Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at PBEPBE/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -158.243814 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -158.254322 |
| HF Energy | -158.243814 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 129.933779 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBE/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
|
Au |
124 |
123 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
213 |
210 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
250 |
247 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
252 |
249 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
416 |
411 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
718 |
711 |
4.51 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
792 |
784 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
827 |
818 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
942 |
932 |
1.41 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
955 |
945 |
8.27 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
1008 |
997 |
0.08 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1055 |
1044 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1139 |
1128 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
1174 |
1162 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
1261 |
1248 |
0.08 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
1283 |
1270 |
1.66 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
1307 |
1293 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1355 |
1341 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1373 |
1359 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
1376 |
1362 |
8.77 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1452 |
1437 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
1459 |
1443 |
2.07 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
1468 |
1453 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
1470 |
1455 |
19.35 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1475 |
1460 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
1480 |
1465 |
12.74 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
2942 |
2912 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
2951 |
2921 |
49.94 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
2962 |
2931 |
95.21 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
2963 |
2932 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
2964 |
2933 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
2988 |
2957 |
25.36 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
3027 |
2995 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
3030 |
2999 |
129.28 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
3035 |
3003 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
3035 |
3004 |
88.60 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28258.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9896) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27964.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBEPBE/6-311G*
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.421 |
0.641 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.421 |
-0.641 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
0.421 |
1.919 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
-0.421 |
-1.919 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-1.089 |
0.636 |
0.881 |
| H6 |
-1.089 |
0.636 |
-0.881 |
| H7 |
1.089 |
-0.636 |
0.881 |
| H8 |
1.089 |
-0.636 |
-0.881 |
| H9 |
-0.209 |
2.823 |
0.000 |
| H10 |
1.072 |
1.970 |
0.888 |
| H11 |
1.072 |
1.970 |
-0.888 |
| H12 |
0.209 |
-2.823 |
0.000 |
| H13 |
-1.072 |
-1.970 |
0.888 |
| H14 |
-1.072 |
-1.970 |
-0.888 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
| C1 | | 1.5334 | 1.5309 | 2.5603 | 1.1056 | 1.1056 | 2.1646 | 2.1646 | 2.1921 | 2.1876 | 2.1876 | 3.5203 | 2.8337 | 2.8337 |
C2 | 1.5334 | | 2.5603 | 1.5309 | 2.1646 | 2.1646 | 1.1056 | 1.1056 | 3.5203 | 2.8337 | 2.8337 | 2.1921 | 2.1876 | 2.1876 | C3 | 1.5309 | 2.5603 | | 3.9301 | 2.1685 | 2.1685 | 2.7843 | 2.7843 | 1.1013 | 1.1025 | 1.1025 | 4.7468 | 4.2599 | 4.2599 | C4 | 2.5603 | 1.5309 | 3.9301 | | 2.7843 | 2.7843 | 2.1685 | 2.1685 | 4.7468 | 4.2599 | 4.2599 | 1.1013 | 1.1025 | 1.1025 | H5 | 1.1056 | 2.1646 | 2.1685 | 2.7843 | | 1.7626 | 2.5214 | 3.0764 | 2.5162 | 2.5396 | 3.0951 | 3.7978 | 2.6061 | 3.1499 | H6 | 1.1056 | 2.1646 | 2.1685 | 2.7843 | 1.7626 | | 3.0764 | 2.5214 | 2.5162 | 3.0951 | 2.5396 | 3.7978 | 3.1499 | 2.6061 | H7 | 2.1646 | 1.1056 | 2.7843 | 2.1685 | 2.5214 | 3.0764 | | 1.7626 | 3.7978 | 2.6061 | 3.1499 | 2.5162 | 2.5396 | 3.0951 | H8 | 2.1646 | 1.1056 | 2.7843 | 2.1685 | 3.0764 | 2.5214 | 1.7626 | | 3.7978 | 3.1499 | 2.6061 | 2.5162 | 3.0951 | 2.5396 | H9 | 2.1921 | 3.5203 | 1.1013 | 4.7468 | 2.5162 | 2.5162 | 3.7978 | 3.7978 | | 1.7770 | 1.7770 | 5.6608 | 4.9501 | 4.9501 | H10 | 2.1876 | 2.8337 | 1.1025 | 4.2599 | 2.5396 | 3.0951 | 2.6061 | 3.1499 | 1.7770 | | 1.7760 | 4.9501 | 4.4861 | 4.8248 | H11 | 2.1876 | 2.8337 | 1.1025 | 4.2599 | 3.0951 | 2.5396 | 3.1499 | 2.6061 | 1.7770 | 1.7760 | | 4.9501 | 4.8248 | 4.4861 | H12 | 3.5203 | 2.1921 | 4.7468 | 1.1013 | 3.7978 | 3.7978 | 2.5162 | 2.5162 | 5.6608 | 4.9501 | 4.9501 | | 1.7770 | 1.7770 | H13 | 2.8337 | 2.1876 | 4.2599 | 1.1025 | 2.6061 | 3.1499 | 2.5396 | 3.0951 | 4.9501 | 4.4861 | 4.8248 | 1.7770 | | 1.7760 | H14 | 2.8337 | 2.1876 | 4.2599 | 1.1025 | 3.1499 | 2.6061 | 3.0951 | 2.5396 | 4.9501 | 4.8248 | 4.4861 | 1.7770 | 1.7760 | |
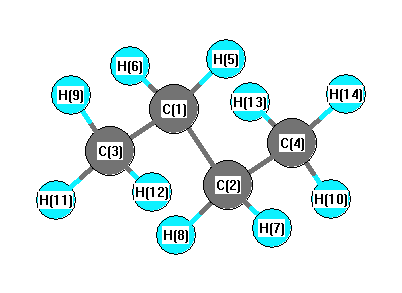 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C4 |
113.340 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H7 |
109.137 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.137 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H9 |
111.738 |
| C1 |
C3 |
H11 |
