Jump to
S1C2
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -235.933128 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -235.946511 |
| HF Energy | -235.933128 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 249.310991 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3084 |
2983 |
119.19 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3072 |
2973 |
26.16 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3069 |
2969 |
30.07 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3043 |
2944 |
12.19 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3030 |
2932 |
7.62 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
3025 |
2927 |
9.11 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
3012 |
2914 |
33.13 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
3011 |
2913 |
29.53 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1503 |
1454 |
8.90 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1498 |
1449 |
1.03 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1494 |
1445 |
3.63 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1413 |
1367 |
5.88 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1410 |
1364 |
1.66 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1383 |
1338 |
0.70 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1364 |
1320 |
9.90 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1277 |
1236 |
3.28 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1251 |
1211 |
0.31 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
1199 |
1160 |
0.33 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
1124 |
1087 |
0.43 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
1043 |
1010 |
1.17 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
964 |
933 |
0.90 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
941 |
911 |
0.50 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
865 |
837 |
0.58 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A' |
794 |
768 |
0.77 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A' |
645 |
624 |
1.29 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A' |
431 |
417 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A' |
324 |
313 |
0.08 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A' |
89 |
86 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
3076 |
2976 |
21.82 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
3072 |
2972 |
24.84 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
3069 |
2970 |
30.83 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
3028 |
2930 |
80.03 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
1498 |
1449 |
4.32 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A" |
1496 |
1447 |
0.26 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A" |
1476 |
1428 |
4.86 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A" |
1291 |
1249 |
0.33 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A" |
1278 |
1236 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A" |
1227 |
1188 |
0.07 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A" |
1145 |
1107 |
0.40 |
|
|
|
| 40 |
A" |
1128 |
1092 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 41 |
A" |
999 |
966 |
2.61 |
|
|
|
| 42 |
A" |
900 |
870 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 43 |
A" |
895 |
866 |
0.15 |
|
|
|
| 44 |
A" |
810 |
784 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 45 |
A" |
378 |
366 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 46 |
A" |
260 |
251 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 47 |
A" |
252 |
244 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 48 |
A" |
235 |
228 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 36435.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9675) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 35250.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.243 |
0.077 |
1.083 |
| C2 |
0.243 |
0.077 |
-1.083 |
| C3 |
-0.655 |
0.732 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
0.834 |
-0.869 |
0.000 |
| C5 |
-0.818 |
2.243 |
0.000 |
| C6 |
0.243 |
-2.274 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
0.987 |
0.779 |
1.464 |
| H8 |
-0.254 |
-0.392 |
1.933 |
| H9 |
0.987 |
0.779 |
-1.464 |
| H10 |
-0.254 |
-0.392 |
-1.933 |
| H11 |
-1.641 |
0.264 |
0.000 |
| H12 |
1.923 |
-0.939 |
0.000 |
| H13 |
0.156 |
2.738 |
0.000 |
| H14 |
-0.848 |
-2.247 |
0.000 |
| H15 |
-1.365 |
2.582 |
-0.882 |
| H16 |
-1.365 |
2.582 |
0.882 |
| H17 |
0.561 |
-2.833 |
-0.883 |
| H18 |
0.561 |
-2.833 |
0.883 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
C5 |
C6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
H15 |
H16 |
H17 |
H18 |
| C1 | | 2.1657 | 1.5523 | 1.5548 | 2.6436 | 2.5886 | 1.0913 | 1.0909 | 2.7441 | 3.0924 | 2.1817 | 2.2416 | 2.8746 | 2.7870 | 3.5672 | 2.9840 | 3.5259 | 2.9340 |
