Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -235.856625 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -235.856625 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 226.223319 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3140 |
3002 |
50.05 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3128 |
2990 |
15.95 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3123 |
2986 |
36.86 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3123 |
2985 |
0.83 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3043 |
2910 |
30.09 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
3042 |
2909 |
51.03 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
3038 |
2905 |
33.86 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
3028 |
2895 |
6.13 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1768 |
1690 |
1.04 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1508 |
1442 |
8.60 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1505 |
1438 |
8.17 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1494 |
1428 |
1.05 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1478 |
1413 |
2.06 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1431 |
1368 |
2.34 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1423 |
1360 |
3.16 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1412 |
1350 |
0.80 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1353 |
1294 |
0.73 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
1343 |
1284 |
1.57 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
1283 |
1227 |
5.78 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
1173 |
1122 |
0.89 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
1101 |
1053 |
8.91 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
1099 |
1051 |
0.85 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
1057 |
1010 |
1.07 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A' |
939 |
897 |
4.21 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A' |
916 |
875 |
3.31 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A' |
530 |
507 |
0.21 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A' |
393 |
376 |
1.13 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A' |
317 |
303 |
0.56 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A' |
142 |
136 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
3112 |
2975 |
56.63 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
3100 |
2964 |
20.87 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
3078 |
2942 |
26.01 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
3053 |
2919 |
1.79 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A" |
1506 |
1440 |
7.59 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A" |
1482 |
1417 |
6.45 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A" |
1343 |
1284 |
0.07 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A" |
1272 |
1216 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A" |
1126 |
1076 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A" |
1081 |
1033 |
0.27 |
|
|
|
| 40 |
A" |
998 |
954 |
36.49 |
|
|
|
| 41 |
A" |
898 |
858 |
0.11 |
|
|
|
| 42 |
A" |
780 |
746 |
1.31 |
|
|
|
| 43 |
A" |
707 |
676 |
1.84 |
|
|
|
| 44 |
A" |
262 |
251 |
3.19 |
|
|
|
| 45 |
A" |
233 |
223 |
0.27 |
|
|
|
| 46 |
A" |
194 |
185 |
0.86 |
|
|
|
| 47 |
A" |
89 |
85 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
| 48 |
A" |
120i |
115i |
0.09 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 36260.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.956) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 34664.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.651 |
3.174 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.927 |
1.705 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
0.000 |
0.760 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
0.270 |
-0.722 |
0.000 |
| C5 |
-1.003 |
-1.563 |
0.000 |
| C6 |
-0.724 |
-3.060 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
-0.421 |
3.375 |
0.000 |
| H8 |
1.088 |
3.656 |
0.877 |
| H9 |
1.088 |
3.656 |
-0.877 |
| H10 |
1.973 |
1.409 |
0.000 |
| H11 |
-1.045 |
1.062 |
0.000 |
| H12 |
0.873 |
-0.988 |
0.874 |
| H13 |
0.873 |