111.304 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H12 |
30.805 |
| C2 |
C1 |
C3 |
113.340 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
109.137 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.137 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H10 |
17.182 |
| C2 |
C4 |
H13 |
111.304 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H14 |
111.304 |
| C3 |
C1 |
H5 |
109.617 |
|
C3 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.617 |
| C4 |
C2 |
H7 |
109.617 |
|
C4 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.617 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
105.707 |
|
H7 |
C2 |
H8 |
105.707 |
| H9 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.482 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H12 |
142.543 |
| H10 |
C4 |
H13 |
94.657 |
|
H10 |
C4 |
H14 |
114.644 |
| H11 |
C3 |
H12 |
94.143 |
|
H13 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.304 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBE/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.413 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.413 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.635 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.635 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.206 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.206 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.206 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.206 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.215 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.211 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.211 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.215 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.211 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.211 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-29.059 |
-0.431 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.431 |
-29.411 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-28.287 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.210 |
-0.431 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.431 |
-0.738 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.948 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 1.896 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.352 |
|---|
| xy | -0.431 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.984 |
0.244 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.244 |
8.342 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.643 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
120.219 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.964 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at PBEPBE/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -158.242615 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 131.694309 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBE/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3042 |
3011 |
44.41 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3030 |
2998 |
3.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
2981 |
2950 |
30.06 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
2966 |
2935 |
34.46 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
2945 |
2915 |
18.68 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1484 |
1468 |
2.41 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1473 |
1458 |
6.40 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1452 |
1437 |
0.12 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1377 |
1363 |
5.59 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1337 |
1323 |
0.64 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1283 |
1269 |
0.29 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1160 |
1148 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1073 |
1062 |
0.12 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
969 |
959 |
0.28 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
819 |
811 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
776 |
768 |
2.21 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
314 |
310 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
264 |
261 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
109 |
107 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B |
3037 |
3005 |
58.91 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
3031 |
2999 |
97.23 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B |
2985 |
2954 |
35.58 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B |
2964 |
2933 |
27.54 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B |
2947 |
2916 |
33.30 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B |
1476 |
1460 |
13.82 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B |
1468 |
1453 |
13.39 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B |
1449 |
1434 |
0.81 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
B |
1376 |
1361 |
8.89 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
B |
1332 |
1318 |
1.23 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
B |
1258 |
1245 |
0.47 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
B |
1122 |
1110 |
2.70 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
B |
955 |
945 |
1.89 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
B |
944 |
934 |
3.60 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
B |
728 |
720 |
5.07 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
B |
422 |
417 |
0.47 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
B |
208 |
206 |
0.07 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28276.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9896) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27982.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBEPBE/6-311G*
Point Group is C2h
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
