Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at CCSD(T)=FULL/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -275.252467 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -274.237135 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 117.708710 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCSD(T)=FULL/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
2107 |
2107 |
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
744 |
744 |
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
539 |
539 |
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
A1 |
84 |
84 |
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
A2 |
485 |
485 |
|
|
|
|
| 6 |
B1 |
513 |
513 |
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
B2 |
2113 |
2113 |
|
|
|
|
| 8 |
B2 |
1254 |
1254 |
|
|
|
|
| 9 |
B2 |
477 |
477 |
|
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4158.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4158.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
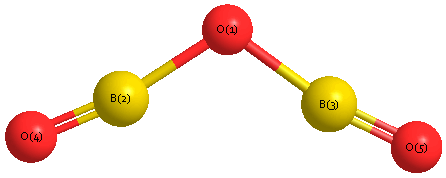
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD(T)=FULL/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| O1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.498 |
| B2 |
0.000 |
1.250 |
0.065 |
| B3 |
0.000 |
-1.250 |
0.065 |
| O4 |
0.000 |
2.404 |
-0.290 |
| O5 |
0.000 |
-2.404 |
-0.290 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
O1 |
B2 |
B3 |
O4 |
O5 |
| O1 | | 1.3226 | 1.3226 | 2.5298 | 2.5298 |
B2 | 1.3226 | | 2.4998 | 1.2076 | 3.6712 | B3 | 1.3226 | 2.4998 | | 3.6712 | 1.2076 | O4 | 2.5298 | 1.2076 | 3.6712 | | 4.8082 | O5 | 2.5298 | 3.6712 | 1.2076 | 4.8082 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| O1 |
B2 |
O4 |
178.022 |
|
O1 |
B3 |
O5 |
178.022 |
| B2 |
O1 |
B3 |
141.836 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at CCSD(T)=FULL/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -275.251294 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -274.236040 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 117.124169 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCSD(T)=FULL/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σg |
2111 |
2111 |
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
Σg |
679 |
679 |
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
Σu |
2142 |
2142 |
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
Σu |
1325 |
1325 |
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
Πg |
489 |
489 |
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
Πg |
489 |
489 |
|
|
|
|
| 6 |
Πu |
493 |
493 |
|
|
|
|
| 6 |
Πu |
493 |
493 |
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
Πu |
66i |
66i |
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
Πu |
67i |
67i |
|
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4044.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4044.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD(T)=FULL/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Point Group is D∞h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| O1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| B2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.309 |
| B3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.309 |
| O4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.517 |
| O5 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.517 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
O1 |
B2 |
B3 |
O4 |
O5 |
| O1 | | 1.3085 | 1.3085 | 2.5172 | 2.5172 |
B2 | 1.3085 | | 2.6170 | 1.2087 | 3.8258 | B3 | 1.3085 | 2.6170 | | 3.8258 | 1.2087 | O4 | 2.5172 | 1.2087 | 3.8258 | | 5.0345 | O5 | 2.5172 | 3.8258 | 1.2087 | 5.0345 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| O1 |
B2 |
O4 |
180.000 |
|
O1 |
B3 |
O5 |
180.000 |
| B2 |
O1 |
B3 |
180.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