-0.988 |
-0.874 |
| H14 |
-1.604 |
-1.301 |
-0.875 |
| H15 |
-1.604 |
-1.301 |
0.875 |
| H16 |
-1.649 |
-3.638 |
0.000 |
| H17 |
-0.149 |
-3.351 |
-0.881 |
| H18 |
-0.149 |
-3.351 |
0.881 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
C5 |
C6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
H15 |
H16 |
H17 |
H18 |
| C1 | | 1.4953 | 2.5000 | 3.9147 | 5.0178 | 6.3844 | 1.0901 | 1.0922 | 1.0922 | 2.2055 | 2.7080 | 4.2585 | 4.2585 | 5.0869 | 5.0869 | 7.1897 | 6.6325 | 6.6325 |
C2 | 1.4953 | | 1.3234 | 2.5140 | 3.7954 | 5.0432 | 2.1462 | 2.1457 | 2.1457 | 1.0870 | 2.0738 | 2.8312 | 2.8312 | 4.0257 | 4.0257 | 5.9311 | 5.2432 | 5.2432 | C3 | 2.5000 | 1.3234 | | 1.5068 | 2.5309 | 3.8888 | 2.6480 | 3.2155 | 3.2155 | 2.0773 | 1.0874 | 2.1404 | 2.1404 | 2.7545 | 2.7545 | 4.6971 | 4.2071 | 4.2071 | C4 | 3.9147 | 2.5140 | 1.5068 | | 1.5260 | 2.5411 | 4.1546 | 4.5395 | 4.5395 | 2.7281 | 2.2166 | 1.0941 | 1.0941 | 2.1478 | 2.1478 | 3.4907 | 2.8040 | 2.8040 | C5 | 5.0178 | 3.7954 | 2.5309 | 1.5260 | | 1.5227 | 4.9723 | 5.6908 | 5.6908 | 4.2064 | 2.6262 | 2.1477 | 2.1477 | 1.0933 | 1.0933 | 2.1727 | 2.1678 | 2.1678 | C6 | 6.3844 | 5.0432 | 3.8888 | 2.5411 | 1.5227 | | 6.4423 | 7.0120 | 7.0120 | 5.2207 | 4.1353 | 2.7585 | 2.7585 | 2.1527 | 2.1527 | 1.0900 | 1.0915 | 1.0915 | H7 | 1.0901 | 2.1462 | 2.6480 | 4.1546 | 4.9723 | 6.4423 | | 1.7676 | 1.7676 | 3.0975 | 2.3949 | 4.6335 | 4.6335 | 4.9018 | 4.9018 | 7.1193 | 6.7883 | 6.7883 | H8 | 1.0922 | 2.1457 | 3.2155 | 4.5395 | 5.6908 | 7.0120 | 1.7676 | | 1.7542 | 2.5696 | 3.4705 | 4.6492 | 4.9679 | 5.9068 | 5.6410 | 7.8399 | 7.3294 | 7.1154 | H9 | 1.0922 | 2.1457 | 3.2155 | 4.5395 | 5.6908 | 7.0120 | 1.7676 | 1.7542 | | 2.5696 | 3.4705 | 4.9679 | 4.6492 | 5.6410 | 5.9068 | 7.8399 | 7.1154 | 7.3294 | H10 | 2.2055 | 1.0870 | 2.0773 | 2.7281 | 4.2064 | 5.2207 | 3.0975 | 2.5696 | 2.5696 | | 3.0378 | 2.7786 | 2.7786 | 4.5725 | 4.5725 | 6.2124 | 5.2857 | 5.2857 | H11 | 2.7080 | 2.0738 | 1.0874 | 2.2166 | 2.6262 | 4.1353 | 2.3949 | 3.4705 | 3.4705 | 3.0378 | | 2.9401 | 2.9401 | 2.5815 | 2.5815 | 4.7390 | 4.5885 | 4.5885 | H12 | 4.2585 | 2.8312 | 2.1404 | 1.0941 | 2.1477 | 2.7585 | 4.6335 | 4.6492 | 4.9679 | 2.7786 | 2.9401 | | 1.7471 | 3.0478 | 2.4966 | 3.7609 | 3.1155 | 2.5744 | H13 | 4.2585 | 2.8312 | 2.1404 | 1.0941 | 2.1477 | 2.7585 | 4.6335 | 4.9679 | 4.6492 | 2.7786 | 2.9401 | 1.7471 | | 2.4966 | 3.0478 | 3.7609 | 2.5744 | 3.1155 | H14 | 5.0869 | 4.0257 | 2.7545 | 2.1478 | 1.0933 | 2.1527 | 4.9018 | 5.9068 | 5.6410 | 4.5725 | 2.5815 | 3.0478 | 2.4966 | | 1.7494 | 2.4955 | 2.5135 | 3.0659 | H15 | 5.0869 | 4.0257 | 2.7545 | 2.1478 | 1.0933 | 2.1527 | 4.9018 | 5.6410 | 5.9068 | 4.5725 | 2.5815 | 2.4966 | 3.0478 | 1.7494 | | 2.4955 | 3.0659 | 2.5135 | H16 | 7.1897 | 5.9311 | 4.6971 | 3.4907 | 2.1727 | 1.0900 | 7.1193 | 7.8399 | 7.8399 | 6.2124 | 4.7390 | 3.7609 | 3.7609 | 2.4955 | 2.4955 | | 1.7629 | 1.7629 | H17 | 6.6325 | 5.2432 | 4.2071 | 2.8040 | 2.1678 | 1.0915 | 6.7883 | 7.3294 | 7.1154 | 5.2857 | 4.5885 | 3.1155 | 2.5744 | 2.5135 | 3.0659 | 1.7629 | | 1.7621 | H18 | 6.6325 | 5.2432 | 4.2071 | 2.8040 | 2.1678 | 1.0915 | 6.7883 | 7.1154 | 7.3294 | 5.2857 | 4.5885 | 2.5744 | 3.1155 | 3.0659 | 2.5135 | 1.7629 | 1.7621 | |
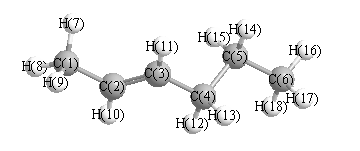 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
124.868 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H10 |
116.423 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
111.257 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H8 |
111.091 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H9 |
111.091 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
125.190 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
118.346 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H10 |
118.709 |
| C3 |
C4 |
C5 |
113.128 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H12 |
109.749 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H13 |
109.749 |
|
C4 |
C3 |
H11 |
116.465 |
| C4 |
C5 |
C6 |
112.923 |
|
C4 |
C5 |
H14 |
109.051 |
| C4 |
C5 |
H15 |
109.051 |
|
C5 |
C4 |
H12 |
108.999 |
| C5 |
C4 |
H13 |
108.999 |
|
C5 |
C6 |
H16 |
111.449 |
| C5 |
C6 |
H17 |
110.969 |
|
C5 |
C6 |
H18 |
110.969 |
| C6 |
