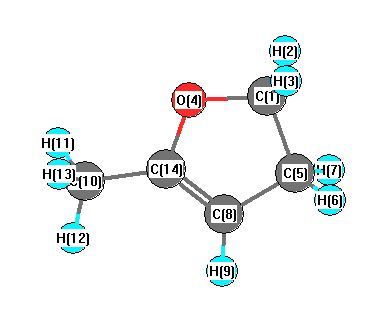
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3199 |
3136 |
8.23 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3095 |
3035 |
18.61 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3065 |
3004 |
49.35 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3046 |
2986 |
20.22 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3010 |
2951 |
61.63 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2990 |
2932 |
33.07 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2987 |
2928 |
45.12 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2954 |
2896 |
67.91 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1704 |
1670 |
48.27 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1516 |
1486 |
0.21 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1495 |
1466 |
0.18 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1490 |
1461 |
4.97 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1472 |
1443 |
6.62 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1413 |
1385 |
10.87 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1388 |
1361 |
8.99 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1306 |
1280 |
12.73 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1251 |
1226 |
34.08 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1236 |
1211 |
9.84 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1194 |
1170 |
7.98 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1183 |
1160 |
38.76 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1072 |
1051 |
0.88 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1049 |
1029 |
3.02 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1022 |
1002 |
13.95 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
998 |
979 |
23.09 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
963 |
944 |
37.94 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
920 |
902 |
15.82 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
894 |
876 |
18.01 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
841 |
825 |
4.99 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
698 |
684 |
12.97 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
685 |
672 |
11.71 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
624 |
611 |
0.89 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
536 |
526 |
2.42 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
328 |
321 |
2.09 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
214 |
210 |
6.41 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
161 |
157 |
2.10 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
92 |
91 |
1.29 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 26044.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9804) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25533.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.049 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.154 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.485 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.332 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.151 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.152 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.238 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.128 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
C |
-0.535 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.173 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.166 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.172 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
0.394 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.399 |
0.626 |
0.108 |
0.750 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-31.965 |
1.219 |
-0.023 |
| y |
1.219 |
-37.144 |
-0.154 |
| z |
-0.023 |
-0.154 |
-36.811 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.013 |
1.219 |
-0.023 |
| y |
1.219 |
-2.756 |
-0.154 |
| z |
-0.023 |
-0.154 |
-2.256 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.513 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.179 |
|---|
| xy | 1.219 |
|---|
| xz | -0.023 |
|---|
| yz | -0.154 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.988 |
-0.529 |
0.023 |
| y |
-0.529 |
8.394 |
0.005 |
| z |
0.023 |
0.005 |
5.798 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
157.320 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
12.543 |