Vibrational Frequencies calculated at TPSSh/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3176 |
3057 |
5.09 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3147 |
3029 |
19.08 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3125 |
3008 |
26.07 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3111 |
2994 |
13.17 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3100 |
2984 |
8.53 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3091 |
2975 |
2.64 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3052 |
2937 |
25.05 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3046 |
2932 |
6.67 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1516 |
1459 |
3.91 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1508 |
1451 |
3.93 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1506 |
1449 |
7.32 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1493 |
1437 |
1.36 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1426 |
1372 |
4.70 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1394 |
1342 |
11.72 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1346 |
1296 |
8.08 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1327 |
1277 |
10.35 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1285 |
1237 |
18.37 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1272 |
1224 |
27.79 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1180 |
1135 |
8.15 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1125 |
1083 |
8.16 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1115 |
1073 |
1.87 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1066 |
1026 |
2.86 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1023 |
984 |
15.65 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
958 |
922 |
1.89 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
910 |
876 |
7.80 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
778 |
749 |
9.16 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
738 |
711 |
41.63 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
609 |
586 |
36.66 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
428 |
412 |
3.18 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
401 |
386 |
6.57 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
329 |
317 |
3.83 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
250 |
241 |
0.37 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
236 |
228 |
0.26 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
146 |
141 |
2.55 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
113 |
109 |
1.38 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
76 |
73 |
3.86 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25200.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9625) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24255.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
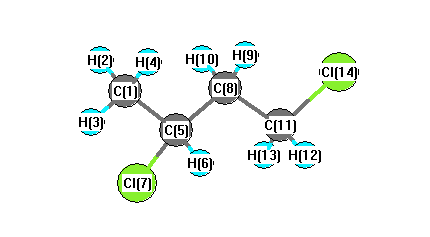
Charges from optimized geometry at TPSSh/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.645 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.174 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.180 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.162 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
0.135 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.201 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
Cl |
-0.120 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.373 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.178 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.192 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
C |
-0.546 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.200 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.224 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
Cl |
0.037 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.464 |
1.837 |
1.095 |
2.591 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
12.859 |
0.339 |
-0.219 |
| y |
0.339 |
10.618 |
0.086 |
| z |
-0.219 |
0.086 |
8.658 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
370.982 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
19.261 |