C5 |
H14 |
109.661 |
|
C6 |
C5 |
H15 |
109.661 |
| H7 |
C1 |
H8 |
108.189 |
|
H7 |
C1 |
H9 |
108.189 |
| H8 |
C1 |
H9 |
106.851 |
|
H12 |
C4 |
H13 |
105.963 |
| H14 |
C5 |
H15 |
106.273 |
|
H16 |
C6 |
H17 |
107.822 |
| H16 |
C6 |
H18 |
107.822 |
|
H17 |
C6 |
H18 |
107.647 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.233 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.128 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.183 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.130 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.170 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.280 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.084 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.085 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.085 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.116 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.121 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.095 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.095 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.091 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.091 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
H |
0.093 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
H |
0.084 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
H |
0.084 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.044 |
-0.012 |
0.000 |
0.045 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-38.796 |
0.490 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.490 |
-39.139 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-40.810 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.178 |
0.490 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.490 |
0.664 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.842 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -3.685 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.343 |
|---|
| xy | 0.490 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
10.471 |
1.620 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.620 |
14.142 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.384 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
302.961 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
17.406 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -235.859789 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -235.872023 |
| HF Energy | -235.859789 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 227.352237 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3149 |
3011 |
47.29 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3137 |
2999 |
19.33 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3128 |
2990 |
6.79 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3123 |
2985 |
38.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3117 |
2980 |
55.32 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3100 |
2964 |
20.10 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3089 |
2953 |
17.08 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3068 |
2933 |
7.10 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
3046 |
2912 |
55.49 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
3045 |
2911 |
10.54 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
3044 |
2910 |
39.71 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
3029 |
2896 |
21.35 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1770 |
1692 |
0.44 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1508 |
1442 |
6.37 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1506 |
1440 |
8.38 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1502 |
1436 |
10.97 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1492 |
1427 |
6.73 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1492 |
1426 |
1.01 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1481 |
1416 |
1.84 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1425 |
1362 |
2.14 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1421 |
1359 |
2.98 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1399 |
1337 |
0.79 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1354 |
1294 |
0.79 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1347 |
