Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -232.324727 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -232.324727 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3114 |
3053 |
15.23 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3082 |
3021 |
28.01 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3008 |
2949 |
27.49 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
2990 |
2932 |
11.64 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
2966 |
2907 |
20.20 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1761 |
1727 |
121.95 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1501 |
1472 |
7.04 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1468 |
1439 |
16.10 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1451 |
1422 |
4.31 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1408 |
1381 |
4.78 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1375 |
1348 |
33.70 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1354 |
1328 |
15.08 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1170 |
1147 |
81.72 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1096 |
1074 |
1.41 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
991 |
971 |
2.65 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
923 |
905 |
14.66 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
744 |
729 |
3.43 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
575 |
563 |
6.22 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
397 |
390 |
3.82 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
246 |
241 |
4.85 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
3090 |
3029 |
28.80 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
3053 |
2993 |
15.68 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
2996 |
2938 |
13.39 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
1497 |
1468 |
5.68 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
1478 |
1449 |
9.54 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
1271 |
1246 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
1116 |
1094 |
0.32 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
939 |
921 |
4.29 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
744 |
730 |
3.10 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
461 |
451 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
202 |
198 |
0.18 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
100 |
98 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
57i |
56i |
0.11 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24252.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9804) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 23777.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.071 |
1.644 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.556 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
0.509 |
-0.887 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
-0.606 |
-1.933 |
0.000 |
| O5 |
-1.193 |
0.826 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
0.601 |
2.634 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
1.720 |
1.543 |
0.884 |
| H8 |
1.720 |
1.543 |
-0.884 |
| H9 |
-0.187 |
-2.949 |
0.000 |
| H10 |
-1.247 |
-1.819 |
0.884 |
| H11 |
-1.247 |
-1.819 |
-0.884 |
| H12 |
1.172 |
-1.010 |
-0.875 |
| H13 |
1.172 |
-1.010 |
0.875 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
| C1 | | 1.5260 | 2.5921 | 3.9503 | 2.4070 | 1.0958 | 1.1015 | 1.1015 | 4.7616 | 4.2596 | 4.2596 | 2.7958 | 2.7958 |
C2 | 1.5260 | | 1.5305 | 2.5621 | 1.2230 | 2.1623 | 2.1710 | 2.1710 | 3.5103 | 2.8248 | 2.8248 | 2.1429 | 2.1429 | C3 | 2.5921 | 1.5305 | | 1.5292 | 2.4144 | 3.5216 | 2.8551 | 2.8551 | 2.1763 | 2.1760 | 2.1760 | 1.1047 | 1.1047 | C4 | 3.9503 | 2.5621 | 1.5292 | | 2.8201 | 4.7234 | 4.2749 | 4.2749 | 1.0991 | 1.0980 | 1.0980 | 2.1864 | 2.1864 | O5 | 2.4070 | 1.2230 | 2.4144 | 2.8201 | | 2.5470 | 3.1276 | 3.1276 | 3.9061 | 2.7889 | 2.7889 | 3.1187 | 3.1187 | H6 | 1.0958 | 2.1623 | 3.5216 | 4.7234 | 2.5470 | | 1.7955 | 1.7955 | 5.6378 | 4.9012 | 4.9012 | 3.7901 | 3.7901 | H7 | 1.1015 | 2.1710 | 2.8551 | 4.2749 | 3.1276 | 1.7955 | | 1.7680 | 4.9592 | 4.4840 | 4.8201 | 3.1481 | 2.6107 | H8 | 1.1015 | 2.1710 | 2.8551 | 4.2749 | 3.1276 | 1.7955 | 1.7680 | | 4.9592 | 4.8201 | 4.4840 | 2.6107 | 3.1481 | H9 | 4.7616 | 3.5103 | 2.1763 | 1.0991 | 3.9061 | 5.6378 | 4.9592 | 4.9592 | | 1.7840 | 1.7840 | 2.5245 | 2.5245 | H10 | 4.2596 | 2.8248 | 2.1760 | 1.0980 | 2.7889 | 4.9012 | 4.4840 | 4.8201 | 1.7840 | | 1.7686 | 3.0988 | 2.5508 | H11 | 4.2596 | 2.8248 | 2.1760 | 1.0980 | 2.7889 | 4.9012 | 4.8201 | 4.4840 | 1.7840 | 1.7686 | | 2.5508 | 3.0988 | H12 | 2.7958 | 2.1429 | 1.1047 | 2.1864 | 3.1187 | 3.7901 | 3.1481 | 2.6107 | 2.5245 | 3.0988 | 2.5508 | | 1.7505 | H13 | 2.7958 | 2.1429 | 1.1047 | 2.1864 | 3.1187 | 3.7901 | 2.6107 | 3.1481 | 2.5245 | 2.5508 | 3.0988 | 1.7505 | |
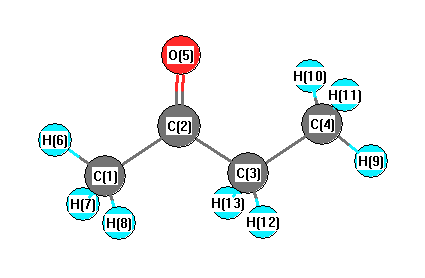 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
115.656 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
O5 |
122.015 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.830 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.564 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H8 |
110.564 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
113.688 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H12 |
107.892 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H13 |
107.892 |
| C3 |
C2 |
O5 |
122.329 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H9 |
110.637 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H10 |
110.843 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H11 |
110.843 |
| C4 |
C3 |
H12 |
110.997 |
|
C4 |
C3 |
H13 |
110.997 |
| H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.522 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H8 |
109.522 |
| H7 |
C1 |
H8 |
106.784 |
|
H9 |
C4 |
H10 |
108.514 |
| H9 |
C4 |
H11 |
108.514 |
|
H10 |
C4 |
H11 |
107.384 |
| H12 |
C3 |
H13 |
104.934 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.540 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.441 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.357 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.446 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.419 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.183 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.170 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.170 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.144 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.166 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.166 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.161 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.161 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.563 |
-0.623 |
0.000 |
2.637 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-33.307 |
2.256 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.256 |
-30.873 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-30.154 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.794 |
2.256 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.256 |
0.858 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.936 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.873 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.434 |
|---|
| xy | 2.256 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.270 |
0.272 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.272 |
7.549 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.415 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
138.198 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
11.756 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -232.324746 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -232.324746 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3114 |
3053 |
15.17 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3091 |
3030 |
28.63 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3083 |
3022 |
27.88 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3053 |
2993 |
15.74 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3009 |
2950 |
27.61 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2996 |
2937 |
13.47 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2991 |
2932 |
11.47 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2965 |
2907 |
20.18 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1761 |
1726 |
121.88 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1501 |
1472 |
7.10 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1496 |
1467 |
5.72 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1478 |
1449 |
9.51 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1468 |
1440 |
16.68 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1452 |
1424 |
3.52 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1411 |
1383 |
4.77 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1378 |
1351 |
33.47 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1356 |
1330 |
15.67 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1275 |
1250 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1171 |
1148 |
81.43 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1117 |
1095 |
0.31 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1095 |
1074 |
1.51 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
991 |
972 |
2.65 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
942 |
923 |
4.33 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
924 |
906 |
14.76 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
748 |
733 |
3.03 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
745 |
730 |
3.41 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
575 |
564 |
6.28 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
462 |
453 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
397 |
390 |
3.80 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
246 |
241 |
4.92 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
197 |
193 |
0.17 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
99 |
97 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
35i |
34i |
0.13 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24275.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9804) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 23799.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-1.895 |
-0.507 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
-0.529 |
0.172 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
0.685 |
-0.759 |
-0.000 |
| C4 |
2.025 |
-0.023 |
0.000 |
| O5 |
-0.414 |
1.390 |
-0.000 |
| H6 |
-2.689 |
0.247 |
-0.000 |
| H7 |
-2.002 |
-1.156 |
-0.883 |
| H8 |
-2.002 |
-1.155 |
0.884 |
| H9 |
2.861 |
-0.737 |
-0.000 |
| H10 |
2.116 |
0.622 |
-0.884 |
| H11 |
2.116 |
0.621 |
0.884 |
| H12 |
0.597 |
-1.428 |
0.875 |
| H13 |
0.597 |
-1.428 |
-0.875 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
| C1 | | 1.5257 | 2.5921 | 3.9499 | 2.4067 | 1.0957 | 1.1015 | 1.1015 | 4.7611 | 4.2591 | 4.2591 | 2.7966 | 2.7967 |
C2 | 1.5257 | | 1.5300 | 2.5615 | 1.2229 | 2.1617 | 2.1713 | 2.1712 | 3.5093 | 2.8243 | 2.8243 | 2.1430 | 2.1430 | C3 | 2.5921 | 1.5300 | | 1.5291 | 2.4136 | 3.5212 | 2.8558 | 2.8562 | 2.1758 | 2.1760 | 2.1760 | 1.1048 | 1.1048 | C4 | 3.9499 | 2.5615 | 1.5291 | | 2.8187 | 4.7222 | 4.2755 | 4.2757 | 1.0990 | 1.0980 | 1.0980 | 2.1862 | 2.1862 | O5 | 2.4067 | 1.2229 | 2.4136 | 2.8187 | | 2.5460 | 3.1279 | 3.1276 | 3.9046 | 2.7874 | 2.7877 | 3.1186 | 3.1185 | H6 | 1.0957 | 2.1617 | 3.5212 | 4.7222 | 2.5460 | | 1.7954 | 1.7954 | 5.6365 | 4.8997 | 4.8999 | 3.7909 | 3.7907 | H7 | 1.1015 | 2.1713 | 2.8558 | 4.2755 | 3.1279 | 1.7954 | | 1.7676 | 4.9595 | 4.4846 | 4.8204 | 3.1492 | 2.6125 | H8 | 1.1015 | 2.1712 | 2.8562 | 4.2757 | 3.1276 | 1.7954 | 1.7676 | | 4.9599 | 4.8206 | 4.4844 | 2.6128 | 3.1500 | H9 | 4.7611 | 3.5093 | 2.1758 | 1.0990 | 3.9046 | 5.6365 | 4.9595 | 4.9599 | | 1.7841 | 1.7841 | 2.5235 | 2.5234 | H10 | 4.2591 | 2.8243 | 2.1760 | 1.0980 | 2.7874 | 4.8997 | 4.4846 | 4.8206 | 1.7841 | | 1.7687 | 3.0986 | 2.5507 | H11 | 4.2591 | 2.8243 | 2.1760 | 1.0980 | 2.7877 | 4.8999 | 4.8204 | 4.4844 | 1.7841 | 1.7687 | | 2.5506 | 3.0986 | H12 | 2.7966 | 2.1430 | 1.1048 | 2.1862 | 3.1186 | 3.7909 | 3.1492 | 2.6128 | 2.5235 | 3.0986 | 2.5506 | | 1.7503 | H13 | 2.7967 | 2.1430 | 1.1048 | 2.1862 | 3.1185 | 3.7907 | 2.6125 | 3.1500 | 2.5234 | 2.5507 | 3.0986 | 1.7503 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
116.380 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
O5 |
121.601 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
110.067 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.417 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H8 |
110.413 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
113.979 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H12 |
107.720 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H13 |
107.720 |
| C3 |
C2 |
O5 |
122.018 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H9 |
110.849 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H10 |
110.792 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H11 |
110.792 |
| C4 |
C3 |
H12 |
111.101 |
|
C4 |
C3 |
H13 |
111.102 |
| H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.554 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H8 |
109.550 |
| H7 |
C1 |
H8 |
106.779 |
|
H9 |
C4 |
H10 |
108.524 |
| H9 |
C4 |
H11 |
108.524 |
|
H10 |
C4 |
H11 |
107.244 |
| H12 |
C3 |
H13 |
104.726 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.540 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.441 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.358 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.446 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.419 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.183 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.170 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.170 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.144 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.166 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.166 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.161 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.161 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.205 |
-2.630 |
0.000 |
2.637 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-29.776 |
1.102 |
-0.000 |
| y |
1.102 |
-34.399 |
0.001 |
| z |
-0.000 |
0.001 |
-30.154 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.500 |
1.102 |
-0.000 |
| y |
1.102 |
-4.434 |
0.001 |
| z |
-0.000 |
0.001 |
1.934 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.867 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 4.623 |
|---|
| xy | 1.102 |
|---|
| xz | -0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.001 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.679 |
0.138 |
-0.000 |
| y |
0.138 |
7.136 |
-0.000 |
| z |
-0.000 |
-0.000 |
5.414 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
138.166 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
11.754 |
