Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -233.610523 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -233.621500 |
| HF Energy | -233.610523 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 184.389329 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3777 |
3728 |
18.48 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3038 |
2998 |
45.64 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
2970 |
2931 |
68.75 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
2966 |
2927 |
21.03 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
2951 |
2913 |
24.71 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
2905 |
2867 |
59.92 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1492 |
1473 |
2.63 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1479 |
1460 |
5.61 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1467 |
1448 |
0.44 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1461 |
1442 |
0.16 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1414 |
1396 |
5.60 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1383 |
1365 |
1.87 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1359 |
1341 |
3.33 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1289 |
1272 |
13.11 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1219 |
1203 |
33.50 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1090 |
1076 |
0.40 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1038 |
1024 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
1015 |
1002 |
104.74 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
973 |
960 |
2.67 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
888 |
877 |
14.73 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
432 |
427 |
13.06 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
390 |
385 |
0.22 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
183 |
181 |
2.20 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
3034 |
2995 |
74.24 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
3011 |
2972 |
38.27 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
2975 |
2936 |
4.57 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
2931 |
2893 |
42.27 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
1472 |
1453 |
6.92 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
1303 |
1286 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
1290 |
1273 |
1.01 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
1222 |
1207 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
1158 |
1143 |
1.04 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
939 |
927 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A" |
800 |
790 |
0.62 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A" |
730 |
720 |
1.97 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A" |
246 |
243 |
72.96 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A" |
239 |
236 |
31.93 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A" |
107 |
105 |
0.74 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A" |
99 |
98 |
5.51 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 29367.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.987) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28985.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.348 |
-0.359 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.346 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
-1.177 |
-0.634 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
-2.535 |
0.074 |
0.000 |
| O5 |
2.383 |
0.634 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.433 |
-1.004 |
0.890 |
| H7 |
1.433 |
-1.004 |
-0.890 |
| H8 |
-0.056 |
0.999 |
0.880 |
| H9 |
-0.056 |
0.999 |
-0.880 |
| H10 |
-1.107 |
-1.290 |
0.878 |
| H11 |
-1.107 |
-1.290 |
-0.878 |
| H12 |
-3.361 |
-0.645 |
0.000 |
| H13 |
-2.646 |
0.712 |
0.884 |
| H14 |
-2.646 |
0.712 |
-0.884 |
| H15 |
3.235 |
0.185 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
H15 |
| C1 | | 1.5213 | 2.5404 | 3.9071 | 1.4339 | 1.1024 | 1.1024 | 2.1429 | 2.1429 | 2.7686 | 2.7686 | 4.7183 | 4.2284 | 4.2284 | 1.9637 |
C2 | 1.5213 | | 1.5315 | 2.5494 | 2.4000 | 2.1602 | 2.1602 | 1.0976 | 1.0976 | 2.1616 | 2.1616 | 3.5042 | 2.8134 | 2.8134 | 3.2391 | C3 | 2.5404 | 1.5315 | | 1.5311 | 3.7789 | 2.7821 | 2.7821 | 2.1673 | 2.1673 | 1.0986 | 1.0986 | 2.1843 | 2.1793 | 2.1793 | 4.4877 | C4 | 3.9071 | 2.5494 | 1.5311 | | 4.9493 | 4.2065 | 4.2065 | 2.7880 | 2.7880 | 2.1614 | 2.1614 | 1.0951 | 1.0960 | 1.0960 | 5.7710 | O5 | 1.4339 | 2.4000 | 3.7789 | 4.9493 | | 2.0925 | 2.0925 | 2.6186 | 2.6186 | 4.0804 | 4.0804 | 5.8846 | 5.1059 | 5.1059 | 0.9635 | H6 | 1.1024 | 2.1602 | 2.7821 | 4.2065 | 2.0925 | | 1.7794 | 2.4963 | 3.0600 | 2.5554 | 3.1074 | 4.8892 | 4.4247 | 4.7670 | 2.3357 | H7 | 1.1024 | 2.1602 | 2.7821 | 4.2065 | 2.0925 | 1.7794 | | 3.0600 | 2.4963 | 3.1074 | 2.5554 | 4.8892 | 4.7670 | 4.4247 | 2.3357 | H8 | 2.1429 | 1.0976 | 2.1673 | 2.7880 | 2.6186 | 2.4963 | 3.0600 | | 1.7602 | 2.5187 | 3.0718 | 3.7946 | 2.6050 | 3.1462 | 3.5031 | H9 | 2.1429 | 1.0976 | 2.1673 | 2.7880 | 2.6186 | 3.0600 | 2.4963 | 1.7602 | | 3.0718 | 2.5187 | 3.7946 | 3.1462 | 2.6050 | 3.5031 | H10 | 2.7686 | 2.1616 | 1.0986 | 2.1614 | 4.0804 | 2.5554 | 3.1074 | 2.5187 | 3.0718 | | 1.7565 | 2.5044 | 2.5253 | 3.0795 | 4.6690 | H11 | 2.7686 | 2.1616 | 1.0986 | 2.1614 | 4.0804 | 3.1074 | 2.5554 | 3.0718 | 2.5187 | 1.7565 | | 2.5044 | 3.0795 | 2.5253 | 4.6690 | H12 | 4.7183 | 3.5042 | 2.1843 | 1.0951 | 5.8846 | 4.8892 | 4.8892 | 3.7946 | 3.7946 | 2.5044 | 2.5044 | | 1.7704 | 1.7704 | 6.6485 | H13 | 4.2284 | 2.8134 | 2.1793 | 1.0960 | 5.1059 | 4.4247 | 4.7670 | 2.6050 | 3.1462 | 2.5253 | 3.0795 | 1.7704 | | 1.7681 | 5.9701 | H14 | 4.2284 | 2.8134 | 2.1793 | 1.0960 | 5.1059 | 4.7670 | 4.4247 | 3.1462 | 2.6050 | 3.0795 | 2.5253 | 1.7704 | 1.7681 | | 5.9701 | H15 | 1.9637 | 3.2391 | 4.4877 | 5.7710 | 0.9635 | 2.3357 | 2.3357 | 3.5031 | 3.5031 | 4.6690 | 4.6690 | 6.6485 | 5.9701 | 5.9701 | |
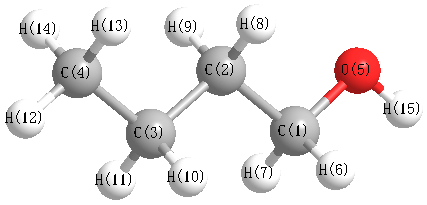 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
112.690 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
108.703 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H9 |
108.703 |
|
C1 |
O5 |
H15 |
108.437 |
| C2 |
C1 |
O5 |
108.382 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.830 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.830 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
112.678 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.446 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
109.446 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.959 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H9 |
109.959 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H12 |
111.389 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H13 |
111.059 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H14 |
111.059 |
|
C4 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.440 |
| C4 |
C3 |
H11 |
109.440 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
110.572 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.572 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.655 |
| H8 |
C2 |
H9 |
106.631 |
|
H10 |
C3 |
H11 |
106.181 |
| H12 |
C4 |
H13 |
107.803 |
|
H12 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.803 |
| H13 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.557 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.019 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.114 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.166 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.432 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.588 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.111 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.111 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.122 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.122 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.125 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.125 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.114 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.125 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.125 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.203 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.079 |
-1.530 |
0.000 |
1.532 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-30.604 |
-3.646 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.646 |
-35.327 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-33.552 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
3.836 |
-3.646 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.646 |
-3.249 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.586 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.172 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 4.723 |
|---|
| xy | -3.646 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
10.467 |
0.091 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.091 |
8.269 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
