Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -323.453158 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -323.453158 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3074 |
3014 |
36.20 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3002 |
2943 |
44.79 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
2991 |
2933 |
29.31 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
2981 |
2922 |
19.89 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1728 |
1694 |
251.07 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1516 |
1486 |
9.17 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1504 |
1475 |
2.00 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1493 |
1464 |
2.99 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1415 |
1387 |
3.51 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1395 |
1368 |
21.24 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1318 |
1292 |
19.04 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1139 |
1117 |
1.99 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1038 |
1018 |
10.01 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1017 |
997 |
14.48 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
914 |
896 |
51.18 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
777 |
762 |
319.52 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
593 |
581 |
102.96 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
363 |
356 |
0.62 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
337 |
330 |
7.44 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
149 |
146 |
0.32 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
3067 |
3007 |
83.11 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
3044 |
2984 |
9.62 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
3022 |
2963 |
10.14 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
1505 |
1475 |
6.76 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
1309 |
1283 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
1253 |
1229 |
0.09 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
1167 |
1144 |
0.45 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
888 |
870 |
1.33 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
755 |
740 |
2.27 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
236 |
231 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
209 |
204 |
0.94 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
93 |
91 |
1.17 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
79i |
78i |
0.12 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22605.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9804) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22162.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-1.882 |
2.274 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
-1.512 |
0.784 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
0.000 |
0.581 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
0.252 |
-0.847 |
0.000 |
| N5 |
1.698 |
-1.091 |
0.000 |
| O6 |
1.920 |
-2.255 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
-2.973 |
2.405 |
0.000 |
| H8 |
-1.483 |
2.785 |
0.889 |
| H9 |
-1.483 |
2.785 |
-0.889 |
| H10 |
-1.938 |
0.285 |
-0.884 |
| H11 |
-1.938 |
0.285 |
0.884 |
| H12 |
0.460 |
1.034 |
0.893 |
| H13 |
0.460 |
1.034 |
-0.893 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
N5 |
O6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
| C1 | | 1.5353 | 2.5318 | 3.7810 | 4.9141 | 5.9133 | 1.0987 | 1.1006 | 1.1006 | 2.1772 | 2.1772 | 2.7966 | 2.7966 |
C2 | 1.5353 | | 1.5259 | 2.4027 | 3.7183 | 4.5841 | 2.1819 | 2.1897 | 2.1897 | 1.1007 | 1.1007 | 2.1789 | 2.1789 | C3 | 2.5318 | 1.5259 | | 1.4497 | 2.3835 | 3.4244 | 3.4880 | 2.8012 | 2.8012 | 2.1507 | 2.1507 | 1.1015 | 1.1015 | O4 | 3.7810 | 2.4027 | 1.4497 | | 1.4666 | 2.1826 | 4.5798 | 4.1218 | 4.1218 | 2.6193 | 2.6193 | 2.0917 | 2.0917 | N5 | 4.9141 | 3.7183 | 2.3835 | 1.4666 | | 1.1842 | 5.8349 | 5.0927 | 5.0927 | 3.9876 | 3.9876 | 2.6167 | 2.6167 | O6 | 5.9133 | 4.5841 | 3.4244 | 2.1826 | 1.1842 | | 6.7566 | 6.1454 | 6.1454 | 4.7029 | 4.7029 | 3.7071 | 3.7071 | H7 | 1.0987 | 2.1819 | 3.4880 | 4.5798 | 5.8349 | 6.7566 | | 1.7769 | 1.7769 | 2.5188 | 2.5188 | 3.8028 | 3.8028 | H8 | 1.1006 | 2.1897 | 2.8012 | 4.1218 | 5.0927 | 6.1454 | 1.7769 | | 1.7782 | 3.0984 | 2.5411 | 2.6153 | 3.1647 | H9 | 1.1006 | 2.1897 | 2.8012 | 4.1218 | 5.0927 | 6.1454 | 1.7769 | 1.7782 | | 2.5411 | 3.0984 | 3.1647 | 2.6153 | H10 | 2.1772 | 1.1007 | 2.1507 | 2.6193 | 3.9876 | 4.7029 | 2.5188 | 3.0984 | 2.5411 | | 1.7676 | 3.0767 | 2.5119 | H11 | 2.1772 | 1.1007 | 2.1507 | 2.6193 | 3.9876 | 4.7029 | 2.5188 | 2.5411 | 3.0984 | 1.7676 | | 2.5119 | 3.0767 | H12 | 2.7966 | 2.1789 | 1.1015 | 2.0917 | 2.6167 | 3.7071 | 3.8028 | 2.6153 | 3.1647 | 3.0767 | 2.5119 | | 1.7858 | H13 | 2.7966 | 2.1789 | 1.1015 | 2.0917 | 2.6167 | 3.7071 | 3.8028 | 3.1647 | 2.6153 | 2.5119 | 3.0767 | 1.7858 | |
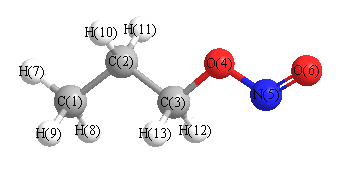 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
