Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/3-21G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -232.318098 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -232.329306 |
| HF Energy | -232.318098 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 184.053600 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/3-21G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3617 |
3428 |
0.59 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3160 |
2995 |
28.92 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3098 |
2937 |
25.30 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3082 |
2921 |
18.04 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3075 |
2914 |
20.29 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
3012 |
2854 |
46.08 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1592 |
1509 |
2.88 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1572 |
1490 |
11.11 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1560 |
1478 |
3.66 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1554 |
1473 |
0.26 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1492 |
1414 |
1.43 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1471 |
1394 |
9.57 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1420 |
1346 |
2.67 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1364 |
1293 |
23.54 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1285 |
1218 |
46.90 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1149 |
1089 |
1.33 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1075 |
1018 |
0.53 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
1051 |
996 |
62.45 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
1007 |
955 |
1.16 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
926 |
878 |
23.91 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
436 |
414 |
15.57 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
410 |
388 |
0.44 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
189 |
179 |
4.03 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
3160 |
2995 |
66.65 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
3147 |
2983 |
3.62 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
3108 |
2946 |
3.90 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
3042 |
2883 |
60.75 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
1573 |
1490 |
11.15 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
1374 |
1302 |
0.15 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
1368 |
1297 |
2.05 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
1283 |
1216 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
1203 |
1140 |
1.70 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
1006 |
953 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A" |
859 |
815 |
1.76 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A" |
771 |
731 |
5.08 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A" |
303 |
287 |
150.55 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A" |
245 |
232 |
0.90 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A" |
112 |
106 |
0.14 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A" |
103 |
97 |
7.17 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 30626.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9478) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 29027.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/3-21G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.351 |
-0.359 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.340 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
-1.163 |
-0.660 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
-2.525 |
0.048 |
0.000 |
| O5 |
2.354 |
0.686 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.413 |
-1.008 |
0.888 |
| H7 |
1.413 |
-1.008 |
-0.888 |
| H8 |
-0.055 |
0.986 |
0.883 |
| H9 |
-0.055 |
0.986 |
-0.883 |
| H10 |
-1.087 |
-1.308 |
0.883 |
| H11 |
-1.087 |
-1.308 |
-0.883 |
| H12 |
-3.344 |
-0.678 |
0.000 |
| H13 |
-2.629 |
0.683 |
0.887 |
| H14 |
-2.629 |
0.683 |
-0.887 |
| H15 |
3.245 |
0.271 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
H15 |
| C1 | | 1.5207 | 2.5316 | 3.8971 | 1.4485 | 1.1022 | 1.1022 | 2.1365 | 2.1365 | 2.7611 | 2.7611 | 4.7061 | 4.2082 | 4.2082 | 1.9957 |
