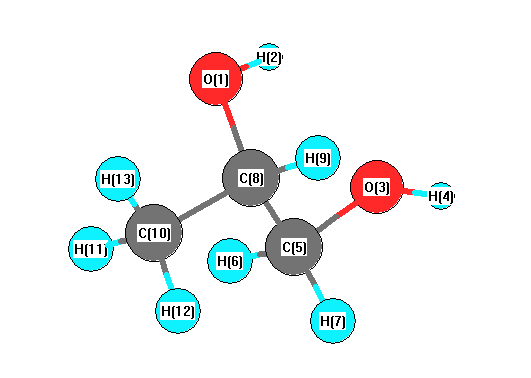
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3752 |
3704 |
19.59 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3703 |
3655 |
38.46 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3061 |
3022 |
22.72 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3051 |
3011 |
38.12 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3030 |
2990 |
19.99 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2981 |
2942 |
24.86 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2946 |
2908 |
50.51 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2858 |
2821 |
75.31 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1474 |
1455 |
2.81 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1461 |
1442 |
5.81 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1455 |
1436 |
1.61 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1397 |
1379 |
23.21 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1381 |
1363 |
27.94 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1364 |
1346 |
12.89 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1343 |
1325 |
2.53 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1317 |
1300 |
27.81 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1262 |
1245 |
41.41 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1196 |
1181 |
14.17 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1131 |
1116 |
21.01 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1066 |
1052 |
13.26 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1042 |
1029 |
34.99 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1001 |
988 |
120.38 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
913 |
901 |
7.15 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
894 |
882 |
17.53 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
822 |
811 |
16.46 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
518 |
511 |
35.82 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
477 |
471 |
60.04 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
462 |
456 |
51.22 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
354 |
349 |
14.15 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
309 |
305 |
64.41 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
241 |
238 |
3.66 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
212 |
209 |
0.30 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
139 |
137 |
3.36 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24304.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.987) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 23988.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
O |
-0.662 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.252 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.626 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.215 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
0.082 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.119 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.115 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
0.388 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.092 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
C |
-0.348 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.132 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.128 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.115 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.318 |
-1.687 |
1.470 |
2.260 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-33.867 |
2.136 |
2.660 |
| y |
2.136 |
-33.011 |
0.200 |
| z |
2.660 |
0.200 |
-30.284 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.220 |
2.136 |
2.660 |
| y |
2.136 |
-0.935 |
0.200 |
| z |
2.660 |
0.200 |
3.155 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 6.310 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.856 |
|---|
| xy | 2.136 |
|---|
| xz | 2.660 |
|---|
| yz | 0.200 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.462 |
0.202 |
0.138 |
| y |
0.202 |
7.595 |
-0.025 |
| z |
0.138 |
-0.025 |
7.031 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
134.327 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
11.590 |