111.674 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H10 |
110.249 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H11 |
110.249 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.739 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H8 |
111.328 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H9 |
111.328 |
| C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
107.976 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H12 |
111.061 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H13 |
111.061 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H10 |
108.845 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H11 |
108.845 |
|
C3 |
O4 |
N5 |
111.897 |
| O4 |
C3 |
H12 |
109.234 |
|
O4 |
C3 |
H13 |
109.234 |
| O4 |
N5 |
O6 |
112.590 |
|
H7 |
C1 |
H8 |
107.740 |
| H7 |
C1 |
H9 |
107.740 |
|
H8 |
C1 |
H9 |
107.801 |
| H10 |
C2 |
H11 |
106.842 |
|
H12 |
C3 |
H13 |
108.245 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.466 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.286 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.032 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.361 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
N |
0.262 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
O |
-0.214 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.161 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.154 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.154 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.161 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.161 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.153 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.153 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.188 |
2.273 |
0.000 |
2.565 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-36.886 |
1.137 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.137 |
-38.581 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-34.460 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.365 |
1.137 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.137 |
-2.907 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.273 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 6.545 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 1.695 |
|---|
| xy | 1.137 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.323 |
-2.434 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.434 |
8.608 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.532 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
249.044 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
15.781 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -323.456298 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -323.465136 |
| HF Energy | -323.456298 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3081 |
3021 |
34.80 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3068 |
3008 |
47.64 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3047 |
2987 |
34.85 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3028 |
2968 |
19.09 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
2995 |
2937 |
20.35 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2988 |
2930 |
51.83 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2984 |
2925 |
15.31 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1738 |
1704 |
271.49 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1510 |
1480 |
6.76 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1502 |
1472 |
5.73 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1481 |
1452 |
0.25 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1477 |
1448 |
3.68 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1413 |
1385 |
5.66 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1381 |
1353 |
15.23 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1366 |
1339 |
7.12 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1290 |
1265 |
1.81 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1274 |
1249 |
6.02 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1168 |
1145 |
3.26 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1099 |
1077 |
4.07 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1051 |
1031 |
13.85 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
977 |
958 |
11.72 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
917 |
899 |
30.24 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
859 |
842 |
4.11 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
797 |
781 |
121.70 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
742 |
728 |
155.47 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
546 |
536 |
60.25 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
427 |
418 |
30.99 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
364 |
357 |
1.83 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
282 |
277 |
1.84 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
244 |
239 |
0.96 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
185 |
181 |
0.29 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
99 |
97 |
0.81 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
68 |
67 |
0.07 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22722.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9804) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22276.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.747 |
1.196 |
0.049 |
| C2 |
1.792 |
-0.317 |
-0.194 |
| C3 |
0.541 |
-1.045 |
0.303 |
| O4 |
-0.625 |
-0.629 |
-0.440 |
| N5 |
-1.514 |
0.166 |
0.431 |
| O6 |
-2.457 |
0.546 |
-0.171 |
| H7 |
2.670 |
1.678 |
-0.302 |
| H8 |
1.631 |
1.423 |
1.120 |
| H9 |
0.903 |
1.654 |
-0.485 |
| H10 |
1.923 |
-0.526 |
-1.267 |
| H11 |
2.659 |
-0.761 |
0.323 |
| H12 |
0.627 |
-2.132 |
0.157 |
| H13 |
0.362 |
-0.843 |
1.371 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
N5 |
O6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
| C1 | | 1.5332 | 2.5580 | 3.0320 | 3.4410 | 4.2596 | 1.0991 | 1.1007 | 1.0986 | 2.1749 | 2.1766 | 3.5138 | 2.7976 |
C2 | 1.5332 | | 1.5305 | 2.4492 | 3.3991 | 4.3362 | 2.1825 | 2.1861 | 2.1821 | 1.1012 | 1.1029 | 2.1857 | 2.1846 | C3 | 2.5580 | 1.5305 | | 1.4437 | 2.3890 | 3.4277 | 3.5096 | 2.8195 | 2.8356 | 2.1549 | 2.1372 | 1.0999 | 1.1021 | O4 | 3.0320 | 2.4492 | 1.4437 | | 1.4763 | 2.1934 | 4.0246 | 3.4249 | 2.7473 | 2.6809 | 3.3740 | 2.0452 | 2.0732 | N5 | 3.4410 | 3.3991 | 2.3890 | 1.4763 | | 1.1818 | 4.5091 | 3.4566 | 2.9825 | 3.8957 | 4.2762 | 3.1526 | 2.3283 | O6 | 4.2596 | 4.3362 | 3.4277 | 2.1934 | 1.1818 | | 5.2525 | 4.3760 | 3.5519 | 4.6412 | 5.3038 | 4.0980 | 3.5009 | H7 | 1.0991 | 2.1825 | 3.5096 | 4.0246 | 4.5091 | 5.2525 | | 1.7793 | 1.7769 | 2.5199 | 2.5178 | 4.3483 | 3.8061 | H8 | 1.1007 | 2.1861 | 2.8195 | 3.4249 | 3.4566 | 4.3760 | 1.7793 | | 1.7771 | 3.0955 | 2.5415 | 3.8180 | 2.6098 | H9 | 1.0986 | 2.1821 | 2.8356 | 2.7473 | 2.9825 | 3.5519 | 1.7769 | 1.7771 | | 2.5317 | 3.0936 | 3.8507 | 3.1584 | H10 | 2.1749 | 1.1012 | 2.1549 | 2.6809 | 3.8957 | 4.6412 | 2.5199 | 3.0955 | 2.5317 | | 1.7681 | 2.5075 | 3.0820 | H11 | 2.1766 | 1.1029 | 2.1372 | 3.3740 | 4.2762 | 5.3038 | 2.5178 | 2.5415 | 3.0936 | 1.7681 | | 2.4579 | 2.5264 | H12 | 3.5138 | 2.1857 | 1.0999 | 2.0452 | 3.1526 | 4.0980 | 4.3483 | 3.8180 | 3.8507 | 2.5075 | 2.4579 | | 1.7906 | H13 | 2.7976 | 2.1846 | 1.1021 | 2.0732 | 2.3283 | 3.5009 | 3.8061 | 2.6098 | 3.1584 | 3.0820 | 2.5264 | 1.7906 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
113.219 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H10 |
110.220 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H11 |
110.315 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.913 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H8 |
111.157 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H9 |
110.934 |
| C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
110.368 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H12 |
111.427 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H13 |
111.355 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H10 |
108.859 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H11 |
107.334 |
|
C3 |
O4 |
N5 |
110.720 |
| O4 |
C3 |
H12 |
106.582 |
|
O4 |
C3 |
H13 |
108.017 |
| O4 |
N5 |
O6 |
111.274 |
|
H7 |
C1 |
H8 |
107.943 |
| H7 |
C1 |
H9 |
107.933 |
|
H8 |
C1 |
H9 |
107.820 |
| H10 |
C2 |
H11 |
106.642 |
|
H12 |
C3 |
H13 |
108.917 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.462 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.276 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.056 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.342 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
N |
0.255 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
O |
-0.209 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.155 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.151 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.165 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.159 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.146 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.159 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.154 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.102 |
-0.655 |
0.712 |
2.314 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-37.446 |
0.102 |
-0.643 |
| y |
0.102 |
-34.609 |
-0.913 |
| z |
-0.643 |
-0.913 |
-36.364 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.959 |
0.102 |
-0.643 |
| y |
0.102 |
2.296 |
-0.913 |
| z |
-0.643 |
-0.913 |
-0.337 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.673 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.837 |
|---|
| xy | 0.102 |
|---|
| xz | -0.643 |
|---|
| yz | -0.913 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.481 |
-1.280 |
-0.014 |
| y |
-1.280 |
6.828 |
0.015 |
| z |
-0.014 |
0.015 |
5.853 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
195.525 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.983 |