C2 | 1.5207 | | 1.5334 | 2.5418 | 2.3798 | 2.1450 | 2.1450 | 1.0960 | 1.0960 | 2.1626 | 2.1626 | 3.4959 | 2.7954 | 2.7954 | 3.2453 | C3 | 2.5316 | 1.5334 | | 1.5350 | 3.7659 | 2.7464 | 2.7464 | 2.1722 | 2.1722 | 1.0980 | 1.0980 | 2.1817 | 2.1770 | 2.1770 | 4.5046 | C4 | 3.8971 | 2.5418 | 1.5350 | | 4.9210 | 4.1723 | 4.1723 | 2.7862 | 2.7862 | 2.1649 | 2.1649 | 1.0949 | 1.0958 | 1.0958 | 5.7738 | O5 | 1.4485 | 2.3798 | 3.7659 | 4.9210 | | 2.1321 | 2.1321 | 2.5835 | 2.5835 | 4.0741 | 4.0741 | 5.8599 | 5.0615 | 5.0615 | 0.9819 | H6 | 1.1022 | 2.1450 | 2.7464 | 4.1723 | 2.1321 | | 1.7764 | 2.4762 | 3.0446 | 2.5173 | 3.0778 | 4.8503 | 4.3810 | 4.7269 | 2.4046 | H7 | 1.1022 | 2.1450 | 2.7464 | 4.1723 | 2.1321 | 1.7764 | | 3.0446 | 2.4762 | 3.0778 | 2.5173 | 4.8503 | 4.7269 | 4.3810 | 2.4046 | H8 | 2.1365 | 1.0960 | 2.1722 | 2.7862 | 2.5835 | 2.4762 | 3.0446 | | 1.7663 | 2.5163 | 3.0741 | 3.7913 | 2.5918 | 3.1385 | 3.4895 | H9 | 2.1365 | 1.0960 | 2.1722 | 2.7862 | 2.5835 | 3.0446 | 2.4762 | 1.7663 | | 3.0741 | 2.5163 | 3.7913 | 3.1385 | 2.5918 | 3.4895 | H10 | 2.7611 | 2.1626 | 1.0980 | 2.1649 | 4.0741 | 2.5173 | 3.0778 | 2.5163 | 3.0741 | | 1.7655 | 2.5046 | 2.5188 | 3.0782 | 4.6942 | H11 | 2.7611 | 2.1626 | 1.0980 | 2.1649 | 4.0741 | 3.0778 | 2.5173 | 3.0741 | 2.5163 | 1.7655 | | 2.5046 | 3.0782 | 2.5188 | 4.6942 | H12 | 4.7061 | 3.4959 | 2.1817 | 1.0949 | 5.8599 | 4.8503 | 4.8503 | 3.7913 | 3.7913 | 2.5046 | 2.5046 | | 1.7755 | 1.7755 | 6.6570 | H13 | 4.2082 | 2.7954 | 2.1770 | 1.0958 | 5.0615 | 4.3810 | 4.7269 | 2.5918 | 3.1385 | 2.5188 | 3.0782 | 1.7755 | | 1.7734 | 5.9542 | H14 | 4.2082 | 2.7954 | 2.1770 | 1.0958 | 5.0615 | 4.7269 | 4.3810 | 3.1385 | 2.5918 | 3.0782 | 2.5188 | 1.7755 | 1.7734 | | 5.9542 | H15 | 1.9957 | 3.2453 | 4.5046 | 5.7738 | 0.9819 | 2.4046 | 2.4046 | 3.4895 | 3.4895 | 4.6942 | 4.6942 | 6.6570 | 5.9542 | 5.9542 | |
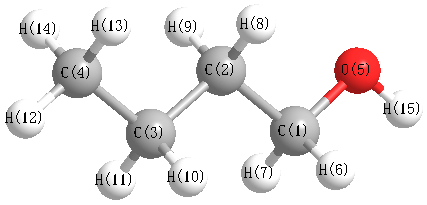 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
111.977 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
108.380 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H9 |
108.380 |
|
C1 |
O5 |
H15 |
108.880 |
| C2 |
C1 |
O5 |
106.522 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
108.685 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
108.685 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
111.861 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.425 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
109.425 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.294 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H9 |
110.294 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H12 |
110.997 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H13 |
110.572 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H14 |
110.572 |
|
C4 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.495 |
| C4 |
C3 |
H11 |
109.495 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
112.720 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
112.720 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.393 |
| H8 |
C2 |
H9 |
107.373 |
|
H10 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.020 |
| H12 |
C4 |
H13 |
108.282 |
|
H12 |
C4 |
H14 |
108.282 |
| H13 |
C4 |
H14 |
108.036 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/3-21G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.153 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.417 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.434 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.604 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.582 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.183 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.183 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.221 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.221 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.205 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.205 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.206 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.207 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.207 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.351 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.369 |
-1.666 |
0.000 |
1.706 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.247 |
-3.805 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.805 |
-34.540 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-32.702 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.374 |
-3.805 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.805 |
-4.065 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.309 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -2.618 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 6.292 |
|---|
| xy | -3.805 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.725 |
0.108 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.108 |
