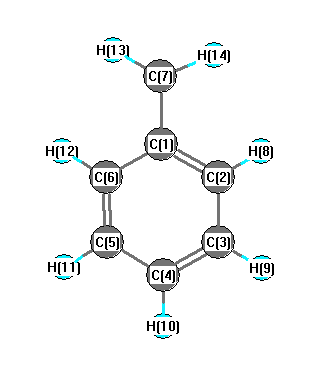
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at TPSSh/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3209 |
3089 |
18.17 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
3190 |
3070 |
6.96 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
3175 |
3056 |
9.75 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A1 |
3162 |
3044 |
9.33 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A1 |
1603 |
1543 |
0.54 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A1 |
1514 |
1457 |
5.77 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A1 |
1502 |
1446 |
1.28 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A1 |
1287 |
1239 |
1.36 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A1 |
1189 |
1144 |
0.16 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A1 |
1036 |
997 |
2.35 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A1 |
990 |
952 |
0.66 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A1 |
826 |
795 |
0.30 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A1 |
522 |
503 |
0.31 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A2 |
972 |
935 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A2 |
832 |
801 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A2 |
491 |
473 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A2 |
384 |
370 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
B1 |
985 |
948 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
B1 |
897 |
864 |
5.32 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B1 |
765 |
737 |
78.89 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B1 |
701 |
674 |
1.99 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B1 |
677 |
652 |
53.03 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B1 |
470 |
453 |
16.42 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B1 |
197 |
190 |
1.64 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B2 |
3261 |
3139 |
11.54 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B2 |
3196 |
3076 |
47.97 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B2 |
3177 |
3058 |
2.21 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
B2 |
1583 |
1523 |
0.48 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
B2 |
1477 |
1421 |
4.26 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
B2 |
1363 |
1312 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
B2 |
1346 |
1295 |
1.25 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
B2 |
1178 |
1133 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
B2 |
1117 |
1075 |
3.05 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
B2 |
972 |
936 |
2.26 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
B2 |
616 |
593 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
B2 |
344 |
331 |
0.10 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25101.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9625) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24160.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at TPSSh/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.616 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.337 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.157 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.178 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.157 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.337 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
C |
-0.494 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.146 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.146 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.151 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.151 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.116 |
0.116 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.937 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
12.614 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
17.622 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
191.719 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.846 |