Jump to
S1C2
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVTZ
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVTZ
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -235.857087 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -235.870533 |
| HF Energy | -235.857087 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 255.728206 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3147 |
3009 |
66.22 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3120 |
2983 |
30.21 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3113 |
2976 |
47.51 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3110 |
2974 |
10.55 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3092 |
2956 |
30.34 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
3074 |
2939 |
8.99 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
3037 |
2903 |
32.48 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
3032 |
2898 |
31.86 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1523 |
1456 |
2.73 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1500 |
1434 |
2.36 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1495 |
1429 |
5.81 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1480 |
1415 |
0.64 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1424 |
1361 |
3.78 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1412 |
1350 |
12.61 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1331 |
1272 |
6.24 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1313 |
1255 |
4.37 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1246 |
1191 |
1.05 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
1212 |
1159 |
0.41 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
1022 |
977 |
0.38 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
997 |
953 |
0.70 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
962 |
920 |
0.36 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
932 |
891 |
0.25 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
883 |
844 |
0.16 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A' |
722 |
690 |
1.04 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A' |
613 |
586 |
1.13 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A' |
400 |
383 |
0.30 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A' |
357 |
341 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A' |
144 |
138 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
3124 |
2987 |
12.93 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
3108 |
2972 |
40.39 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
3100 |
2964 |
17.32 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
3070 |
2935 |
79.42 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
1515 |
1448 |
8.37 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A" |
1490 |
1425 |
0.10 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A" |
1475 |
1410 |
5.75 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A" |
1278 |
1221 |
0.08 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A" |
1266 |
1210 |
0.50 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A" |
1231 |
1177 |
0.31 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A" |
1194 |
1141 |
2.26 |
|
|
|
| 40 |
A" |
1095 |
1047 |
0.08 |
|
|
|
| 41 |
A" |
996 |
952 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 42 |
A" |
957 |
915 |
1.95 |
|
|
|
| 43 |
A" |
891 |
852 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 44 |
A" |
784 |
750 |
0.11 |
|
|
|
| 45 |
A" |
397 |
380 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 46 |
A" |
304 |
290 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 47 |
A" |
250 |
239 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 48 |
A" |
199 |
190 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 36706.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.956) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 35091.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.107 |
0.402 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.414 |
-1.736 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
-0.107 |
-0.686 |
1.123 |
| C4 |
-0.107 |
-0.686 |
-1.123 |
| C5 |
1.122 |
1.309 |
0.000 |
| C6 |
-1.282 |
1.377 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
1.345 |
-2.296 |
0.000 |
| H8 |
-0.381 |
-2.474 |
0.000 |
| H9 |
0.890 |
-0.958 |
1.464 |
| H10 |
0.890 |
-0.958 |
-1.464 |
| H11 |
-0.954 |
-1.352 |
1.143 |
| H12 |
-0.954 |
-1.352 |
-1.143 |
| H13 |
2.049 |
0.736 |
0.000 |
| H14 |
-2.238 |
0.854 |
0.000 |
| H15 |
1.129 |
1.947 |
-0.881 |
| H16 |
1.129 |
1.947 |
0.881 |
| H17 |
-1.255 |
2.015 |
0.881 |
| H18 |
-1.255 |
2.015 |
-0.881 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
C5 |
C6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
H15 |
H16 |
H17 |
H18 |
| C1 | | 2.2006 | 1.5636 | 1.5636 | 1.5272 | 1.5273 | 3.0637 | 2.8890 | 2.2330 | 2.2330 | 2.2581 | 2.2581 | 2.1813 | 2.1784 | 2.1661 | 2.1661 | 2.1674 | 2.1674 |