7.629 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
188.421 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.727 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -233.610642 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -233.621731 |
| HF Energy | -233.610642 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 187.164460 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3779 |
3730 |
21.76 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3036 |
2996 |
52.40 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3033 |
2994 |
73.74 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3010 |
2971 |
2.01 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
2992 |
2953 |
31.42 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2965 |
2926 |
64.66 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2961 |
2922 |
46.97 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2954 |
2916 |
10.87 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
2936 |
2898 |
38.46 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
2907 |
2869 |
70.93 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1485 |
1466 |
4.31 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1481 |
1462 |
5.02 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1473 |
1454 |
6.91 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1467 |
1448 |
1.15 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1446 |
1427 |
3.05 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1409 |
1391 |
6.45 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1386 |
1368 |
1.60 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1367 |
1349 |
0.56 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1312 |
1295 |
2.23 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1304 |
1287 |
3.95 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1275 |
1259 |
21.80 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1228 |
1213 |
3.08 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1211 |
1195 |
21.12 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1133 |
1118 |
2.76 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1095 |
1081 |
1.23 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
1045 |
1031 |
44.36 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
1008 |
995 |
36.10 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
958 |
946 |
5.07 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
941 |
929 |
9.93 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
835 |
824 |
11.90 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
818 |
808 |
1.33 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
731 |
721 |
0.93 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
500 |
494 |
9.77 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
341 |
336 |
2.52 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
271 |
268 |
27.40 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
241 |
238 |
5.16 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
221 |
218 |
73.12 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
137 |
135 |
6.74 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
86 |
85 |
0.74 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 29387.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.987) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 29005.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.437 |
0.522 |
0.235 |
| C2 |
-0.001 |
0.690 |
-0.231 |
| C3 |
-0.969 |
-0.343 |
0.355 |
| C4 |
-2.407 |
-0.146 |
-0.133 |
| O5 |
1.940 |
-0.727 |
-0.262 |
| H6 |
2.052 |
1.356 |
-0.139 |
| H7 |
1.478 |
0.540 |
1.337 |
| H8 |
-0.330 |
1.702 |
0.043 |
| H9 |
-0.023 |
0.639 |
-1.328 |
| H10 |
-0.939 |
-0.279 |
1.452 |
| H11 |
-0.621 |
-1.349 |
0.095 |
| H12 |
-3.083 |
-0.890 |
0.301 |
| H13 |
-2.785 |
0.847 |
0.136 |
| H14 |
-2.467 |
-0.238 |
-1.224 |
| H15 |
2.840 |
-0.843 |
0.063 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
H15 |
| C1 | | 1.5218 | 2.5605 | 3.9190 | 1.4356 | 1.1013 | 1.1027 | 2.1339 | 2.1422 | 2.7879 | 2.7852 | 4.7367 | 4.2364 | 4.2369 | 1.9649 |
