6718 | 6.0855 | 6.0855 | 4.6172 | 4.6172 | 3.6755 | 3.6755 | H7 | 1.0930 | 2.1700 | 3.4684 | 4.5518 | 5.7405 | 6.6718 | | 1.7673 | 1.7673 | 2.5047 | 2.5047 | 3.7831 | 3.7831 | H8 | 1.0950 | 2.1801 | 2.7865 | 4.0963 | 5.0261 | 6.0855 | 1.7673 | | 1.7710 | 3.0832 | 2.5274 | 2.6035 | 3.1512 | H9 | 1.0950 | 2.1801 | 2.7865 | 4.0963 | 5.0261 | 6.0855 | 1.7673 | 1.7710 | | 2.5274 | 3.0832 | 3.1512 | 2.6035 | H10 | 2.1664 | 1.0950 | 2.1406 | 2.6053 | 3.8863 | 4.6172 | 2.5047 | 3.0832 | 2.5274 | | 1.7609 | 3.0617 | 2.4980 | H11 | 2.1664 | 1.0950 | 2.1406 | 2.6053 | 3.8863 | 4.6172 | 2.5047 | 2.5274 | 3.0832 | 1.7609 | | 2.4980 | 3.0617 | H12 | 2.7828 | 2.1685 | 1.0955 | 2.0739 | 2.5789 | 3.6755 | 3.7831 | 2.6035 | 3.1512 | 3.0617 | 2.4980 | | 1.7800 | H13 | 2.7828 | 2.1685 | 1.0955 | 2.0739 | 2.5789 | 3.6755 | 3.7831 | 3.1512 | 2.6035 | 2.4980 | 3.0617 | 1.7800 | |
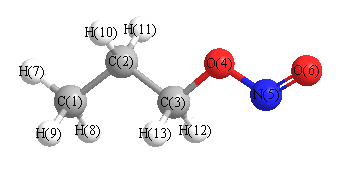 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
111.430 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H10 |
110.224 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H11 |
110.224 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.633 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H8 |
111.313 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H9 |
111.313 |
| C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
107.662 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H12 |
111.076 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H13 |
111.076 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H10 |
108.902 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H11 |
108.902 |
|
C3 |
O4 |
N5 |
111.818 |
| O4 |
C3 |
H12 |
109.164 |
|
O4 |
C3 |
H13 |
109.164 |
| O4 |
N5 |
O6 |
112.708 |
|
H7 |
C1 |
H8 |
107.747 |
| H7 |
C1 |
H9 |
107.747 |
|
H8 |
C1 |
H9 |
107.930 |
| H10 |
C2 |
H11 |
107.041 |
|
H12 |
C3 |
H13 |
108.663 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.525 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.176 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.199 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.105 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
N |
-0.118 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
O |
-0.031 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.170 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.159 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.159 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.172 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.172 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.162 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.162 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.692 |
2.826 |
0.000 |
3.294 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-38.468 |
1.847 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.847 |
-40.370 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-34.960 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.803 |
1.847 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.847 |
-3.656 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.459 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 8.918 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 1.902 |
|---|
| xy | 1.847 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.740 |
-1.999 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.999 |
9.017 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.194 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
243.272 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
15.597 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -323.556006 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -323.565191 |
| HF Energy | -323.556006 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 242.596227 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3154 |
3004 |
28.93 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3153 |
3003 |
25.99 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3146 |
2997 |
33.20 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3116 |
2969 |
11.49 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3083 |
2937 |
26.92 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3070 |
2925 |
20.30 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3065 |
2920 |
24.33 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1792 |
1707 |
251.23 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1522 |
1450 |
12.76 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1516 |
1444 |
8.05 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1504 |
1433 |
4.98 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1499 |
1428 |
2.88 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1442 |
1373 |
7.98 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1424 |
1357 |
10.34 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1393 |
1327 |
1.71 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1321 |
1258 |
10.29 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1309 |
1247 |
11.50 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1200 |
1143 |
13.08 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1131 |
1077 |
14.94 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1106 |
1054 |
30.14 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1027 |
979 |
9.54 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
960 |
914 |
203.51 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
896 |
854 |
