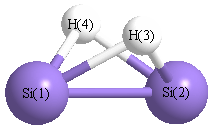Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at QCISD(T)=FULL/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.280395 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.881678 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 66.854945 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at QCISD(T)=FULL/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σg |
2368 |
2266 |
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
Σg |
742 |
710 |
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
Σu |
2378 |
2275 |
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
Πg |
522i |
500i |
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
Πg |
522i |
500i |
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
Πu |
421 |
403 |
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
Πu |
421 |
403 |
|
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2643.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9569) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2529.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at QCISD(T)=FULL/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is D∞h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.992 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.992 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.448 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.448 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 1.9845 | 1.4558 | 3.4404 |
Si2 | 1.9845 | | 3.4404 | 1.4558 | H3 | 1.4558 | 3.4404 | | 4.8962 | H4 | 3.4404 | 1.4558 | 4.8962 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
180.000 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
180.000 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at QCISD(T)=FULL/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.310672 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.907522 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 63.741959 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at QCISD(T)=FULL/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
2209 |
2114 |
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
Ag |
616 |
589 |
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
Ag |
569 |
544 |
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
Au |
127 |
122 |
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
Bu |
2201 |
2106 |
|
|
|
|
| 6 |
Bu |
223 |
213 |
|
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2972.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9569) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2844.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at QCISD(T)=FULL/cc-pVTZ
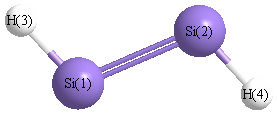
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.057 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.057 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
1.220 |
1.910 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-1.220 |
-1.910 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1144 | 1.4885 | 3.2084 |
Si2 | 2.1144 | | 3.2084 | 1.4885 | H3 | 1.4885 | 3.2084 | | 4.5330 | H4 | 3.2084 | 1.4885 | 4.5330 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
124.971 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
124.971 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C4
Energy calculated at QCISD(T)=FULL/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.339533 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.950197 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.810030 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at QCISD(T)=FULL/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
1657 |
1586 |
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
930 |
890 |
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
529 |
506 |
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
A2 |
1165 |
1114 |
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
B1 |
1575 |
1508 |
|
|
|
|
| 6 |
B2 |
1232 |
1179 |
|
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3543.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9569) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3391.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at QCISD(T)=FULL/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.108 |
-0.051 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.108 |
-0.051 |
| H3 |
0.986 |
0.000 |
0.720 |
| H4 |
-0.986 |
0.000 |
0.720 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.2156 | 1.6714 | 1.6714 |
Si2 | 2.2156 | | 1.6714 | 1.6714 | H3 | 1.6714 | 1.6714 | | 1.9713 | H4 | 1.6714 | 1.6714 | 1.9713 | |
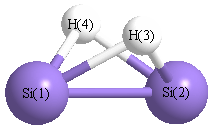 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
48.487 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
48.487 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at QCISD(T)=FULL/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.323747 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.928089 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 65.001464 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at QCISD(T)=FULL/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
2209 |
2114 |
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1674 |
1602 |
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
1131 |
1082 |
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
618 |
591 |
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
463 |
443 |
|
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
212 |
203 |
|
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3153.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9569) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3017.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at QCISD(T)=FULL/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.060 |
-1.145 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.060 |
0.976 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
-1.240 |
-0.016 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.426 |
2.381 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1213 | 1.7217 | 3.5595 |
Si2 | 2.1213 | | 1.6352 | 1.4865 | H3 | 1.7217 | 1.6352 | | 2.5316 | H4 | 3.5595 | 1.4865 | 2.5316 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
160.930 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
49.018 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability