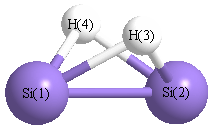Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at B3LYP/SDD
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -580.013155 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -580.013155 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 66.376516 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/SDD
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σg |
2339 |
2248 |
0.00 |
248.14 |
0.31 |
0.47 |
| 2 |
Σg |
743 |
714 |
0.00 |
66.47 |
0.32 |
0.49 |
| 3 |
Σu |
2334 |
2244 |
0.41 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 4 |
Πg |
604i |
581i |
0.00 |
84.79 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 4 |
Πg |
604i |
581i |
0.00 |
84.79 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
Πu |
414 |
398 |
5.48 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 5 |
Πu |
414 |
398 |
5.48 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2518.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9613) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2420.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/SDD
Point Group is D∞h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.000 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.000 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.464 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.464 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 1.9996 | 1.4641 | 3.4636 |
Si2 | 1.9996 | | 3.4636 | 1.4641 | H3 | 1.4641 | 3.4636 | | 4.9277 | H4 | 3.4636 | 1.4641 | 4.9277 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
180.000 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
180.000 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/SDD
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
-0.030 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
-0.030 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.030 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.030 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-30.183 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-30.183 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-21.688 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-4.248 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-4.248 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.496 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 16.991 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.699 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.699 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
13.799 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
57.212 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.564 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at B3LYP/SDD
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -580.046458 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -580.046458 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 63.182555 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/SDD
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
2137 |
2054 |
0.00 |
383.92 |
0.44 |
0.61 |
| 2 |
Ag |
623 |
599 |
0.00 |
54.08 |
0.53 |
0.69 |
| 3 |
Ag |
546 |
525 |
0.00 |
61.46 |
0.06 |
0.12 |
| 4 |
Au |
256 |
246 |
75.25 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 5 |
Bu |
2144 |
2061 |
152.63 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 6 |
Bu |
251 |
241 |
46.32 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2978.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9613) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2863.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/SDD
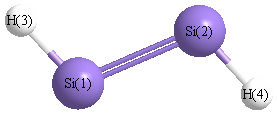
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.066 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.066 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
1.217 |
1.948 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-1.217 |
-1.948 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1319 | 1.5030 | 3.2504 |
Si2 | 2.1319 | | 3.2504 | 1.5030 | H3 | 1.5030 | 3.2504 | | 4.5939 | H4 | 3.2504 | 1.5030 | 4.5939 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
125.938 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
125.938 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/SDD
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.056 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.056 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.056 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.056 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.965 |
0.233 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.233 |
-24.113 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-30.825 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.496 |
0.233 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.233 |
5.782 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-4.286 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -8.572 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -4.852 |
|---|
| xy | 0.233 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.509 |
0.046 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.046 |
14.620 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.475 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
59.835 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.735 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C4
Energy calculated at B3LYP/SDD
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -580.051671 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -580.051671 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 61.709481 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/SDD
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
1441 |
1385 |
12.10 |
68.29 |
0.12 |
0.21 |
| 2 |
A1 |
911 |
876 |
87.90 |
13.37 |
0.41 |
0.58 |
| 3 |
A1 |
437 |
421 |
4.54 |
61.23 |
0.44 |
0.61 |
| 4 |
A2 |
825 |
793 |
0.00 |
0.57 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
B1 |
1320 |
1269 |
73.32 |
39.56 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 6 |
B2 |
955 |
918 |
365.19 |
1.59 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2944.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9613) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2830.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/SDD
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.168 |
-0.053 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.168 |
-0.053 |
| H3 |
1.013 |
0.000 |
0.745 |
| H4 |
-1.013 |
0.000 |
0.745 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.3353 | 1.7396 | 1.7396 |
Si2 | 2.3353 | | 1.7396 | 1.7396 | H3 | 1.7396 | 1.7396 | | 2.0253 | H4 | 1.7396 | 1.7396 | 2.0253 | |
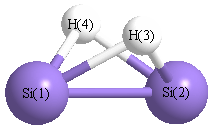 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
47.839 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
47.839 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/SDD
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.216 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.216 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.216 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.216 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.460 |
0.460 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.167 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-32.265 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-29.507 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
3.719 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-3.928 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.209 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 0.418 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.098 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.638 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
13.692 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.262 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
59.933 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.742 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B3LYP/SDD
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -580.049259 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -580.049259 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 63.272811 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/SDD
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
2173 |
2089 |
78.22 |
237.49 |
0.39 |
0.57 |
| 2 |
A' |
1556 |
1496 |
86.70 |
103.29 |
0.32 |
0.48 |
| 3 |
A' |
779 |
749 |
63.59 |
14.10 |
0.68 |
0.81 |
| 4 |
A' |
553 |
532 |
28.65 |
51.07 |
0.36 |
0.53 |
| 5 |
A' |
288 |
277 |
40.90 |
1.99 |
0.58 |
0.74 |
| 6 |
A" |
198 |
191 |
52.38 |
11.45 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2773.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9613) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2666.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/SDD
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.056 |
-1.180 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.056 |
0.996 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
-1.333 |
0.122 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.241 |
2.460 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1756 | 1.9036 | 3.6519 |
Si2 | 2.1756 | | 1.6408 | 1.4940 | H3 | 1.9036 | 1.6408 | | 2.5803 | H4 | 3.6519 | 1.4940 | 2.5803 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
168.533 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
46.851 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/SDD
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.219 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
-0.025 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.170 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.025 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.251 |
0.534 |
0.000 |
0.590 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.726 |
-0.332 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.332 |
-26.430 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-31.226 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.102 |
-0.332 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.332 |
3.046 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-4.147 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -8.295 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.296 |
|---|
| xy | -0.332 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.330 |
0.080 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.080 |
14.087 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.109 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
59.135 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.690 |