C2 | 2.2006 | | 1.6238 | 1.6238 | 3.1264 | 3.5452 | 1.0859 | 1.0847 | 1.7246 | 1.7246 | 1.8238 | 1.8238 | 2.9635 | 3.7069 | 3.8542 | 3.8542 | 4.1995 | 4.1995 | C3 | 1.5636 | 1.6238 | | 2.2467 | 2.5982 | 2.6264 | 2.4418 | 2.1297 | 1.0881 | 2.7859 | 1.0781 | 2.5093 | 2.8159 | 2.8589 | 3.5324 | 2.9187 | 2.9449 | 3.5540 | C4 | 1.5636 | 1.6238 | 2.2467 | | 2.5982 | 2.6264 | 2.4418 | 2.1297 | 2.7859 | 1.0881 | 2.5093 | 1.0781 | 2.8159 | 2.8589 | 2.9187 | 3.5324 | 3.5540 | 2.9449 | C5 | 1.5272 | 3.1264 | 2.5982 | 2.5982 | | 2.4053 | 3.6123 | 4.0707 | 2.7087 | 2.7087 | 3.5631 | 3.5631 | 1.0899 | 3.3903 | 1.0879 | 1.0879 | 2.6316 | 2.6316 | C6 | 1.5273 | 3.5452 | 2.6264 | 2.6264 | 2.4053 | | 4.5158 | 3.9550 | 3.5092 | 3.5092 | 2.9761 | 2.9761 | 3.3924 | 1.0890 | 2.6303 | 2.6303 | 1.0882 | 1.0882 | H7 | 3.0637 | 1.0859 | 2.4418 | 2.4418 | 3.6123 | 4.5158 | | 1.7344 | 2.0346 | 2.0346 | 2.7355 | 2.7355 | 3.1129 | 4.7703 | 4.3394 | 4.3394 | 5.1112 | 5.1112 | H8 | 2.8890 | 1.0847 | 2.1297 | 2.1297 | 4.0707 | 3.9550 | 1.7344 | | 2.4609 | 2.4609 | 1.7013 | 1.7013 | 4.0258 | 3.8110 | 4.7545 | 4.7545 | 4.6577 | 4.6577 | H9 | 2.2330 | 1.7246 | 1.0881 | 2.7859 | 2.7087 | 3.5092 | 2.0346 | 2.4609 | | 2.9275 | 1.9132 | 3.2171 | 2.5209 | 3.9000 | 3.7412 | 2.9729 | 3.7126 | 4.3521 | H10 | 2.2330 | 1.7246 | 2.7859 | 1.0881 | 2.7087 | 3.5092 | 2.0346 | 2.4609 | 2.9275 | | 3.2171 | 1.9132 | 2.5209 | 3.9000 | 2.9729 | 3.7412 | 4.3521 | 3.7126 | H11 | 2.2581 | 1.8238 | 1.0781 | 2.5093 | 3.5631 | 2.9761 | 2.7355 | 1.7013 | 1.9132 | 3.2171 | | 2.2851 | 3.8318 | 2.7959 | 4.3954 | 3.9106 | 3.3904 | 3.9396 | H12 | 2.2581 | 1.8238 | 2.5093 | 1.0781 | 3.5631 | 2.9761 | 2.7355 | 1.7013 | 3.2171 | 1.9132 | 2.2851 | | 3.8318 | 2.7959 | 3.9106 | 4.3954 | 3.9396 | 3.3904 | H13 | 2.1813 | 2.9635 | 2.8159 | 2.8159 | 1.0899 | 3.3924 | 3.1129 | 4.0258 | 2.5209 | 2.5209 | 3.8318 | 3.8318 | | 4.2882 | 1.7577 | 1.7577 | 3.6510 | 3.6510 | H14 | 2.1784 | 3.7069 | 2.8589 | 2.8589 | 3.3903 | 1.0890 | 4.7703 | 3.8110 | 3.9000 | 3.9000 | 2.7959 | 2.7959 | 4.2882 | | 3.6481 | 3.6481 | 1.7578 | 1.7578 | H15 | 2.1661 | 3.8542 | 3.5324 | 2.9187 | 1.0879 | 2.6303 | 4.3394 | 4.7545 | 3.7412 | 2.9729 | 4.3954 | 3.9106 | 1.7577 | 3.6481 | | 1.7622 | 2.9656 | 2.3855 | H16 | 2.1661 | 3.8542 | 2.9187 | 3.5324 | 1.0879 | 2.6303 | 4.3394 | 4.7545 | 2.9729 | 3.7412 | 3.9106 | 4.3954 | 1.7577 | 3.6481 | 1.7622 | | 2.3855 | 2.9656 | H17 | 2.1674 | 4.1995 | 2.9449 | 3.5540 | 2.6316 | 1.0882 | 5.1112 | 4.6577 | 3.7126 | 4.3521 | 3.3904 | 3.9396 | 3.6510 | 1.7578 | 2.9656 | 2.3855 | | 1.7617 | H18 | 2.1674 | 4.1995 | 3.5540 | 2.9449 | 2.6316 | 1.0882 | 5.1112 | 4.6577 | 4.3521 | 3.7126 | 3.9396 | 3.3904 | 3.6510 | 1.7578 | 2.3855 | 2.9656 | 1.7617 | |
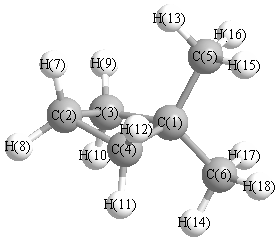 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C3 |
C2 |
87.302 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H9 |
113.514 |
| C1 |
C3 |
H11 |
116.260 |
|
C1 |
C4 |
C2 |
87.302 |
| C1 |
C4 |
H10 |
113.514 |
|
C1 |
C4 |
H12 |
116.260 |
| C1 |
C5 |
H13 |
111.824 |
|
C1 |
C5 |
H15 |
110.727 |
| C1 |
C5 |
H16 |
110.727 |
|
C1 |
C6 |
H14 |
111.641 |
| C1 |
C6 |
H17 |
110.807 |
|
C1 |
C6 |
H18 |
110.807 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
76.141 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
82.239 |
| C2 |
C4 |
H10 |
76.141 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H12 |
82.239 |
| C3 |
C1 |
C4 |
91.856 |
|
C3 |
C1 |
C5 |
114.404 |
| C3 |
C1 |
C6 |
116.358 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
C4 |
87.546 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H7 |
127.485 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
101.828 |
| C4 |
C1 |
C5 |
114.404 |
|
C4 |
C1 |
C6 |
116.358 |
| C4 |
C2 |
H7 |
127.485 |
|
C4 |
C2 |
H8 |
101.828 |
| C5 |
C1 |
C6 |
103.892 |
|
H7 |
C2 |
H8 |
106.076 |
| H9 |
C3 |
H11 |
124.059 |
|
H10 |
C4 |
H12 |
124.059 |
| H13 |
C5 |
H15 |
107.620 |
|
H13 |
C5 |
H16 |
107.620 |
| H14 |
C6 |
H17 |
107.675 |
|
H14 |
C6 |
H18 |
107.675 |
| H15 |
C5 |
H16 |
108.168 |
|
H17 |
C6 |
H18 |
108.082 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.092 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.187 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.187 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.187 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.332 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.299 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.089 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.087 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.087 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.087 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.090 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.090 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.100 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.090 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.096 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
H |
0.096 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
H |
0.095 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
H |
0.095 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.013 |
0.028 |
0.000 |
0.031 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-39.752 |
0.339 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.339 |
-40.565 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-40.367 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.713 |
0.339 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.339 |
-0.505 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.208 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.416 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.813 |
|---|
| xy | 0.339 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.998 |
-0.152 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.152 |
10.918 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
9.887 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
167.307 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
12.935 |