293.49 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
887 |
845 |
14.70 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
807 |
769 |
5.50 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
650 |
619 |
7.12 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
471 |
448 |
4.76 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
397 |
379 |
2.88 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
296 |
282 |
0.72 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
247 |
236 |
0.58 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
187 |
178 |
0.36 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
118 |
112 |
1.00 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
69 |
66 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 23478.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9526) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22365.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.779 |
1.162 |
0.065 |
| C2 |
1.770 |
-0.340 |
-0.207 |
| C3 |
0.512 |
-1.030 |
0.293 |
| O4 |
-0.636 |
-0.554 |
-0.428 |
| N5 |
-1.510 |
0.134 |
0.427 |
| O6 |
-2.433 |
0.549 |
-0.171 |
| H7 |
2.705 |
1.617 |
-0.297 |
| H8 |
1.697 |
1.369 |
1.138 |
| H9 |
0.943 |
1.657 |
-0.438 |
| H10 |
1.878 |
-0.532 |
-1.280 |
| H11 |
2.623 |
-0.820 |
0.288 |
| H12 |
0.555 |
-2.110 |
0.129 |
| H13 |
0.348 |
-0.837 |
1.359 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
N5 |
O6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
| C1 | | 1.5264 | 2.5422 | 3.0030 | 3.4644 | 4.2623 | 1.0933 | 1.0954 | 1.0939 | 2.1653 | 2.1659 | 3.4940 | 2.7786 |
C2 | 1.5264 | | 1.5198 | 2.4254 | 3.3738 | 4.2958 | 2.1707 | 2.1756 | 2.1733 | 1.0955 | 1.0968 | 2.1730 | 2.1731 | C3 | 2.5422 | 1.5198 | | 1.4361 | 2.3360 | 3.3726 | 3.4878 | 2.8061 | 2.8174 | 2.1420 | 2.1223 | 1.0934 | 1.0959 | O4 | 3.0030 | 2.4254 | 1.4361 | | 1.4028 | 2.1241 | 3.9860 | 3.4047 | 2.7164 | 2.6538 | 3.3473 | 2.0372 | 2.0600 | N5 | 3.4644 | 3.3738 | 2.3360 | 1.4028 | | 1.1751 | 4.5259 | 3.5092 | 3.0138 | 3.8509 | 4.2439 | 3.0639 | 2.2944 | O6 | 4.2623 | 4.2958 | 3.3726 | 2.1241 | 1.1751 | | 5.2485 | 4.4089 | 3.5628 | 4.5800 | 5.2580 | 4.0109 | 3.4634 | H7 | 1.0933 | 2.1707 | 3.4878 | 3.9860 | 4.5259 | 5.2485 | | 1.7706 | 1.7675 | 2.5037 | 2.5077 | 4.3236 | 3.7846 | H8 | 1.0954 | 2.1756 | 2.8061 | 3.4047 | 3.5092 | 4.4089 | 1.7706 | | 1.7706 | 3.0807 | 2.5244 | 3.7981 | 2.5959 | H9 | 1.0939 | 2.1733 | 2.8174 | 2.7164 | 3.0138 | 3.5628 | 1.7675 | 1.7706 | | 2.5240 | 3.0795 | 3.8287 | 3.1316 | H10 | 2.1653 | 1.0955 | 2.1420 | 2.6538 | 3.8509 | 4.5800 | 2.5037 | 3.0807 | 2.5240 | | 1.7596 | 2.4948 | 3.0658 | H11 | 2.1659 | 1.0968 | 2.1223 | 3.3473 | 4.2439 | 5.2580 | 2.5077 | 2.5244 | 3.0795 | 1.7596 | | 2.4426 | 2.5152 | H12 | 3.4940 | 2.1730 | 1.0934 | 2.0372 | 3.0639 | 4.0109 | 4.3236 | 3.7981 | 3.8287 | 2.4948 | 2.4426 | | 1.7822 | H13 | 2.7786 | 2.1731 | 1.0959 | 2.0600 | 2.2944 | 3.4634 | 3.7846 | 2.5959 | 3.1316 | 3.0658 | 2.5152 | 1.7822 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
113.135 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H10 |
110.263 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H11 |
110.241 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.827 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H8 |
111.097 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H9 |
111.003 |
| C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
110.243 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H12 |
111.467 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H13 |
111.331 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H10 |
108.894 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H11 |
107.301 |
|
C3 |
O4 |
N5 |
110.737 |
| O4 |
C3 |
H12 |
106.501 |
|
O4 |
C3 |
H13 |
108.143 |
| O4 |
N5 |
O6 |
110.652 |
|
H7 |
C1 |
H8 |
107.996 |
| H7 |
C1 |
H9 |
107.824 |
|
H8 |
C1 |
H9 |
107.957 |
| H10 |
C2 |
H11 |
106.766 |
|
H12 |
C3 |
H13 |
108.982 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.520 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.261 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.100 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.073 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
N |
-0.181 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
O |
-0.017 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.164 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.160 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.171 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.172 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.159 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.163 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.163 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.838 |
-0.994 |
0.816 |
3.116 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-39.359 |
0.482 |
-0.827 |
| y |
0.482 |
-35.055 |
-1.119 |
| z |
-0.827 |
-1.119 |
-37.256 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.204 |
0.482 |
-0.827 |
| y |
0.482 |
3.253 |
-1.119 |
| z |
-0.827 |
-1.119 |
-0.049 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.097 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -4.305 |
|---|
| xy | 0.482 |
|---|
| xz | -0.827 |
|---|
| yz | -1.119 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.601 |
-1.075 |
0.045 |
| y |
-1.075 |
7.470 |
0.016 |
| z |
0.045 |
0.016 |
6.612 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
191.524 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.839 |
