Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -323.573930 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -323.573930 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 232.280583 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3050 |
3010 |
33.82 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
2983 |
2944 |
45.29 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
2973 |
2934 |
26.05 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
2964 |
2925 |
18.07 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1712 |
1690 |
298.58 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1488 |
1469 |
12.08 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1475 |
1456 |
1.34 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1465 |
1446 |
3.04 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1390 |
1372 |
6.67 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1372 |
1354 |
13.33 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1305 |
1288 |
11.05 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1127 |
1112 |
3.07 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1027 |
1014 |
9.63 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1005 |
992 |
13.20 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
905 |
893 |
47.45 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
753 |
743 |
328.49 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
589 |
582 |
166.68 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
363 |
358 |
1.24 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
334 |
329 |
13.82 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
150 |
148 |
0.49 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
3043 |
3004 |
74.15 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
3021 |
2982 |
6.10 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
3000 |
2961 |
4.38 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
1475 |
1456 |
6.89 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
1294 |
1277 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
1241 |
1225 |
0.21 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
1154 |
1139 |
0.54 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
880 |
869 |
0.82 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
747 |
737 |
1.96 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
230 |
227 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
208 |
205 |
1.04 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
92 |
91 |
1.24 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
65i |
64i |
0.09 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22375.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.987) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22084.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-1.849 |
2.291 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
-1.505 |
0.799 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
0.000 |
0.576 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
0.244 |
-0.851 |
0.000 |
| N5 |
1.680 |
-1.111 |
0.000 |
| O6 |
1.897 |
-2.262 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
-2.932 |
2.441 |
0.000 |
| H8 |
-1.443 |
2.794 |
0.885 |
| H9 |
-1.443 |
2.794 |
-0.885 |
| H10 |
-1.938 |
0.309 |
-0.880 |
| H11 |
-1.938 |
0.309 |
0.880 |
| H12 |
0.463 |
1.019 |
0.891 |
| H13 |
0.463 |
1.019 |
-0.891 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
N5 |
O6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
| C1 | | 1.5319 | 2.5220 | 3.7755 | 4.9021 | 5.8961 | 1.0939 | 1.0957 | 1.0957 | 2.1704 | 2.1704 | 2.7851 | 2.7851 |
C2 | 1.5319 | | 1.5214 | 2.4042 | 3.7137 | 4.5761 | 2.1759 | 2.1835 | 2.1835 | 1.0961 | 1.0961 | 2.1713 | 2.1713 | C3 | 2.5220 | 1.5214 | | 1.4477 | 2.3810 | 3.4135 | 3.4751 | 2.7897 | 2.7897 | 2.1453 | 2.1453 | 1.0970 | 1.0970 | O4 | 3.7755 | 2.4042 | 1.4477 | | 1.4592 | 2.1734 | 4.5744 | 4.1123 | 4.1123 | 2.6236 | 2.6236 | 2.0825 | 2.0825 | N5 | 4.9021 | 3.7137 | 2.3810 | 1.4592 | | 1.1706 | 5.8216 | 5.0776 | 5.0776 | 3.9854 | 3.9854 | 2.6099 | 2.6099 | O6 | 5.8961 | 4.5761 | 3.4135 | 2.1734 | 1.1706 | | 6.7409 | 6.1233 | 6.1233 | 4.7007 | 4.7007 | 3.6894 | 3.6894 | H7 | 1.0939 | 2.1759 | 3.4751 | 4.5744 | 5.8216 | 6.7409 | | 1.7684 | 1.7684 | 2.5111 | 2.5111 | 3.7873 | 3.7873 | H8 | 1.0957 | 2.1835 | 2.7897 | 4.1123 | 5.0776 | 6.1233 | 1.7684 | | 1.7702 | 3.0875 | 2.5332 | 2.6041 | 3.1518 | H9 | 1.0957 | 2.1835 | 2.7897 | 4.1123 | 5.0776 | 6.1233 | 1.7684 | 1.7702 | | 2.5332 | 3.0875 | 3.1518 | 2.6041 | H10 | 2.1704 | 1.0961 | 2.1453 | 2.6236 | 3.9854 | 4.7007 | 2.5111 | 3.0875 | 2.5332 | | 1.7602 | 3.0666 | 2.5038 | H11 | 2.1704 | 1.0961 | 2.1453 | 2.6236 | 3.9854 | 4.7007 | 2.5111 | 2.5332 | 3.0875 | 1.7602 | | 2.5038 | 3.0666 | H12 | 2.7851 | 2.1713 | 1.0970 | 2.0825 | 2.6099 | 3.6894 | 3.7873 | 2.6041 | 3.1518 | 3.0666 | 2.5038 | | 1.7810 | H13 | 2.7851 | 2.1713 | 1.0970 | 2.0825 | 2.6099 | 3.6894 | 3.7873 | 3.1518 | 2.6041 | 2.5038 | 3.0666 | 1.7810 | |
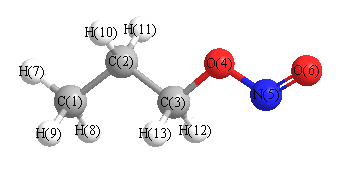 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
111.559 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H10 |
110.235 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H11 |
110.235 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.772 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H8 |
111.341 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H9 |
111.341 |
| C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
108.246 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H12 |
111.045 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H13 |
111.045 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H10 |
108.912 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H11 |
108.912 |
|
C3 |
O4 |
N5 |
112.332 |
| O4 |
C3 |
H12 |
109.031 |
|
O4 |
C3 |
H13 |
109.031 |
| O4 |
N5 |
O6 |
113.780 |
|
H7 |
C1 |
H8 |
107.715 |
| H7 |
C1 |
H9 |
107.715 |
|
H8 |
C1 |
H9 |
107.789 |
| H10 |
C2 |
H11 |
106.857 |
|
H12 |
C3 |
H13 |
108.403 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.426 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.096 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.124 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.486 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
N |
0.267 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
O |
-0.245 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.120 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.132 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.132 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.115 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.115 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.123 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.123 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.199 |
2.305 |
0.000 |
2.599 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-37.699 |
0.944 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.944 |
-39.638 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-35.214 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.272 |
0.944 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.944 |
-3.182 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.454 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 6.908 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 1.939 |
|---|
| xy | 0.944 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
10.013 |
-2.518 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.518 |
10.422 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.838 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
248.479 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
15.763 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -323.576136 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -323.584958 |
| HF Energy | -323.576136 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 239.775610 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3053 |
3013 |
32.65 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3043 |
3004 |
43.81 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3024 |
2985 |
27.50 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3004 |
2965 |
17.11 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
2976 |
2937 |
21.10 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2970 |
2932 |
47.34 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2965 |
2927 |
13.47 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1718 |
1696 |
311.67 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1479 |
1460 |
7.07 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1472 |
1452 |
6.79 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1453 |
1434 |
2.91 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1450 |
1431 |
2.69 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1387 |
1369 |
5.00 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1359 |
1341 |
12.08 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1346 |
1329 |
2.30 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1273 |
1257 |
3.22 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1260 |
1244 |
6.54 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1152 |
1137 |
3.99 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1087 |
1073 |
3.17 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1040 |
1026 |
12.35 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
969 |
956 |
10.37 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
906 |
894 |
28.96 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
848 |
837 |
3.92 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
785 |
775 |
91.11 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
722 |
712 |
197.77 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
540 |
533 |
90.76 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
420 |
415 |
49.13 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
361 |
356 |
0.89 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
282 |
278 |
2.33 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