1288 |
0.40 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1324 |
1266 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
1298 |
1240 |
3.48 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
1259 |
1204 |
0.14 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
1188 |
1136 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
1126 |
1076 |
0.93 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
1104 |
1055 |
2.60 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
1081 |
1034 |
0.66 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
1066 |
1019 |
4.97 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
1046 |
1000 |
5.29 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
1015 |
970 |
36.92 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
937 |
896 |
4.81 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
917 |
876 |
2.69 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
879 |
841 |
0.24 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
796 |
761 |
0.36 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
738 |
706 |
2.49 |
|
|
|
| 40 |
A |
546 |
522 |
0.16 |
|
|
|
| 41 |
A |
394 |
377 |
1.35 |
|
|
|
| 42 |
A |
320 |
306 |
0.81 |
|
|
|
| 43 |
A |
289 |
276 |
1.42 |
|
|
|
| 44 |
A |
239 |
228 |
0.08 |
|
|
|
| 45 |
A |
218 |
208 |
0.69 |
|
|
|
| 46 |
A |
159 |
152 |
0.40 |
|
|
|
| 47 |
A |
82 |
78 |
0.26 |
|
|
|
| 48 |
A |
52 |
50 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 36420.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.956) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 34818.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
3.164 |
0.224 |
-0.156 |
| C2 |
1.789 |
-0.357 |
-0.231 |
| C3 |
0.741 |
0.081 |
0.449 |
| C4 |
-0.641 |
-0.487 |
0.363 |
| C5 |
-1.666 |
0.523 |
-0.159 |
| C6 |
-3.081 |
-0.041 |
-0.195 |
| H7 |
3.201 |
1.067 |
0.535 |
| H8 |
3.888 |
-0.522 |
0.178 |
| H9 |
3.498 |
0.572 |
-1.136 |
| H10 |
1.656 |
-1.205 |
-0.898 |
| H11 |
0.870 |
0.933 |
1.113 |
| H12 |
-0.959 |
-0.824 |
1.355 |
| H13 |
-0.638 |
-1.370 |
-0.281 |
| H14 |
-1.367 |
0.844 |
-1.159 |
| H15 |
-1.643 |
1.417 |
0.470 |
| H16 |
-3.794 |
0.692 |
-0.571 |
| H17 |
-3.134 |
-0.921 |
-0.838 |
| H18 |
-3.406 |
-0.341 |
0.803 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
C5 |
C6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
H15 |
H16 |
H17 |
H18 |
| C1 | | 1.4952 | 2.5016 | 3.9056 | 4.8396 | 6.2506 | 1.0900 | 1.0921 | 1.0922 | 2.2064 | 2.7154 | 4.5151 | 4.1250 | 4.6821 | 4.9920 | 6.9862 | 6.4375 | 6.6642 |
C2 | 1.4952 | | 1.3239 | 2.5047 | 3.5659 | 4.8798 | 2.1468 | 2.1453 | 2.1459 | 1.0867 | 2.0771 | 3.2073 | 2.6303 | 3.5018 | 3.9261 | 5.6906 | 4.9917 | 5.2970 | C3 | 2.5016 | 1.3239 | | 1.4965 | 2.5219 | 3.8776 | 2.6515 | 3.2157 | 3.2180 | 2.0749 | 1.0876 | 2.1287 | 2.1309 | 2.7592 | 2.7327 | 4.6885 | 4.2043 | 4.1839 | C4 | 3.9056 | 2.5047 | 1.4965 | | 1.5304 | 2.5420 | 4.1477 | 4.5331 | 4.5279 | 2.7170 | 2.2048 | 1.0951 | 1.0932 | 2.1480 | 2.1536 | 3.4934 | 2.8011 | 2.8038 | C5 | 4.8396 | 3.5659 | 2.5219 | 1.5304 | | 1.5233 | 4.9464 | 5.6617 | 5.2563 | 3.8166 | 2.8671 | 2.1461 | 2.1576 | 1.0923 | 1.0933 | 2.1741 | 2.1680 | 2.1679 | C6 | 6.2506 | 4.8798 | 3.8776 | 2.5420 | 1.5233 | | 6.4203 | 6.9954 | 6.6742 | 4.9278 | 4.2744 | 2.7414 | 2.7820 | 2.1563 | 2.1531 | 1.0901 | 1.0914 | 1.0915 | H7 | 1.0900 | 2.1468 | 2.6515 | 4.1477 | 4.9464 | 6.4203 | | 1.7671 | 1.7674 | 3.0984 | 2.4050 | 4.6429 | 4.6198 | 4.8772 | 4.8569 | 7.0919 | 6.7798 | 6.7611 | H8 | 1.0921 | 2.1453 | 3.2157 | 4.5331 | 5.6617 | 6.9954 | 1.7671 | | 1.7540 | 2.5707 | 3.4779 | 4.9974 | 4.6279 | 5.5921 | 5.8681 | 7.8135 | 7.1063 | 7.3234 | H9 | 1.0922 | 2.1459 | 3.2180 | 4.5279 | 5.2563 | 6.6742 | 1.7674 | 1.7540 | | 2.5708 | 3.4774 | 5.2939 | 4.6492 | 4.8730 | 5.4517 | 7.3150 | 6.8045 | 7.2296 | H10 | 2.2064 | 1.0867 | 2.0749 | 2.7170 | 3.8166 | 4.9278 | 3.0984 | 2.5707 | 2.5708 | | 3.0382 | 3.4730 | 2.3815 | 3.6609 | 4.4300 | 5.7797 | 4.7983 | 5.4097 | H11 | 2.7154 | 2.0771 | 1.0876 | 2.2048 | 2.8671 | 4.2744 | 2.4050 | 3.4779 | 3.4774 | 3.0382 | | 2.5481 | 3.0857 | 3.1902 | 2.6390 | 4.9652 | 4.8247 | 4.4734 | H12 | 4.5151 | 3.2073 | 2.1287 | 1.0951 | 2.1461 | 2.7414 | 