Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -232.410678 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -232.410678 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 175.521600 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3090 |
3050 |
13.91 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3056 |
3017 |
24.64 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
2988 |
2949 |
27.59 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
2975 |
2937 |
11.44 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
2952 |
2914 |
19.83 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1734 |
1712 |
156.03 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1472 |
1453 |
6.93 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1438 |
1420 |
22.05 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1418 |
1399 |
6.46 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1384 |
1366 |
5.01 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1347 |
1330 |
36.80 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1332 |
1315 |
16.02 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1156 |
1141 |
74.81 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1082 |
1067 |
1.29 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
982 |
969 |
2.45 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
911 |
900 |
18.46 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
737 |
728 |
4.96 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
574 |
567 |
5.79 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
398 |
393 |
3.48 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
244 |
241 |
5.02 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
3062 |
3023 |
27.08 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
3033 |
2994 |
11.92 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
2978 |
2939 |
8.93 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
1466 |
1447 |
7.49 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
1448 |
1429 |
8.90 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
1255 |
1239 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
1102 |
1088 |
0.09 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
926 |
914 |
2.89 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
732 |
723 |
2.47 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
460 |
454 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
201 |
198 |
0.17 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
90 |
89 |
0.10 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
65i |
64i |
0.05 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 23980.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.987) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 23668.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.078 |
1.630 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.558 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
0.497 |
-0.884 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
-0.613 |
-1.930 |
0.000 |
| O5 |
-1.182 |
0.837 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
0.625 |
2.622 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
1.723 |
1.517 |
0.880 |
| H8 |
1.723 |
1.517 |
-0.880 |
| H9 |
-0.192 |
-2.940 |
0.000 |
| H10 |
-1.252 |
-1.821 |
0.880 |
| H11 |
-1.252 |
-1.821 |
-0.880 |
| H12 |
1.158 |
-1.003 |
-0.871 |
| H13 |
1.158 |
-1.003 |
0.871 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
| C1 | | 1.5202 | 2.5801 | 3.9412 | 2.3955 | 1.0908 | 1.0965 | 1.0965 | 4.7431 | 4.2562 | 4.2562 | 2.7745 | 2.7745 |
C2 | 1.5202 | | 1.5252 | 2.5626 | 1.2150 | 2.1566 | 2.1595 | 2.1595 | 3.5034 | 2.8292 | 2.8292 | 2.1300 | 2.1300 | C3 | 2.5801 | 1.5252 | | 1.5253 | 2.4048 | 3.5084 | 2.8365 | 2.8365 | 2.1684 | 2.1709 | 2.1709 | 1.0999 | 1.0999 | C4 | 3.9412 | 2.5626 | 1.5253 | | 2.8254 | 4.7176 | 4.2566 | 4.2566 | 1.0943 | 1.0933 | 1.0933 | 2.1804 | 2.1804 | O5 | 2.3955 | 1.2150 | 2.4048 | 2.8254 | | 2.5403 | 3.1110 | 3.1110 | 3.9051 | 2.8014 | 2.8014 | 3.1022 | 3.1022 | H6 | 1.0908 | 2.1566 | 3.5084 | 4.7176 | 2.5403 | | 1.7885 | 1.7885 | 5.6218 | 4.9033 | 4.9033 | 3.7663 | 3.7663 | H7 | 1.0965 | 2.1595 | 2.8365 | 4.2566 | 3.1110 | 1.7885 | | 1.7596 | 4.9308 | 4.4722 | 4.8061 | 3.1209 | 2.5835 | H8 | 1.0965 | 2.1595 | 2.8365 | 4.2566 | 3.1110 | 1.7885 | 1.7596 | | 4.9308 | 4.8061 | 4.4722 | 2.5835 | 3.1209 | H9 | 4.7431 | 3.5034 | 2.1684 | 1.0943 | 3.9051 | 5.6218 | 4.9308 | 4.9308 | | 1.7752 | 1.7752 | 2.5163 | 2.5163 | H10 | 4.2562 | 2.8292 | 2.1709 | 1.0933 | 2.8014 | 4.9033 | 4.4722 | 4.8061 | 1.7752 | | 1.7607 | 3.0895 | 2.5452 | H11 | 4.2562 | 2.8292 | 2.1709 | 1.0933 | 2.8014 | 4.9033 | 4.8061 | 4.4722 | 1.7752 | 1.7607 | | 2.5452 | 3.0895 | H12 | 2.7745 | 2.1300 | 1.0999 | 2.1804 | 3.1022 | 3.7663 | 3.1209 | 2.5835 | 2.5163 | 3.0895 | 2.5452 | | 1.7421 | H13 | 2.7745 | 2.1300 | 1.0999 | 2.1804 | 3.1022 | 3.7663 | 2.5835 | 3.1209 | 2.5163 | 2.5452 | 3.0895 | 1.7421 | |
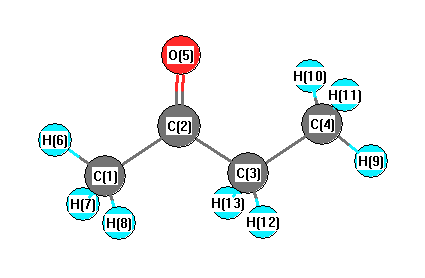 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
115.640 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
O5 |
121.938 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
110.030 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.333 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H8 |
110.333 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
114.143 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H12 |
107.555 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H13 |
107.555 |
| C3 |
C2 |
O5 |
122.422 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H9 |
110.574 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H10 |
110.943 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H11 |
110.943 |
| C4 |
C3 |
H12 |
111.079 |
|
C4 |
C3 |
H13 |
111.079 |
| H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.636 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H8 |
