Jump to
S1C2
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at G4
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -115.880020 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -115.881807 |
| HF Energy | -115.961472 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 58.022421 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3307 |
3191 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3054 |
2947 |
58.68 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
1670 |
1612 |
0.18 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1244 |
1200 |
9.68 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1003 |
968 |
19.56 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
936 |
903 |
3.48 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
640 |
618 |
50.04 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A" |
3259 |
3145 |
0.91 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A" |
1046 |
1010 |
25.57 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
983 |
949 |
3.89 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
900 |
868 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
706 |
681 |
26.47 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9373.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.965) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9045.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.037 |
0.888 |
0.000 |
| H2 |
0.744 |
1.653 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
-0.037 |
-0.418 |
0.655 |
| C4 |
-0.037 |
-0.418 |
-0.655 |
| H5 |
-0.040 |
-0.983 |
1.572 |
| H6 |
-0.040 |
-0.983 |
-1.572 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
H2 |
C3 |
C4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.0930 | 1.4615 | 1.4615 | 2.4437 | 2.4437 |
H2 | 1.0930 | | 2.3084 | 2.3084 | 3.1674 | 3.1674 | C3 | 1.4615 | 2.3084 | | 1.3108 | 1.0767 | 2.2980 | C4 | 1.4615 | 2.3084 | 1.3108 | | 2.2980 | 1.0767 | H5 | 2.4437 | 3.1674 | 1.0767 | 2.2980 | | 3.1443 | H6 | 2.4437 | 3.1674 | 2.2980 | 1.0767 | 3.1443 | |
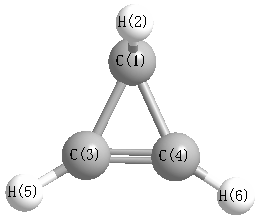 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C3 |
C4 |
63.367 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H5 |
148.271 |
| C1 |
C4 |
C3 |
63.367 |
|
C1 |
C4 |
H6 |
148.271 |
| H2 |
C1 |
C3 |
128.640 |
|
H2 |
C1 |
C4 |
128.640 |
| C3 |
C1 |
C4 |
53.266 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H6 |
148.362 |
| C4 |
C3 |
H5 |
148.362 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.272 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.110 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.069 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.069 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.578 |
-1.339 |
0.000 |
1.459 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
33.030 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
5.747 |
