Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at PBEPBEultrafine/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -244.978091 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -244.978091 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 122.741098 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBEultrafine/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3684 |
3659 |
61.11 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3680 |
3655 |
58.40 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3548 |
3523 |
42.73 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1786 |
1774 |
449.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1558 |
1547 |
110.48 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1384 |
1375 |
107.28 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1189 |
1181 |
186.41 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1039 |
1031 |
36.94 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
916 |
910 |
52.00 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
562 |
558 |
29.46 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
469 |
466 |
7.15 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
751 |
746 |
15.75 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A" |
579 |
575 |
53.03 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A" |
463 |
460 |
56.70 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A" |
209i |
207i |
191.93 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10699.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9931) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10625.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBEPBEultrafine/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.132 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-0.078 |
1.349 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.151 |
-0.594 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
-1.092 |
-0.702 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
2.029 |
-0.097 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.136 |
-1.604 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
-1.856 |
-0.098 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
O4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
| C1 | | 1.2190 | 1.3608 | 1.3744 | 2.0417 | 2.0749 | 1.8706 |
O2 | 1.2190 | | 2.2991 | 2.2878 | 2.5556 | 3.1928 | 2.2920 | N3 | 1.3608 | 2.2991 | | 2.2453 | 1.0090 | 1.0100 | 3.0478 | O4 | 1.3744 | 2.2878 | 2.2453 | | 3.1789 | 2.4035 | 0.9746 | H5 | 2.0417 | 2.5556 | 1.0090 | 3.1789 | | 1.7516 | 3.8852 | H6 | 2.0749 | 3.1928 | 1.0100 | 2.4035 | 1.7516 | | 3.3501 | H7 | 1.8706 | 2.2920 | 3.0478 | 0.9746 | 3.8852 | 3.3501 | |
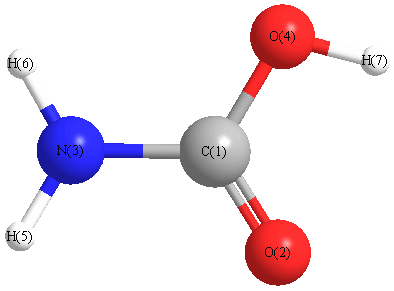 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N3 |
H5 |
118.223 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
121.421 |
| C1 |
O4 |
H7 |
104.272 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
125.953 |
| O2 |
C1 |
O4 |
123.699 |
|
N3 |
C1 |
O4 |
110.348 |
| H5 |
N3 |
H6 |
120.356 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBEultrafine/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.245 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.324 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.204 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.263 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.166 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.160 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.220 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.918 |
-2.307 |
0.000 |
2.483 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-15.489 |
-2.270 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.270 |
-25.982 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-23.969 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
9.486 |
-2.270 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.270 |
-6.253 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.233 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -6.466 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 10.493 |
|---|
| xy | -2.270 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.976 |
-0.326 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.326 |
4.718 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.593 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
65.001 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.062 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at PBEPBEultrafine/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -244.978185 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -244.982856 |
| HF Energy | -244.978185 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 122.696561 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBEultrafine/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3680 |
3655 |
63.72 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3660 |
3634 |
48.51 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3531 |
3506 |
35.82 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
1786 |
1774 |
435.22 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1563 |
1552 |
99.24 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1383 |
1373 |
109.82 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1192 |
1184 |
164.08 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1047 |
1040 |
59.95 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
919 |
912 |
50.43 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
750 |
745 |
21.19 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
572 |
568 |
61.54 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
560 |
557 |
34.73 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
479 |
476 |
23.05 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
449 |
446 |
28.79 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
294 |
292 |
215.21 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10932.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9931) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10856.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBEPBEultrafine/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.038 |
0.127 |
-0.001 |
| O2 |
-0.459 |
1.270 |
0.005 |
| N3 |
1.276 |
-0.243 |
-0.048 |
| O4 |
-0.846 |
-0.984 |
0.002 |
| H5 |
1.957 |
0.484 |
0.127 |
| H6 |
1.533 |
-1.202 |
0.147 |
| H7 |
-1.752 |
-0.625 |
0.005 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
O4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
| C1 | | 1.2183 | 1.3659 | 1.3738 | 2.0303 | 2.0625 | 1.8720 |
O2 | 1.2183 | | 2.3027 | 2.2867 | 2.5435 | 3.1775 | 2.2936 | N3 | 1.3659 | 2.3027 | | 2.2490 | 1.0106 | 1.0117 | 3.0532 | O4 | 1.3738 | 2.2867 | 2.2490 | | 3.1666 | 2.3936 | 0.9746 | H5 | 2.0303 | 2.5435 | 1.0106 | 3.1666 | | 1.7381 | 3.8731 | H6 | 2.0625 | 3.1775 | 1.0117 | 2.3936 | 1.7381 | | 3.3386 | H7 | 1.8720 | 2.2936 | 3.0532 | 0.9746 | 3.8731 | 3.3386 | |
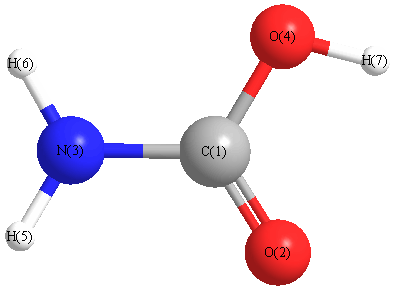 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N3 |
H5 |
116.573 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
119.588 |
| C1 |
O4 |
H7 |
104.421 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
125.927 |
| O2 |
C1 |
O4 |
123.704 |
|
N3 |
C1 |
O4 |
110.348 |
| H5 |
N3 |
H6 |
118.512 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBEultrafine/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.247 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.321 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.207 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.261 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.164 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.159 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.220 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.410 |
-1.906 |
0.516 |
2.426 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-15.384 |
1.038 |
1.043 |
| y |
1.038 |
-26.408 |
-0.276 |
| z |
1.043 |
-0.276 |
-23.896 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
9.769 |
1.038 |
1.043 |
| y |
1.038 |
-6.769 |
-0.276 |
| z |
1.043 |
-0.276 |
-3.000 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -6.000 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 11.025 |
|---|
| xy | 1.038 |
|---|
| xz | 1.043 |
|---|
| yz | -0.276 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.139 |
-0.195 |
0.011 |
| y |
-0.195 |
4.578 |
0.001 |
| z |
0.011 |
0.001 |
2.615 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
65.030 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.064 |