6.103 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.775 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
187.126 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.679 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/3-21G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -232.319438 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -232.330795 |
| HF Energy | -232.319438 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 187.855515 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/3-21G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3624 |
3435 |
1.40 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3178 |
3012 |
31.02 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3153 |
2988 |
33.26 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3141 |
2977 |
3.16 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3138 |
2974 |
28.03 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3094 |
2933 |
40.62 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3082 |
2921 |
11.88 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3076 |
2915 |
23.24 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
3057 |
2897 |
58.15 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
3021 |
2863 |
51.70 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1592 |
1509 |
4.27 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1575 |
1493 |
10.26 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1572 |
1490 |
10.64 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1567 |
1485 |
2.43 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1540 |
1460 |
5.02 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1480 |
1403 |
2.56 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1468 |
1391 |
7.81 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1428 |
1353 |
1.08 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1386 |
1314 |
5.47 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1378 |
1306 |
1.44 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1343 |
1273 |
24.55 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1283 |
1216 |
0.89 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1273 |
1206 |
32.21 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1178 |
1117 |
5.73 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1158 |
1098 |
3.29 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
1077 |
1020 |
33.58 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
1040 |
985 |
24.60 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
1021 |
967 |
12.95 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
986 |
935 |
2.12 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
882 |
836 |
14.17 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
857 |
812 |
2.37 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
776 |
736 |
2.19 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
521 |
493 |
12.21 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
355 |
337 |
2.92 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
298 |
282 |
79.23 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
252 |
239 |
0.55 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
243 |
230 |
71.76 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
163 |
154 |
6.41 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
95 |
90 |
0.71 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 30674.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9478) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 29073.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/3-21G*
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.444 |
0.536 |
0.221 |
| C2 |
0.005 |
0.734 |
-0.234 |
| C3 |
-0.926 |
-0.329 |
0.360 |
| C4 |
-2.374 |
-0.164 |
-0.128 |
| O5 |
1.852 |
-0.767 |
-0.250 |
| H6 |
2.059 |
1.357 |
-0.182 |
| H7 |
1.470 |
0.615 |
1.321 |
| H8 |
-0.330 |
1.740 |
0.050 |
| H9 |
-0.018 |
0.668 |
-1.328 |
| H10 |
-0.893 |
-0.264 |
1.455 |
| H11 |
-0.538 |
-1.314 |
0.081 |
| H12 |
-3.023 |
-0.934 |
0.303 |
| H13 |
-2.772 |
0.817 |
0.158 |
| H14 |
-2.425 |
-0.246 |
-1.219 |
| H15 |
2.760 |
-0.971 |
0.054 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
H15 |
| C1 | | 1.5218 | 2.5264 | 3.8968 | 1.4441 | 1.1025 | 1.1031 | 2.1503 | 2.1344 | 2.7614 | 2.7143 | 4.7030 | 4.2256 | 4.2014 | 2.0076 |
