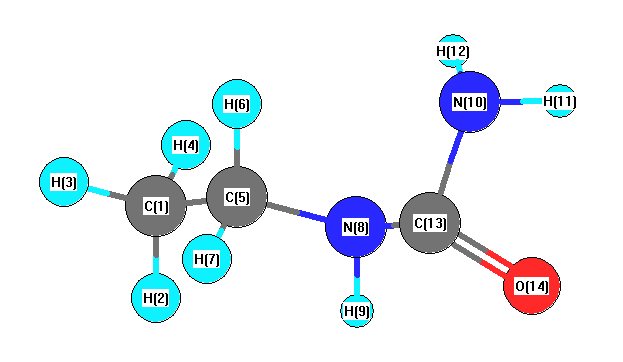
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3607 |
3537 |
19.17 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3539 |
3469 |
16.69 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3487 |
3418 |
7.16 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3085 |
3025 |
29.23 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3070 |
3010 |
39.24 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2997 |
2938 |
25.99 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2977 |
2918 |
42.12 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2951 |
2893 |
47.76 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1778 |
1743 |
388.21 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1628 |
1596 |
122.83 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1526 |
1497 |
2.55 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1505 |
1476 |
5.42 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1497 |
1468 |
6.10 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1446 |
1417 |
8.45 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1413 |
1386 |
3.83 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1401 |
1373 |
247.41 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1349 |
1323 |
42.35 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1290 |
1264 |
5.58 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1178 |
1155 |
15.78 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1151 |
1128 |
1.60 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1116 |
1094 |
44.99 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1049 |
1029 |
13.56 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
973 |
954 |
1.39 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
885 |
867 |
1.04 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
817 |
801 |
1.02 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
751 |
737 |
75.34 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
605 |
593 |
39.70 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
586 |
575 |
159.70 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
542 |
531 |
29.63 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
490 |
481 |
48.25 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
399 |
391 |
72.78 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
358 |
351 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
272 |
267 |
2.49 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
194 |
191 |
2.17 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
114 |
112 |
7.70 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
46 |
45 |
0.13 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 26034.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9804) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25523.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.486 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.161 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.164 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.168 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.123 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.143 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.162 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
N |
-0.586 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.329 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
N |
-0.739 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.336 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.320 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
C |
0.659 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
O |
-0.508 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-2.927 |
2.466 |
-0.655 |
3.883 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-37.521 |
6.629 |
-1.891 |
| y |
6.629 |
-34.582 |
-2.046 |
| z |
-1.891 |
-2.046 |
-37.514 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.473 |
6.629 |
-1.891 |
| y |
6.629 |
2.936 |
-2.046 |
| z |
-1.891 |
-2.046 |
-1.463 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -2.926 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.939 |
|---|
| xy | 6.629 |
|---|
| xz | -1.891 |
|---|
| yz | -2.046 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.372 |
-0.145 |
0.170 |
| y |
-0.145 |
7.647 |
-0.127 |
| z |
0.170 |
-0.127 |
4.983 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
204.050 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.285 |