C2 | 2.1657 | | 1.5523 | 1.5548 | 2.6436 | 2.5886 | 2.7441 | 3.0924 | 1.0913 | 1.0909 | 2.1817 | 2.2416 | 2.8746 | 2.7870 | 2.9840 | 3.5672 | 2.9340 | 3.5259 | C3 | 1.5523 | 1.5523 | | 2.1873 | 1.5191 | 3.1379 | 2.2004 | 2.2722 | 2.2004 | 2.2722 | 1.0915 | 3.0723 | 2.1637 | 2.9859 | 2.1690 | 2.1690 | 3.8690 | 3.8690 | C4 | 1.5548 | 1.5548 | 2.1873 | | 3.5234 | 1.5241 | 2.2097 | 2.2690 | 2.2097 | 2.2690 | 2.7229 | 1.0906 | 3.6711 | 2.1749 | 4.1869 | 4.1869 | 2.1700 | 2.1700 | C5 | 2.6436 | 2.6436 | 1.5191 | 3.5234 | | 4.6399 | 2.7463 | 3.3163 | 2.7463 | 3.3163 | 2.1430 | 4.1991 | 1.0922 | 4.4902 | 1.0922 | 1.0922 | 5.3331 | 5.3331 | C6 | 2.5886 | 2.5886 | 3.1379 | 1.5241 | 4.6399 | | 3.4666 | 2.7433 | 3.4666 | 2.7433 | 3.1616 | 2.1455 | 5.0133 | 1.0921 | 5.1915 | 5.1915 | 1.0919 | 1.0919 | H7 | 1.0913 | 2.7441 | 2.2004 | 2.2097 | 2.7463 | 3.4666 | | 1.7697 | 2.9271 | 3.8011 | 3.0522 | 2.4431 | 2.5831 | 3.8302 | 3.7798 | 3.0204 | 4.3281 | 3.6830 | H8 | 1.0909 | 3.0924 | 2.2722 | 2.2690 | 3.3163 | 2.7433 | 1.7697 | | 3.8011 | 3.8662 | 2.4685 | 2.9618 | 3.7020 | 2.7445 | 4.2436 | 3.3449 | 3.8144 | 2.7792 | H9 | 2.7441 | 1.0913 | 2.2004 | 2.2097 | 2.7463 | 3.4666 | 2.9271 | 3.8011 | | 1.7697 | 3.0522 | 2.4431 | 2.5831 | 3.8302 | 3.0204 | 3.7798 | 3.6830 | 4.3281 | H10 | 3.0924 | 1.0909 | 2.2722 | 2.2690 | 3.3163 | 2.7433 | 3.8011 | 3.8662 | 1.7697 | | 2.4685 | 2.9618 | 3.7020 | 2.7445 | 3.3449 | 4.2436 | 2.7792 | 3.8144 | H11 | 2.1817 | 2.1817 | 1.0915 | 2.7229 | 2.1430 | 3.1616 | 3.0522 | 2.4685 | 3.0522 | 2.4685 | | 3.7616 | 3.0578 | 2.6338 | 2.4956 | 2.4956 | 3.9015 | 3.9015 | H12 | 2.2416 | 2.2416 | 3.0723 | 1.0906 | 4.1991 | 2.1455 | 2.4431 | 2.9618 | 2.4431 | 2.9618 | 3.7616 | | 4.0799 | 3.0645 | 4.8976 | 4.8976 | 2.4940 | 2.4940 | H13 | 2.8746 | 2.8746 | 2.1637 | 3.6711 | 1.0922 | 5.0133 | 2.5831 | 3.7020 | 2.5831 | 3.7020 | 3.0578 | 4.0799 | | 5.0858 | 1.7648 | 1.7648 | 5.6553 | 5.6553 | H14 | 2.7870 | 2.7870 | 2.9859 | 2.1749 | 4.4902 | 1.0921 | 3.8302 | 2.7445 | 3.8302 | 2.7445 | 2.6338 | 3.0645 | 5.0858 | | 4.9367 | 4.9367 | 1.7631 | 1.7631 | H15 | 3.5672 | 2.9840 | 2.1690 | 4.1869 | 1.0922 | 5.1915 | 3.7798 | 4.2436 | 3.0204 | 3.3449 | 2.4956 | 4.8976 | 1.7648 | 4.9367 | | 1.7641 | 5.7476 | 6.0124 | H16 | 2.9840 | 3.5672 | 2.1690 | 4.1869 | 1.0922 | 5.1915 | 3.0204 | 3.3449 | 3.7798 | 4.2436 | 2.4956 | 4.8976 | 1.7648 | 4.9367 | 1.7641 | | 6.0124 | 5.7476 | H17 | 3.5259 | 2.9340 | 3.8690 | 2.1700 | 5.3331 | 1.0919 | 4.3281 | 3.8144 | 3.6830 | 2.7792 | 3.9015 | 2.4940 | 5.6553 | 1.7631 | 5.7476 | 6.0124 | | 1.7655 | H18 | 2.9340 | 3.5259 | 3.8690 | 2.1700 | 5.3331 | 1.0919 | 3.6830 | 2.7792 | 4.3281 | 3.8144 | 3.9015 | 2.4940 | 5.6553 | 1.7631 | 6.0124 | 5.7476 | 1.7655 | |
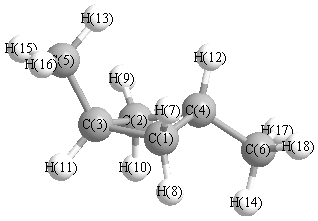 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C3 |
C2 |
88.469 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
C5 |
118.792 |
| C1 |
C3 |
H11 |
109.999 |
|
C1 |
C4 |
C2 |
88.285 |
| C1 |
C4 |
C6 |
114.436 |
|
C1 |
C4 |
H12 |
114.715 |
| C2 |
C3 |
C5 |
118.792 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
109.999 |
| C2 |
C4 |
C6 |
114.436 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H12 |
114.715 |
| C3 |
C1 |
C4 |
89.493 |
|
C3 |
C1 |
H7 |
111.491 |
| C3 |
C1 |
H8 |
117.485 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
C4 |
89.493 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H9 |
111.491 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H10 |
117.485 |
| C3 |
C5 |
H13 |
110.848 |
|
C3 |
C5 |
H15 |
111.272 |
| C3 |
C5 |
H16 |
111.272 |
|
C4 |
C1 |
H7 |
112.055 |
| C4 |
C1 |
H8 |
117.011 |
|
C4 |
C2 |
H9 |
112.055 |
| C4 |
C2 |
H10 |
117.011 |
|
C4 |
C6 |
H14 |
111.408 |
| C4 |
C6 |
H17 |
111.025 |
|
C4 |
C6 |
H18 |
111.025 |
| C5 |
C3 |
H11 |
109.250 |
|
C6 |
C4 |
H12 |
109.161 |
| H7 |
C1 |
H8 |
108.378 |
|
H9 |
C2 |
H10 |
108.378 |
| H13 |
C5 |
H15 |
107.783 |
|
H13 |
C5 |
H16 |
107.783 |
| H14 |
C6 |
H17 |
107.665 |
|
H14 |
C6 |
H18 |
107.665 |
| H15 |
C5 |
H16 |
107.720 |
|
H17 |
C6 |
H18 |
107.887 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.807 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.807 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.646 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
0.309 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.866 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.787 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.108 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.254 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.108 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.254 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.248 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.344 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.240 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.231 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.126 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
H |
0.126 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
H |
0.135 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
H |
0.135 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.011 |
-0.018 |
0.000 |
0.021 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-40.009 |
0.286 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.286 |
-41.403 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-41.022 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.203 |
0.286 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.286 |
-0.888 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.316 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.632 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 1.394 |
|---|
| xy | 0.286 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.951 |
-0.729 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.729 |
12.274 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.553 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
193.214 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.900 |
