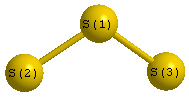Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at CCSD(T)=FULL/aug-cc-pVQZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -1193.435189 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -1193.435600 |
| HF Energy | -1192.613515 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 182.158760 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD(T)=FULL/aug-cc-pVQZ
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| S1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.666 |
| S2 |
0.000 |
1.642 |
-0.333 |
| S3 |
0.000 |
-1.642 |
-0.333 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
S1 |
S2 |
S3 |
| S1 | | 1.9226 | 1.9226 |
S2 | 1.9226 | | 3.2849 | S3 | 1.9226 | 3.2849 | |
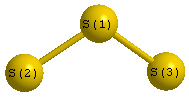 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| S2 |
S1 |
S3 |
117.356 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at CCSD(T)=FULL/aug-cc-pVQZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -1193.427843 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -1193.428349 |
| HF Energy | -1192.624910 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 195.203240 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD(T)=FULL/aug-cc-pVQZ
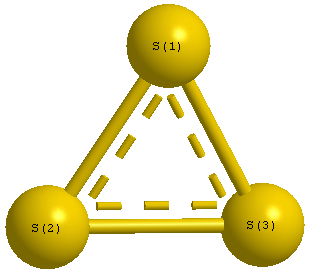
Point Group is D3h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| S1 |
0.000 |
1.202 |
0.000 |
| S2 |
1.041 |
-0.601 |
0.000 |
| S3 |
-1.041 |
-0.601 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
S1 |
S2 |
S3 |
| S1 | | 2.0818 | 2.0818 |
S2 | 2.0818 | | 2.0818 | S3 | 2.0818 | 2.0818 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| S2 |
S1 |
S3 |
60.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability