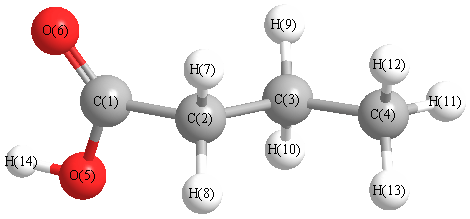Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3675 |
3627 |
40.27 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3060 |
3020 |
32.68 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3043 |
3004 |
37.69 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3038 |
2999 |
30.67 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3008 |
2969 |
1.40 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3001 |
2962 |
21.93 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2977 |
2939 |
15.08 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2970 |
2931 |
27.96 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1763 |
1740 |
318.61 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1482 |
1462 |
7.50 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1471 |
1452 |
6.91 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1468 |
1449 |
1.62 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1455 |
1436 |
3.82 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1384 |
1366 |
0.95 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1344 |
1326 |
16.27 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1329 |
1312 |
38.92 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1296 |
1279 |
4.45 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1267 |
1250 |
1.34 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1233 |
1217 |
12.71 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1164 |
1148 |
127.46 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1085 |
1071 |
7.52 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1040 |
1027 |
139.44 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1018 |
1005 |
2.27 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
893 |
882 |
1.56 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
875 |
864 |
4.06 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
853 |
842 |
12.46 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
741 |
732 |
2.03 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
728 |
719 |
32.10 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
614 |
606 |
64.05 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
570 |
563 |
45.95 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
424 |
418 |
3.37 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
326 |
321 |
0.88 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
239 |
236 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
182 |
180 |
0.09 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
82 |
81 |
0.41 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
21 |
21 |
0.95 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25559.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.987) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25227.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.900 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.204 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.196 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.435 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.502 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
O |
-0.735 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.144 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.145 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.141 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.137 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.118 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.128 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.126 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.233 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.201 |
-1.396 |
0.146 |
1.847 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-35.555 |
4.587 |
0.508 |
| y |
4.587 |
-40.832 |
1.216 |
| z |
0.508 |
1.216 |
-36.230 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.976 |
4.587 |
0.508 |
| y |
4.587 |
-4.940 |
1.216 |
| z |
0.508 |
1.216 |
1.964 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.928 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.277 |
|---|
| xy | 4.587 |
|---|
| xz | 0.508 |
|---|
| yz | 1.216 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
10.843 |
-0.019 |
0.345 |
| y |
-0.019 |
8.604 |
-0.017 |
| z |
0.345 |
-0.017 |
7.555 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
209.575 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.477 |