C2 | 1.5218 | | 1.5321 | 2.5481 | 2.4038 | 2.1605 | 2.1610 | 1.0990 | 1.0982 | 2.1567 | 2.1551 | 3.5037 | 2.8123 | 2.8152 | 3.2417 | C3 | 2.5605 | 1.5321 | | 1.5305 | 2.9990 | 3.5012 | 2.7808 | 2.1653 | 2.1663 | 1.0991 | 1.0953 | 2.1842 | 2.1823 | 2.1790 | 3.8531 | C4 | 3.9190 | 2.5481 | 1.5305 | | 4.3872 | 4.7045 | 4.2097 | 2.7854 | 2.7794 | 2.1641 | 2.1644 | 1.0951 | 1.0967 | 1.0964 | 5.2961 | O5 | 1.4356 | 2.4038 | 2.9990 | 4.3872 | | 2.0902 | 2.0916 | 3.3390 | 2.6183 | 3.3809 | 2.6597 | 5.0575 | 4.9966 | 4.5374 | 0.9634 | H6 | 1.1013 | 2.1605 | 3.5012 | 4.7045 | 2.0902 | | 1.7817 | 2.4136 | 2.4963 | 3.7620 | 3.8098 | 5.6220 | 4.8713 | 4.9128 | 2.3451 | H7 | 1.1027 | 2.1610 | 2.7808 | 4.2097 | 2.0916 | 1.7817 | | 2.5091 | 3.0600 | 2.5549 | 3.0844 | 4.8912 | 4.4400 | 4.7672 | 2.3218 | H8 | 2.1339 | 1.0990 | 2.1653 | 2.7854 | 3.3390 | 2.4136 | 2.5091 | | 1.7618 | 2.5064 | 3.0648 | 3.7900 | 2.6013 | 3.1518 | 4.0654 | H9 | 2.1422 | 1.0982 | 2.1663 | 2.7794 | 2.6183 | 2.4963 | 3.0600 | 1.7618 | | 3.0677 | 2.5163 | 3.7889 | 3.1331 | 2.5986 | 3.5105 | H10 | 2.7879 | 2.1567 | 1.0991 | 2.1641 | 3.3809 | 3.7620 | 2.5549 | 2.5064 | 3.0677 | | 1.7567 | 2.5091 | 2.5316 | 3.0817 | 4.0660 | H11 | 2.7852 | 2.1551 | 1.0953 | 2.1644 | 2.6597 | 3.8098 | 3.0844 | 3.0648 | 2.5163 | 1.7567 | | 2.5129 | 3.0831 | 2.5259 | 3.4980 | H12 | 4.7367 | 3.5037 | 2.1842 | 1.0951 | 5.0575 | 5.6220 | 4.8912 | 3.7900 | 3.7889 | 2.5091 | 2.5129 | | 1.7702 | 1.7692 | 5.9282 | H13 | 4.2364 | 2.8123 | 2.1823 | 1.0967 | 4.9966 | 4.8713 | 4.4400 | 2.6013 | 3.1331 | 2.5316 | 3.0831 | 1.7702 | | 1.7685 | 5.8741 | H14 | 4.2369 | 2.8152 | 2.1790 | 1.0964 | 4.5374 | 4.9128 | 4.7672 | 3.1518 | 2.5986 | 3.0817 | 2.5259 | 1.7692 | 1.7685 | | 5.4940 | H15 | 1.9649 | 3.2417 | 3.8531 | 5.2961 | 0.9634 | 2.3451 | 2.3218 | 4.0654 | 3.5105 | 4.0660 | 3.4980 | 5.9282 | 5.8741 | 5.4940 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
113.861 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
108.067 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H9 |
108.571 |
|
C1 |
O5 |
H15 |
109.452 |
| C2 |
C1 |
O5 |
109.036 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.325 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.387 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
112.611 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.008 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
109.104 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.573 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H9 |
109.751 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H12 |
111.401 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H13 |
111.248 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H14 |
111.016 |
|
C4 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.589 |
| C4 |
C3 |
H11 |
109.845 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
110.755 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.832 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.476 |
| H8 |
C2 |
H9 |
106.764 |
|
H10 |
C3 |
H11 |
106.494 |
| H12 |
C4 |
H13 |
107.744 |
|
H12 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.689 |
| H13 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.563 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.013 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.104 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.191 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.428 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.579 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.097 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.111 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.122 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.136 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.123 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.134 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.113 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.122 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.125 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.206 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.761 |
0.878 |
0.882 |
1.459 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-29.434 |
0.535 |
1.908 |
| y |
0.535 |
-34.197 |
-0.553 |
| z |
1.908 |
-0.553 |
-34.063 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.695 |
0.535 |
1.908 |
| y |
0.535 |
-2.448 |
-0.553 |
| z |
1.908 |
-0.553 |
-2.247 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.494 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 4.762 |
|---|
| xy | 0.535 |
|---|
| xz | 1.908 |
|---|
| yz | -0.553 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
10.178 |
0.061 |
0.159 |
| y |
0.061 |
8.266 |
-0.059 |
| z |
0.159 |
-0.059 |
7.914 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
170.954 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.075 |
