Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBE/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3573 |
3536 |
67.34 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3176 |
3143 |
0.54 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3102 |
3070 |
16.09 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3089 |
3057 |
16.28 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1601 |
1585 |
54.71 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1564 |
1548 |
60.13 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1472 |
1457 |
21.18 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1437 |
1422 |
2.27 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1389 |
1374 |
42.12 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1368 |
1354 |
16.33 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1329 |
1315 |
58.19 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1291 |
1278 |
21.47 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1273 |
1260 |
16.09 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1244 |
1231 |
27.54 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1167 |
1155 |
7.14 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1103 |
1092 |
5.08 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1054 |
1044 |
10.88 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
914 |
905 |
1.65 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
881 |
872 |
12.06 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
784 |
776 |
13.01 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
638 |
631 |
0.60 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
551 |
545 |
4.12 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
431 |
426 |
11.32 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
959 |
950 |
0.52 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
910 |
901 |
6.77 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
838 |
829 |
3.24 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
801 |
793 |
10.64 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
648 |
642 |
3.88 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
609 |
603 |
23.24 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
521 |
516 |
81.41 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
400 |
396 |
2.13 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
234 |
231 |
0.17 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
226 |
224 |
4.10 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20290.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9897) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20081.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
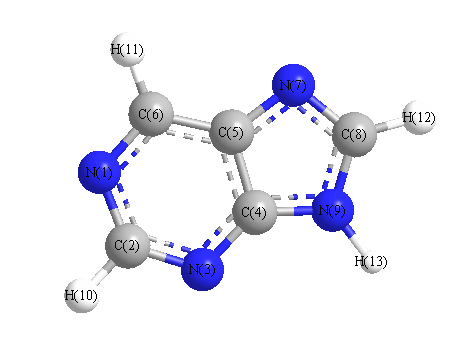
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBE/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.266 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.050 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.368 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
0.442 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
0.227 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.068 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
N |
-0.343 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
0.018 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
N |
-0.378 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.124 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.132 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.279 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.154 |
2.917 |
0.000 |
3.626 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-49.621 |
6.003 |
0.000 |
| y |
6.003 |
-46.310 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-50.753 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.089 |
6.003 |
0.000 |
| y |
6.003 |
3.877 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.788 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -5.575 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.311 |
|---|
| xy | 6.003 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
15.723 |
1.424 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.424 |
12.022 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.024 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
255.501 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
15.984 |