Jump to
S1C2
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Point Group is D5h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
1.204 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
1.145 |
0.372 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
0.707 |
-0.974 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
-0.707 |
-0.974 |
0.000 |
| C5 |
-1.145 |
0.372 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
0.000 |
2.285 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
2.173 |
0.706 |
0.000 |
| H8 |
1.343 |
-1.848 |
0.000 |
| H9 |
-1.343 |
-1.848 |
0.000 |
| H10 |
-2.173 |
0.706 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
C5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
| C1 | | 1.4149 | 2.2893 | 2.2893 | 1.4149 | 1.0812 | 2.2292 | 3.3344 | 3.3344 | 2.2292 |
C2 | 1.4149 | | 1.4149 | 2.2893 | 2.2893 | 2.2292 | 1.0812 | 2.2292 | 3.3344 | 3.3344 | C3 | 2.2893 | 1.4149 | | 1.4149 | 2.2893 | 3.3344 | 2.2292 | 1.0812 | 2.2292 | 3.3344 | C4 | 2.2893 | 2.2893 | 1.4149 | | 1.4149 | 3.3344 | 3.3344 | 2.2292 | 1.0812 | 2.2292 | C5 | 1.4149 | 2.2893 | 2.2893 | 1.4149 | | 2.2292 | 3.3344 | 3.3344 | 2.2292 | 1.0812 | H6 | 1.0812 | 2.2292 | 3.3344 | 3.3344 | 2.2292 | | 2.6859 | 4.3459 | 4.3459 | 2.6859 | H7 | 2.2292 | 1.0812 | 2.2292 | 3.3344 | 3.3344 | 2.6859 | | 2.6859 | 4.3459 | 4.3459 | H8 | 3.3344 | 2.2292 | 1.0812 | 2.2292 | 3.3344 | 4.3459 | 2.6859 | | 2.6859 | 4.3459 | H9 | 3.3344 | 3.3344 | 2.2292 | 1.0812 | 2.2292 | 4.3459 | 4.3459 | 2.6859 | | 2.6859 | H10 | 2.2292 | 3.3344 | 3.3344 | 2.2292 | 1.0812 | 2.6859 | 4.3459 | 4.3459 | 2.6859 | |
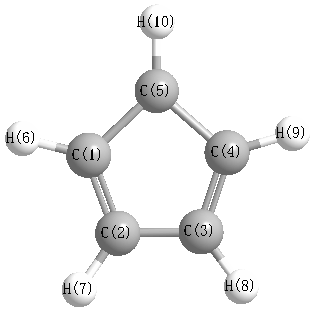 More geometry information
More geometry information
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at G4
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -193.339628 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -193.343963 |
| HF Energy | -193.476180 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 148.809592 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3254 |
3140 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
3246 |
3133 |
10.89 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
3211 |
3099 |
1.43 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A1 |
1577 |
1522 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A1 |
1452 |
1401 |
1.74 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A1 |
1145 |
1105 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A1 |
1089 |
1051 |
8.37 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A1 |
1040 |
1004 |
8.41 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A1 |
842 |
813 |
0.27 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A2 |
907 |
875 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A2 |
827 |
798 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A2 |
529 |
511 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
B1 |
885 |
854 |
5.63 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
B1 |
729 |
704 |
1.16 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
B1 |
695 |
670 |
68.49 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
B1 |
494 |
477 |
7.62 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
B2 |
3229 |
3116 |
15.07 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
B2 |
3213 |
3100 |
9.60 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
B2 |
1400 |
1351 |
37.02 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B2 |
1295 |
1250 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B2 |
1211 |
1169 |
1.56 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B2 |
973 |
939 |
0.50 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B2 |
920 |
888 |
2.51 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B2 |
24i |
24i |
4.99 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 17069.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.965) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 16472.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.224 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
1.123 |
0.393 |
| C3 |
0.000 |
0.678 |
-1.006 |
| C4 |
0.000 |
-0.678 |
-1.006 |
| C5 |
0.000 |
-1.123 |
0.393 |
| H6 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.304 |
| H7 |
0.000 |
2.157 |
0.714 |
| H8 |
0.000 |
1.336 |
-1.864 |
| H9 |
0.000 |
-1.336 |
-1.864 |
| H10 |
0.000 |
-2.157 |
0.714 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
C5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
| C1 | | 1.3968 | 2.3307 | 2.3307 | 1.3968 | 1.0796 | 2.2168 | 3.3641 | 3.3641 | 2.2168 |
C2 | 1.3968 | | 1.4683 | 2.2811 | 2.2462 | 2.2158 | 1.0830 | 2.2670 | 3.3377 | 3.2962 | C3 | 2.3307 | 1.4683 | | 1.3567 | 2.2811 | 3.3782 | 2.2688 | 1.0807 | 2.1892 | 3.3168 | C4 | 2.3307 | 2.2811 | 1.3567 | | 1.4683 | 3.3782 | 3.3168 | 2.1892 | 1.0807 | 2.2688 | C5 | 1.3968 | 2.2462 | 2.2811 | 1.4683 | | 2.2158 | 3.2962 | 3.3377 | 2.2670 | 1.0830 | H6 | 1.0796 | 2.2158 | 3.3782 | 3.3782 | 2.2158 | | 2.6795 | 4.3760 | 4.3760 | 2.6795 | H7 | 2.2168 | 1.0830 | 2.2688 | 3.3168 | 3.2962 | 2.6795 | | 2.7058 | 4.3416 | 4.3149 | H8 | 3.3641 | 2.2670 | 1.0807 | 2.1892 | 3.3377 | 4.3760 | 2.7058 | | 2.6716 | 4.3416 | H9 | 3.3641 | 3.3377 | 2.1892 | 1.0807 | 2.2670 | 4.3760 | 4.3416 | 2.6716 | | 2.7058 | H10 | 2.2168 | 3.2962 | 3.3168 | 2.2688 | 1.0830 | 2.6795 | 4.3149 | 4.3416 | 2.7058 | |
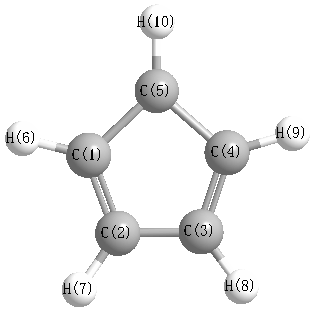 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
110.084 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H7 |
123.179 |
| C1 |
C5 |
C4 |
110.084 |
|
C1 |
C5 |
H10 |
123.179 |
| C2 |
C1 |
C5 |
105.202 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
127.399 |
| C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
107.315 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H8 |
123.731 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H7 |
126.737 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
C5 |
107.315 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H9 |
128.954 |
|
C4 |
C3 |
H8 |
128.954 |
| C4 |
C5 |
H10 |
126.737 |
|
C5 |
C1 |
H6 |
127.399 |
| C5 |
C4 |
H9 |
123.731 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.126 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.081 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.110 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.110 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.081 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.095 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.107 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.100 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.100 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.107 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.047 |
0.047 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
87.476 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.353 |

