Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.831442 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.835611 |
| HF Energy | -169.831442 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 71.225998 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3830 |
3649 |
61.16 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3606 |
3435 |
11.25 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3160 |
3010 |
28.05 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1764 |
1680 |
324.88 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1417 |
1350 |
18.65 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1382 |
1317 |
3.87 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1210 |
1152 |
123.86 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1093 |
1041 |
173.06 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
597 |
569 |
54.89 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1054 |
1004 |
0.42 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
831 |
792 |
36.49 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
635 |
605 |
213.44 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10288.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9526) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9800.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
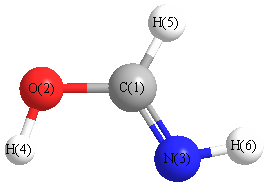
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.415 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.112 |
-0.332 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.158 |
-0.095 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.254 |
1.478 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.843 |
-1.262 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.888 |
0.611 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3396 | 1.2651 | 1.0931 | 1.8768 | 1.8979 |
O2 | 1.3396 | | 2.2820 | 2.0034 | 0.9675 | 3.1444 | N3 | 1.2651 | 2.2820 | | 2.1137 | 2.3164 | 1.0156 | H4 | 1.0931 | 2.0034 | 2.1137 | | 2.8025 | 2.3105 | H5 | 1.8768 | 0.9675 | 2.3164 | 2.8025 | | 3.3115 | H6 | 1.8979 | 3.1444 | 1.0156 | 2.3105 | 3.3115 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
107.783 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
112.184 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
122.332 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
110.467 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
127.201 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.152 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.422 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.524 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.370 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.273 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.088 |
1.201 |
0.000 |
1.204 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-20.002 |
3.659 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.659 |
-14.188 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.191 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.312 |
3.659 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.659 |
5.409 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.097 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.193 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.814 |
|---|
| xy | 3.659 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.910 |
-0.109 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.109 |
3.649 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.411 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
40.768 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.385 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.831442 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.835611 |
| HF Energy | -169.831442 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 71.225667 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3831 |
3650 |
61.26 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3606 |
3436 |
11.26 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3160 |
3010 |
28.01 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1764 |
1681 |
324.55 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1417 |
1350 |
18.57 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1382 |
1316 |
3.92 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1209 |
1152 |
124.02 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1092 |
1040 |
173.24 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
597 |
569 |
54.93 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1054 |
1004 |
0.42 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
831 |
791 |
36.62 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
634 |
604 |
213.41 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10287.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9526) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9800.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
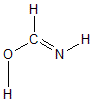
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.421 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.110 |
-0.336 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.154 |
-0.097 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.256 |
1.481 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.820 |
-1.261 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.873 |
0.621 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3429 | 1.2651 | 1.0913 | 1.8706 | 1.8842 |
O2 | 1.3429 | | 2.2765 | 2.0077 | 0.9693 | 3.1330 | N3 | 1.2651 | 2.2765 | | 2.1167 | 2.2918 | 1.0167 | H4 | 1.0913 | 2.0077 | 2.1167 | | 2.7996 | 2.2964 | H5 | 1.8706 | 0.9693 | 2.2918 | 2.7996 | | 3.2861 | H6 | 1.8842 | 3.1330 | 1.0167 | 2.2964 | 3.2861 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
106.895 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
110.870 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
121.572 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
110.713 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
127.715 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.152 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.422 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.524 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.371 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.273 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.090 |
1.201 |
0.000 |
1.204 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-20.000 |
3.657 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.657 |
-14.185 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.191 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.312 |
3.657 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.657 |
5.411 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.099 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.197 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.815 |
|---|
| xy | 3.657 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.909 |
-0.108 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.108 |
3.649 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.410 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
40.767 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.385 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.824788 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.828880 |
| HF Energy | -169.824788 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 70.788063 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3876 |
3692 |
41.71 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3517 |
3351 |
7.47 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3221 |
3068 |
10.08 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1761 |
1678 |
330.21 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1410 |
1343 |
1.01 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1347 |
1283 |
36.45 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1133 |
1079 |
278.53 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1096 |
1044 |
38.33 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
600 |
572 |
40.06 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1077 |
1026 |
73.29 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
852 |
812 |
65.30 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
511 |
487 |
86.11 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10200.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9526) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9717.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
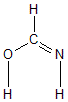
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.443 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.098 |
-0.352 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.222 |
0.120 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.297 |
1.489 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.836 |
-1.281 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.361 |
-0.894 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3556 | 1.2642 | 1.0873 | 1.9168 | 1.9080 |
O2 | 1.3556 | | 2.3673 | 2.0078 | 0.9659 | 2.5179 | N3 | 1.2642 | 2.3673 | | 2.0454 | 2.4897 | 1.0229 | H4 | 1.0873 | 2.0078 | 2.0454 | | 2.8227 | 2.9032 | H5 | 1.9168 | 0.9659 | 2.4897 | 2.8227 | | 2.2310 | H6 | 1.9080 | 2.5179 | 1.0229 | 2.9032 | 2.2310 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
110.184 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
112.644 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
129.248 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
110.058 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
120.694 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.135 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.432 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.445 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.164 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.343 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.234 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.049 |
-1.994 |
0.000 |
2.253 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.818 |
-2.184 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.184 |
-12.943 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.116 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-7.789 |
-2.184 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.184 |
8.524 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.736 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.471 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -10.875 |
|---|
| xy | -2.184 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.879 |
-0.063 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.063 |
3.669 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.386 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
41.330 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.429 |