236 |
233 |
0.72 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
184 |
182 |
0.28 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
99 |
98 |
0.81 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
64 |
63 |
0.12 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22463.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.987) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22171.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.766 |
1.186 |
0.050 |
| C2 |
1.784 |
-0.323 |
-0.203 |
| C3 |
0.536 |
-1.038 |
0.308 |
| O4 |
-0.634 |
-0.630 |
-0.427 |
| N5 |
-1.517 |
0.180 |
0.422 |
| O6 |
-2.455 |
0.546 |
-0.172 |
| H7 |
2.688 |
1.654 |
-0.310 |
| H8 |
1.672 |
1.406 |
1.120 |
| H9 |
0.927 |
1.664 |
-0.464 |
| H10 |
1.897 |
-0.528 |
-1.274 |
| H11 |
2.648 |
-0.781 |
0.296 |
| H12 |
0.617 |
-2.122 |
0.173 |
| H13 |
0.366 |
-0.827 |
1.371 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
N5 |
O6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
| C1 | | 1.5298 | 2.5544 | 3.0473 | 3.4538 | 4.2752 | 1.0944 | 1.0958 | 1.0941 | 2.1704 | 2.1692 | 3.5041 | 2.7851 |
C2 | 1.5298 | | 1.5260 | 2.4476 | 3.3965 | 4.3268 | 2.1760 | 2.1793 | 2.1789 | 1.0967 | 1.0983 | 2.1773 | 2.1777 | C3 | 2.5544 | 1.5260 | | 1.4410 | 2.3897 | 3.4182 | 3.5008 | 2.8146 | 2.8369 | 2.1480 | 2.1276 | 1.0956 | 1.0976 | O4 | 3.0473 | 2.4476 | 1.4410 | | 1.4678 | 2.1821 | 4.0326 | 3.4432 | 2.7746 | 2.6711 | 3.3645 | 2.0383 | 2.0674 | N5 | 3.4538 | 3.3965 | 2.3897 | 1.4678 | | 1.1687 | 4.5150 | 3.4873 | 2.9934 | 3.8771 | 4.2761 | 3.1489 | 2.3368 | O6 | 4.2752 | 4.3268 | 3.4182 | 2.1821 | 1.1687 | | 5.2625 | 4.4094 | 3.5742 | 4.6162 | 5.2933 | 4.0835 | 3.4961 | H7 | 1.0944 | 2.1760 | 3.5008 | 4.0326 | 4.5150 | 5.2625 | | 1.7708 | 1.7673 | 2.5135 | 2.5089 | 4.3333 | 3.7906 | H8 | 1.0958 | 2.1793 | 2.8146 | 3.4432 | 3.4873 | 4.4094 | 1.7708 | | 1.7695 | 3.0858 | 2.5317 | 3.8020 | 2.5988 | H9 | 1.0941 | 2.1789 | 2.8369 | 2.7746 | 2.9934 | 3.5742 | 1.7673 | 1.7695 | | 2.5302 | 3.0846 | 3.8517 | 3.1444 | H10 | 2.1704 | 1.0967 | 2.1480 | 2.6711 | 3.8771 | 4.6162 | 2.5135 | 3.0858 | 2.5302 | | 1.7592 | 2.5046 | 3.0711 | H11 | 2.1692 | 1.0983 | 2.1276 | 3.3645 | 4.2761 | 5.2933 | 2.5089 | 2.5317 | 3.0846 | 1.7592 | | 2.4371 | 2.5229 | H12 | 3.5041 | 2.1773 | 1.0956 | 2.0383 | 3.1489 | 4.0835 | 4.3333 | 3.8020 | 3.8517 | 2.5046 | 2.4371 | | 1.7822 | H13 | 2.7851 | 2.1777 | 1.0976 | 2.0674 | 2.3368 | 3.4961 | 3.7906 | 2.5988 | 3.1444 | 3.0711 | 2.5229 | 1.7822 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
113.373 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H10 |
110.368 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H11 |
110.215 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.879 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H8 |
111.162 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H9 |
111.153 |
| C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
110.609 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H12 |
111.286 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H13 |
111.384 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H10 |
108.929 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H11 |
107.139 |
|
C3 |
O4 |
N5 |
111.303 |
| O4 |
C3 |
H12 |
106.407 |
|
O4 |
C3 |
H13 |
108.115 |
| O4 |
N5 |
O6 |
112.012 |
|
H7 |
C1 |
H8 |
107.877 |
| H7 |
C1 |
H9 |
107.788 |
|
H8 |
C1 |
H9 |
107.830 |
| H10 |
C2 |
H11 |
106.543 |
|
H12 |
C3 |
H13 |
108.860 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.461 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.037 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.068 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.428 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
N |
0.213 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
O |
-0.231 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.117 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.138 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.136 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.126 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.118 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.108 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.133 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.192 |
-0.644 |
0.729 |
2.398 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-38.230 |
0.039 |
-0.717 |
| y |
0.039 |
-35.472 |
-1.010 |
| z |
-0.717 |
-1.010 |
-37.333 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.827 |
0.039 |
-0.717 |
| y |
0.039 |
2.309 |
-1.010 |
| z |
-0.717 |
-1.010 |
-0.482 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.963 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.757 |
|---|
| xy | 0.039 |
|---|
| xz | -0.717 |
|---|
| yz | -1.010 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
11.044 |
-1.131 |
-0.051 |
| y |
-1.131 |
8.457 |
0.064 |
| z |
-0.051 |
0.064 |
7.355 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
196.011 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.000 |