C2 | 1.5218 | | 1.5327 | 2.5450 | 2.3795 | 2.1472 | 2.1398 | 1.0978 | 1.0963 | 2.1583 | 2.1415 | 3.4985 | 2.8060 | 2.7992 | 3.2523 | C3 | 2.5264 | 1.5327 | | 1.5365 | 2.8777 | 3.4710 | 2.7489 | 2.1749 | 2.1602 | 1.0983 | 1.0946 | 2.1831 | 2.1821 | 2.1785 | 3.7540 | C4 | 3.8968 | 2.5450 | 1.5365 | | 4.2704 | 4.6872 | 4.1811 | 2.7989 | 2.7716 | 2.1699 | 2.1763 | 1.0952 | 1.0965 | 1.0961 | 5.2001 | O5 | 1.4441 | 2.3795 | 2.8777 | 4.2704 | | 2.1345 | 2.1269 | 3.3365 | 2.5920 | 3.2708 | 2.4739 | 4.9089 | 4.9047 | 4.4158 | 0.9793 | H6 | 1.1025 | 2.1472 | 3.4710 | 4.6872 | 2.1345 | | 1.7769 | 2.4309 | 2.4709 | 3.7454 | 3.7344 | 5.5958 | 4.8734 | 4.8737 | 2.4421 | H7 | 1.1031 | 2.1398 | 2.7489 | 4.1811 | 2.1269 | 1.7769 | | 2.4737 | 3.0393 | 2.5252 | 3.0479 | 4.8604 | 4.4034 | 4.7292 | 2.4048 | H8 | 2.1503 | 1.0978 | 2.1749 | 2.7989 | 3.3365 | 2.4309 | 2.4737 | | 1.7738 | 2.5115 | 3.0606 | 3.8034 | 2.6129 | 3.1537 | 4.1102 | H9 | 2.1344 | 1.0963 | 2.1602 | 2.7716 | 2.5920 | 2.4709 | 3.0393 | 1.7738 | | 3.0633 | 2.4864 | 3.7753 | 3.1326 | 2.5764 | 3.5095 | H10 | 2.7614 | 2.1583 | 1.0983 | 2.1699 | 3.2708 | 3.7454 | 2.5252 | 2.5115 | 3.0633 | | 1.7655 | 2.5126 | 2.5264 | 3.0823 | 3.9761 | H11 | 2.7143 | 2.1415 | 1.0946 | 2.1763 | 2.4739 | 3.7344 | 3.0479 | 3.0606 | 2.4864 | 1.7655 | | 2.5235 | 3.0882 | 2.5278 | 3.3158 | H12 | 4.7030 | 3.4985 | 2.1831 | 1.0952 | 4.9089 | 5.5958 | 4.8604 | 3.8034 | 3.7753 | 2.5126 | 2.5235 | | 1.7750 | 1.7740 | 5.7883 | H13 | 4.2256 | 2.8060 | 2.1821 | 1.0965 | 4.9047 | 4.8734 | 4.4034 | 2.6129 | 3.1326 | 2.5264 | 3.0882 | 1.7750 | | 1.7744 | 5.8147 | H14 | 4.2014 | 2.7992 | 2.1785 | 1.0961 | 4.4158 | 4.8737 | 4.7292 | 3.1537 | 2.5764 | 3.0823 | 2.5278 | 1.7740 | 1.7744 | | 5.3878 | H15 | 2.0076 | 3.2523 | 3.7540 | 5.2001 | 0.9793 | 2.4421 | 2.4048 | 4.1102 | 3.5095 | 3.9761 | 3.3158 | 5.7883 | 5.8147 | 5.3878 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
111.612 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.272 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H9 |
108.128 |
|
C1 |
O5 |
H15 |
110.405 |
| C2 |
C1 |
O5 |
106.669 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
108.767 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
108.157 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
112.041 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.126 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
108.036 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.453 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H9 |
109.385 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H12 |
110.993 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H13 |
110.834 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H14 |
110.576 |
|
C4 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.768 |
| C4 |
C3 |
H11 |
110.488 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
113.217 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
112.540 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.342 |
| H8 |
C2 |
H9 |
107.888 |
|
H10 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.246 |
| H12 |
C4 |
H13 |
108.168 |
|
H12 |
C4 |
H14 |
108.108 |
| H13 |
C4 |
H14 |
108.051 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/3-21G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.162 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.421 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.419 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.610 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.577 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.190 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.184 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.198 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.222 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.194 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.238 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.205 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.199 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.205 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.354 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.222 |
0.826 |
0.993 |
1.778 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.418 |
-0.098 |
2.158 |
| y |
-0.098 |
-32.951 |
-0.756 |
| z |
2.158 |
-0.756 |
-33.143 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.629 |
-0.098 |
2.158 |
| y |
-0.098 |
-2.671 |
-0.756 |
| z |
2.158 |
-0.756 |
-2.958 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -5.916 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.533 |
|---|
| xy | -0.098 |
|---|
| xz | 2.158 |
|---|
| yz | -0.756 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.443 |
-0.037 |
0.125 |
| y |
-0.037 |
6.268 |
0.024 |
| z |
0.125 |
0.024 |
5.901 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
165.556 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
12.867 |
