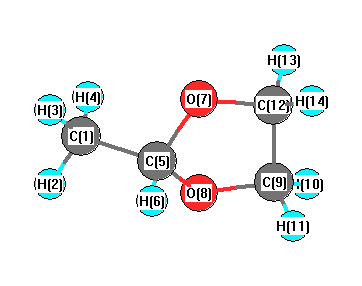
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at TPSSh/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3154 |
3036 |
20.88 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3144 |
3027 |
16.21 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3137 |
3019 |
30.95 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3092 |
2976 |
39.73 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3063 |
2948 |
12.42 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3048 |
2934 |
72.39 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3013 |
2900 |
59.60 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2950 |
2839 |
97.37 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1544 |
1486 |
0.34 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1526 |
1469 |
2.06 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1506 |
1449 |
2.38 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1504 |
1448 |
5.00 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1441 |
1387 |
64.49 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1401 |
1349 |
6.56 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1383 |
1331 |
13.55 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1376 |
1324 |
0.52 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1333 |
1283 |
1.14 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1250 |
1203 |
16.16 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1222 |
1177 |
1.92 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1175 |
1131 |
45.21 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1154 |
1111 |
43.28 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1128 |
1085 |
91.33 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1107 |
1066 |
49.83 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1055 |
1015 |
26.82 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1033 |
994 |
58.39 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
947 |
912 |
11.74 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
872 |
840 |
9.24 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
867 |
835 |
55.42 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
840 |
809 |
13.04 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
687 |
661 |
1.01 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
672 |
647 |
3.33 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
495 |
476 |
4.24 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
321 |
309 |
6.50 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
216 |
208 |
0.51 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
197 |
190 |
5.33 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
45 |
44 |
5.06 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 26450.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9625) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25458.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at TPSSh/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.436 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.168 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.170 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.182 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.047 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.129 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
O |
-0.329 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
O |
-0.301 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
C |
-0.061 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.161 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.146 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
C |
-0.079 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.152 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.145 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.174 |
-0.256 |
0.561 |
1.326 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.470 |
0.029 |
-0.095 |
| y |
0.029 |
7.472 |
-0.097 |
| z |
-0.095 |
-0.097 |
7.294 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
151.245 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
12.298 |