Vibrational Frequencies calculated at TPSSh/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3592 |
3467 |
14.48 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3140 |
3030 |
7.45 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3084 |
2976 |
8.01 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3008 |
2903 |
3.38 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1739 |
1679 |
262.65 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1535 |
1481 |
17.44 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1503 |
1450 |
0.58 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1477 |
1426 |
7.71 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1445 |
1395 |
14.26 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1188 |
1147 |
0.38 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1167 |
1127 |
1.59 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1141 |
1101 |
7.37 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
913 |
882 |
2.83 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
510 |
492 |
30.73 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
390 |
376 |
45.03 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
218 |
210 |
3.91 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
173 |
167 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
74 |
71 |
0.21 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
B |
3587 |
3462 |
6.00 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B |
3139 |
3030 |
2.59 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
3084 |
2977 |
57.28 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B |
3007 |
2902 |
137.27 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B |
1560 |
1505 |
284.01 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B |
1516 |
1463 |
17.11 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B |
1494 |
1442 |
101.58 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B |
1448 |
1398 |
13.41 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B |
1249 |
1206 |
253.57 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
B |
1152 |
1112 |
35.58 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
B |
1137 |
1097 |
3.41 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
B |
1031 |
995 |
1.83 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
B |
757 |
731 |
5.72 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
B |
714 |
689 |
23.08 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
B |
478 |
461 |
115.38 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
B |
316 |
305 |
42.05 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
B |
117 |
113 |
11.53 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
B |
77 |
74 |
0.25 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 26078.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9652) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25170.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
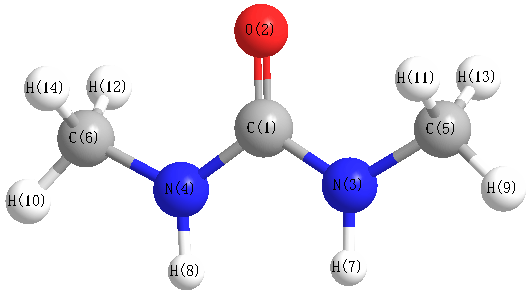
Charges from optimized geometry at TPSSh/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.454 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.731 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.004 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
N |
-0.004 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.273 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.273 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
-0.030 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
-0.030 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.118 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.118 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.224 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.224 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.103 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.103 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.700 |
3.700 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.943 |
-0.501 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.501 |
11.689 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.847 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
193.118 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.897 |