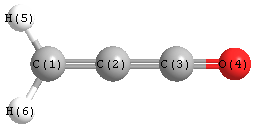Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -190.682395 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -190.682395 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 87.981988 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3075 |
2984 |
31.51 |
241.94 |
0.11 |
0.19 |
| 2 |
A1 |
2313 |
2244 |
978.13 |
47.02 |
0.52 |
0.68 |
| 3 |
A1 |
1783 |
1730 |
44.28 |
2.76 |
0.59 |
0.74 |
| 4 |
A1 |
1466 |
1422 |
3.25 |
12.12 |
0.54 |
0.70 |
| 5 |
A1 |
926 |
899 |
7.08 |
52.32 |
0.17 |
0.28 |
| 6 |
B1 |
1025 |
995 |
23.91 |
1.53 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 7 |
B1 |
617 |
599 |
17.72 |
0.16 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 8 |
B1 |
202 |
196 |
0.57 |
2.14 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 9 |
B2 |
3148 |
3055 |
7.37 |
151.77 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 10 |
B2 |
1050 |
1018 |
2.18 |
0.00 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 11 |
B2 |
429 |
416 |
6.06 |
2.93 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 12 |
B2 |
185i |
179i |
15.77 |
0.15 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7924.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9704) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7689.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVDZ
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.882 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.559 |
| C3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.724 |
| O4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.904 |
| H5 |
0.000 |
0.929 |
-2.465 |
| H6 |
0.000 |
-0.929 |
-2.465 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3234 | 2.6058 | 3.7862 | 1.0964 | 1.0964 |
C2 | 1.3234 | | 1.2824 | 2.4628 | 2.1201 | 2.1201 | C3 | 2.6058 | 1.2824 | | 1.1804 | 3.3208 | 3.3208 | O4 | 3.7862 | 2.4628 | 1.1804 | | 4.4663 | 4.4663 | H5 | 1.0964 | 2.1201 | 3.3208 | 4.4663 | | 1.8578 | H6 | 1.0964 | 2.1201 | 3.3208 | 4.4663 | 1.8578 | |
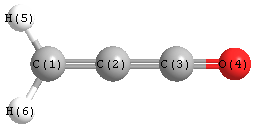 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
180.000 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
122.086 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
122.086 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
180.000 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
115.828 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.677 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.211 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.314 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.355 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
-0.424 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
-0.424 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.867 |
2.867 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-22.932 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-22.780 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-22.436 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.324 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-0.096 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.420 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 0.840 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.152 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.722 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
4.230 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.491 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
83.336 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.129 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -190.684043 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -190.684043 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 88.257398 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3170 |
3076 |
6.34 |
122.99 |
0.71 |
0.83 |
| 2 |
A' |
3087 |
2996 |
29.00 |
186.23 |
0.11 |
0.20 |
| 3 |
A' |
2202 |
2136 |
986.43 |
54.95 |
0.54 |
0.70 |
| 4 |
A' |
1750 |
1698 |
10.14 |
6.01 |
0.19 |
0.33 |
| 5 |
A' |
1469 |
1425 |
1.29 |
12.70 |
0.58 |
0.74 |
| 6 |
A' |
1064 |
1032 |
21.81 |
3.86 |
0.03 |
0.06 |
| 7 |
A' |
949 |
921 |
3.12 |
42.72 |
0.11 |
0.19 |
| 8 |
A' |
498 |
483 |
12.13 |
4.77 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 9 |
A' |
175 |
170 |
22.66 |
6.23 |
0.72 |
0.84 |
| 10 |
A" |
1032 |
1001 |
24.00 |
1.83 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 11 |
A" |
696 |
676 |
11.27 |
0.33 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 12 |
A" |
271 |
263 |
1.76 |
2.64 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 8181.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9704) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7939.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVDZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.030 |
-1.507 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
-0.661 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
-0.348 |
0.601 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
-0.881 |
1.646 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
2.074 |
-1.173 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
0.875 |
-2.590 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3327 | 2.5178 | 3.6864 | 1.0963 | 1.0941 |
C2 | 1.3327 | | 1.3088 | 2.4694 | 2.1365 | 2.1177 | C3 | 2.5178 | 1.3088 | | 1.1733 | 3.0019 | 3.4165 | O4 | 3.6864 | 2.4694 | 1.1733 | | 4.0836 | 4.5849 | H5 | 1.0963 | 2.1365 | 3.0019 | 4.0836 | | 1.8566 | H6 | 1.0941 | 2.1177 | 3.4165 | 4.5849 | 1.8566 | |
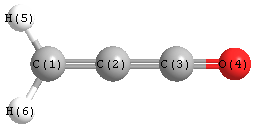 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
144.781 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
122.891 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
121.209 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
168.405 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
115.900 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.580 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.517 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.179 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.317 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
-0.502 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
-0.458 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.932 |
-1.631 |
0.000 |
2.529 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-22.245 |
-0.816 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.816 |
-23.338 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-23.096 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.972 |
-0.816 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.816 |
-0.667 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.305 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.609 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 1.092 |
|---|
| xy | -0.816 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.228 |
-2.725 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.725 |
9.353 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.833 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
80.824 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.990 |