Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/6-311G*
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/6-311G*
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at B3LYP/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -351.861299 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -351.861299 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 81.811890 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/6-311G*
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/6-311G*
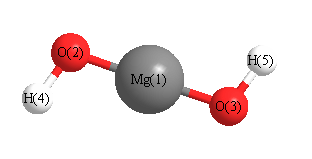
Point Group is C2
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Mg1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.007 |
| O2 |
0.000 |
1.796 |
0.035 |
| O3 |
0.000 |
-1.796 |
0.035 |
| H4 |
-0.492 |
2.531 |
-0.321 |
| H5 |
0.492 |
-2.531 |
-0.321 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Mg1 |
O2 |
O3 |
H4 |
H5 |
| Mg1 | | 1.7958 | 1.7958 | 2.5992 | 2.5992 |
O2 | 1.7958 | | 3.5912 | 0.9537 | 4.3691 | O3 | 1.7958 | 3.5912 | | 4.3691 | 0.9537 | H4 | 2.5992 | 0.9537 | 4.3691 | | 5.1570 | H5 | 2.5992 | 4.3691 | 0.9537 | 5.1570 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Mg1 |
O2 |
H4 |
139.938 |
|
Mg1 |
O3 |
H5 |
139.938 |
| O2 |
Mg1 |
O3 |
178.223 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Mg |
0.962 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.873 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.873 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.392 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.392 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.221 |
1.221 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-18.854 |
-5.150 |
0.000 |
| y |
-5.150 |
-23.950 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.631 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.936 |
-5.150 |
0.000 |
| y |
-5.150 |
-4.707 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.771 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.542 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.095 |
|---|
| xy | -5.150 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.038 |
0.118 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.118 |
4.662 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.061 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
78.110 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.838 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at B3LYP/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -351.859662 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -351.859662 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 82.812132 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σg |
4039 |
3903 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Σg |
624 |
603 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Σu |
4039 |
3902 |
128.47 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Σu |
942 |
911 |
152.72 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Πg |
263i |
255i |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Πg |
263i |
255i |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Πu |
163 |
158 |
32.34 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Πu |
163 |
158 |
32.34 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
Πu |
241i |
233i |
321.17 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
Πu |
241i |
233i |
321.17 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4480.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9663) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4329.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/6-311G*
Point Group is D∞h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Mg1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.764 |
| O3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.764 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.712 |
| H5 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.712 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Mg1 |
O2 |
O3 |
H4 |
H5 |
| Mg1 | | 1.7636 | 1.7636 | 2.7120 | 2.7120 |
O2 | 1.7636 | | 3.5272 | 0.9484 | 4.4756 | O3 | 1.7636 | 3.5272 | | 4.4756 | 0.9484 | H4 | 2.7120 | 0.9484 | 4.4756 | | 5.4240 | H5 | 2.7120 | 4.4756 | 0.9484 | 5.4240 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Mg1 |
O2 |
H4 |
180.000 |
|
Mg1 |
O3 |
H5 |
180.000 |
| O2 |
Mg1 |
O3 |
180.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Mg |
1.037 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.923 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.923 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.404 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.404 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-20.128 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-20.128 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-18.195 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.966 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-0.966 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.932 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.865 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.875 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.875 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.458 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
76.643 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.755 |