4.6429 | 4.9974 | 5.2939 | 3.4730 | 2.5481 | | 1.7541 | 3.0445 | 2.5044 | 3.7477 | 3.0901 | 2.5545 | H13 | 4.1250 | 2.6303 | 2.1309 | 1.0932 | 2.1576 | 2.7820 | 4.6198 | 4.6279 | 4.6492 | 2.3815 | 3.0857 | 1.7541 | | 2.4909 | 3.0562 | 3.7811 | 2.5963 | 3.1456 | H14 | 4.6821 | 3.5018 | 2.7592 | 2.1480 | 1.0923 | 2.1563 | 4.8772 | 5.5921 | 4.8730 | 3.6609 | 3.1902 | 3.0445 | 2.4909 | | 1.7489 | 2.5016 | 2.5176 | 3.0680 | H15 | 4.9920 | 3.9261 | 2.7327 | 2.1536 | 1.0933 | 2.1531 | 4.8569 | 5.8681 | 5.4517 | 4.4300 | 2.6390 | 2.5044 | 3.0562 | 1.7489 | | 2.4976 | 3.0661 | 2.5126 | H16 | 6.9862 | 5.6906 | 4.6885 | 3.4934 | 2.1741 | 1.0901 | 7.0919 | 7.8135 | 7.3150 | 5.7797 | 4.9652 | 3.7477 | 3.7811 | 2.5016 | 2.4976 | | 1.7632 | 1.7627 | H17 | 6.4375 | 4.9917 | 4.2043 | 2.8011 | 2.1680 | 1.0914 | 6.7798 | 7.1063 | 6.8045 | 4.7983 | 4.8247 | 3.0901 | 2.5963 | 2.5176 | 3.0661 | 1.7632 | | 1.7618 | H18 | 6.6642 | 5.2970 | 4.1839 | 2.8038 | 2.1679 | 1.0915 | 6.7611 | 7.3234 | 7.2296 | 5.4097 | 4.4734 | 2.5545 | 3.1456 | 3.0680 | 2.5126 | 1.7627 | 1.7618 | |
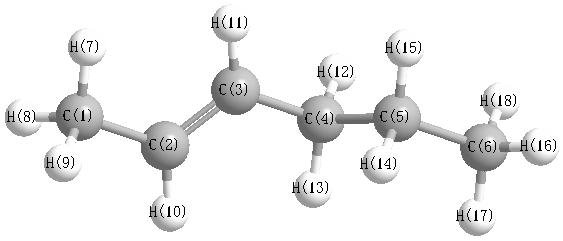 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
124.985 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H10 |
116.534 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
111.320 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H8 |
111.070 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H9 |
111.108 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
125.153 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
118.606 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H10 |
118.480 |
| C3 |
C4 |
C5 |
112.840 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H12 |
109.463 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H13 |
109.754 |
|
C4 |
C3 |
H11 |
116.229 |
| C4 |
C5 |
C6 |
112.699 |
|
C4 |
C5 |
H14 |
108.825 |
| C4 |
C5 |
H15 |
109.199 |
|
C5 |
C4 |
H12 |
108.508 |
| C5 |
C4 |
H13 |
109.516 |
|
C5 |
C6 |
H16 |
111.516 |
| C5 |
C6 |
H17 |
110.945 |
|
C5 |
C6 |
H18 |
110.937 |
| C6 |
C5 |
H14 |
109.965 |
|
C6 |
C5 |
H15 |
109.649 |
| H7 |
C1 |
H8 |
108.155 |
|
H7 |
C1 |
H9 |
108.177 |
| H8 |
C1 |
H9 |
106.834 |
|
H12 |
C4 |
H13 |
106.557 |
| H14 |
C5 |
H15 |
106.295 |
|
H16 |
C6 |
H17 |
107.852 |
| H16 |
C6 |
H18 |
107.801 |
|
H17 |
C6 |
H18 |
107.624 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.232 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.140 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.166 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.146 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.151 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.279 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.083 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.086 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.086 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.118 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.121 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.092 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.089 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.091 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.087 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
H |
0.093 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
H |
0.085 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
H |
0.084 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.025 |
0.054 |
-0.057 |
0.083 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-39.062 |
-0.049 |
-0.693 |
| y |
-0.049 |
-40.075 |
1.270 |
| z |
-0.693 |
1.270 |
-39.687 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.819 |
-0.049 |
-0.693 |
| y |
-0.049 |
-0.701 |
1.270 |
| z |
-0.693 |
1.270 |
-0.118 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.237 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 1.013 |
|---|
| xy | -0.049 |
|---|
| xz | -0.693 |
|---|
| yz | 1.270 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
14.516 |
-0.112 |
-0.852 |
| y |
-0.112 |
9.313 |
0.513 |
| z |
-0.852 |
0.513 |
9.293 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
292.679 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
17.108 |

