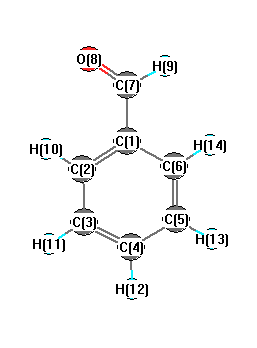
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/cc-pVQZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3196 |
3096 |
7.35 |
204.91 |
0.12 |
0.21 |
| 2 |
A' |
3189 |
3089 |
11.86 |
127.03 |
0.12 |
0.22 |
| 3 |
A' |
3179 |
3080 |
12.29 |
80.10 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 4 |
A' |
3168 |
3069 |
1.25 |
85.95 |
0.69 |
0.82 |
| 5 |
A' |
3158 |
3060 |
3.60 |
42.41 |
0.43 |
0.60 |
| 6 |
A' |
2881 |
2791 |
114.08 |
143.77 |
0.28 |
0.44 |
| 7 |
A' |
1772 |
1716 |
270.28 |
93.28 |
0.36 |
0.53 |
| 8 |
A' |
1640 |
1589 |
31.66 |
87.78 |
0.55 |
0.71 |
| 9 |
A' |
1623 |
1573 |
12.07 |
10.28 |
0.54 |
0.70 |
| 10 |
A' |
1527 |
1479 |
0.57 |
1.41 |
0.51 |
0.67 |
| 11 |
A' |
1491 |
1445 |
12.62 |
2.24 |
0.26 |
0.42 |
| 12 |
A' |
1425 |
1380 |
5.62 |
2.04 |
0.36 |
0.53 |
| 13 |
A' |
1355 |
1313 |
6.39 |
1.36 |
0.68 |
0.81 |
| 14 |
A' |
1337 |
1295 |
16.72 |
0.97 |
0.41 |
0.58 |
| 15 |
A' |
1225 |
1187 |
54.29 |
23.66 |
0.26 |
0.41 |
| 16 |
A' |
1190 |
1153 |
27.63 |
10.79 |
0.12 |
0.21 |
| 17 |
A' |
1186 |
1149 |
3.23 |
7.04 |
0.67 |
0.81 |
| 18 |
A' |
1103 |
1069 |
4.29 |
0.57 |
0.17 |
0.29 |
| 19 |
A' |
1046 |
1013 |
2.68 |
8.63 |
0.07 |
0.14 |
| 20 |
A' |
1021 |
989 |
0.79 |
37.30 |
0.06 |
0.11 |
| 21 |
A' |
840 |
814 |
33.01 |
12.58 |
0.09 |
0.17 |
| 22 |
A' |
664 |
643 |
23.69 |
2.86 |
0.29 |
0.45 |
| 23 |
A' |
632 |
613 |
0.36 |
5.14 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 24 |
A' |
443 |
429 |
0.30 |
5.81 |
0.26 |
0.41 |
| 25 |
A' |
221 |
214 |
7.76 |
0.59 |
0.47 |
0.64 |
| 26 |
A" |
1038 |
1005 |
0.84 |
2.49 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 27 |
A" |
1020 |
988 |
0.06 |
0.22 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 28 |
A" |
1003 |
972 |
0.02 |
0.15 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 29 |
A" |
949 |
920 |
1.15 |
0.25 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 30 |
A" |
870 |
843 |
0.02 |
0.05 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 31 |
A" |
768 |
744 |
42.87 |
0.12 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 32 |
A" |
708 |
686 |
28.63 |
0.01 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 33 |
A" |
466 |
452 |
6.34 |
0.16 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 34 |
A" |
418 |
405 |
0.09 |
0.01 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 35 |
A" |
235 |
227 |
7.23 |
0.93 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 36 |
A" |
116 |
112 |
4.72 |
1.58 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24050.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9688) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 23299.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/cc-pVQZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.078 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.110 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.092 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.104 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.095 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.095 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
C |
0.234 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
O |
-0.338 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.037 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.153 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.126 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.129 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.121 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.113 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.297 |
-2.576 |
0.000 |
3.451 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-45.041 |
6.330 |
0.000 |
| y |
6.330 |
-47.752 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-49.019 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
3.345 |
6.330 |
0.000 |
| y |
6.330 |
-0.722 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.623 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -5.246 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 2.712 |
|---|
| xy | 6.330 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
13.813 |
-1.171 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.171 |
16.498 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.690 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
261.251 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
16.163 |