Vibrational Frequencies calculated at TPSSh/cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3108 |
3022 |
5.32 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3092 |
3006 |
28.40 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3031 |
2947 |
24.13 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3023 |
2940 |
5.67 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1817 |
1767 |
217.44 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1496 |
1454 |
0.71 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1433 |
1393 |
0.18 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1337 |
1300 |
1.20 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1297 |
1261 |
0.22 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1213 |
1179 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1166 |
1134 |
0.57 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1037 |
1009 |
0.69 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
950 |
924 |
0.08 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
904 |
879 |
0.24 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
809 |
787 |
1.36 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
703 |
684 |
0.71 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
552 |
537 |
5.07 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
237 |
230 |
0.15 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
B |
3108 |
3022 |
27.54 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B |
3096 |
3011 |
38.68 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
3035 |
2951 |
44.88 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B |
3023 |
2939 |
9.35 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B |
1480 |
1439 |
3.33 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B |
1434 |
1394 |
16.21 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B |
1334 |
1297 |
6.10 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B |
1289 |
1253 |
7.19 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B |
1242 |
1207 |
4.08 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
B |
1153 |
1122 |
36.67 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
B |
1147 |
1115 |
38.28 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
B |
972 |
945 |
8.70 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
B |
912 |
887 |
0.41 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
B |
840 |
817 |
10.77 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
B |
573 |
557 |
2.31 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
B |
464 |
452 |
4.94 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
B |
442 |
430 |
2.44 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
B |
102 |
99 |
4.40 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 26424.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9724) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25694.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
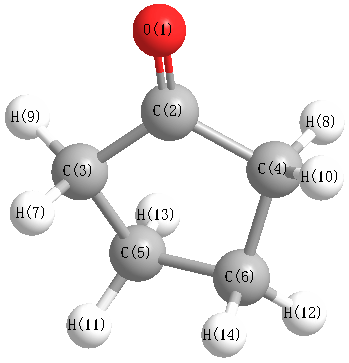
Charges from optimized geometry at TPSSh/cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
O |
-0.226 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.051 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.025 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.025 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.056 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.056 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.060 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.060 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.046 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.046 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.026 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.026 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.036 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.036 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.770 |
2.770 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.726 |
0.078 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.078 |
8.396 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.920 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
153.434 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
12.387 |