109.636 |
| H7 |
C1 |
H8 |
106.818 |
|
H9 |
C4 |
H10 |
108.451 |
| H9 |
C4 |
H11 |
108.451 |
|
H10 |
C4 |
H11 |
107.367 |
| H12 |
C3 |
H13 |
104.931 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.281 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.384 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.159 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.296 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.702 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.128 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.143 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.143 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.113 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.126 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.126 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.137 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.137 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.755 |
-0.759 |
0.000 |
2.858 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-34.391 |
2.522 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.522 |
-31.600 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-30.828 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.177 |
2.522 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.522 |
1.010 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.168 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 4.335 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.791 |
|---|
| xy | 2.522 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.823 |
0.491 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.491 |
9.401 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.605 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
138.080 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
11.751 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -232.410697 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -232.410697 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 175.542383 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3091 |
3051 |
13.84 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3064 |
3024 |
26.85 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3057 |
3018 |
24.59 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3034 |
2994 |
12.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
2989 |
2950 |
27.70 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2978 |
2939 |
8.99 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2976 |
2937 |
11.35 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2952 |
2914 |
19.70 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1734 |
1712 |
155.92 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1473 |
1454 |
7.02 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1465 |
1446 |
7.55 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1448 |
1429 |
8.86 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1438 |
1420 |
22.91 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1420 |
1401 |
5.33 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1386 |
1368 |
5.04 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1351 |
1333 |
36.36 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1334 |
1317 |
16.77 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1259 |
1243 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1156 |
1141 |
74.59 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1103 |
1089 |
0.09 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1082 |
1068 |
1.28 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
982 |
969 |
2.42 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
929 |
917 |
2.91 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
912 |
900 |
18.55 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
739 |
729 |
4.92 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
736 |
726 |
2.41 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
575 |
567 |
5.87 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
462 |
456 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
398 |
393 |
3.49 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
245 |
242 |
5.07 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
199 |
196 |
0.16 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
88 |
87 |
0.13 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
55i |
54i |
0.03 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 23999.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.987) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 23687.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-1.886 |
-0.511 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
-0.529 |
0.175 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
0.683 |
-0.749 |
-0.000 |
| C4 |
2.025 |
-0.024 |
0.000 |
| O5 |
-0.423 |
1.385 |
-0.000 |
| H6 |
-2.685 |
0.231 |
-0.000 |
| H7 |
-1.983 |
-1.159 |
-0.879 |
| H8 |
-1.983 |
-1.158 |
0.880 |
| H9 |
2.851 |
-0.741 |
-0.000 |
| H10 |
2.122 |
0.617 |
-0.880 |
| H11 |
2.122 |
0.617 |
0.880 |
| H12 |
0.590 |
-1.415 |
0.871 |
| H13 |
0.590 |
-1.415 |
-0.871 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
| C1 | | 1.5199 | 2.5802 | 3.9410 | 2.3949 | 1.0907 | 1.0965 | 1.0965 | 4.7426 | 4.2560 | 4.2559 | 2.7755 | 2.7756 |
C2 | 1.5199 | | 1.5247 | 2.5621 | 1.2150 | 2.1560 | 2.1598 | 2.1597 | 3.5025 | 2.8289 | 2.8290 | 2.1301 | 2.1301 | C3 | 2.5802 | 1.5247 | | 1.5252 | 2.4040 | 3.5080 | 2.8374 | 2.8378 | 2.1678 | 2.1709 | 2.1709 | 1.1000 | 1.1000 | C4 | 3.9410 | 2.5621 | 1.5252 | | 2.8242 | 4.7166 | 4.2575 | 4.2577 | 1.0942 | 1.0933 | 1.0933 | 2.1801 | 2.1801 | O5 | 2.3949 | 1.2150 | 2.4040 | 2.8242 | | 2.5391 | 3.1112 | 3.1108 | 3.9038 | 2.8003 | 2.8006 | 3.1021 | 3.1019 | H6 | 1.0907 | 2.1560 | 3.5080 | 4.7166 | 2.5391 | | 1.7882 | 1.7882 | 5.6207 | 4.9021 | 4.9023 | 3.7672 | 3.7670 | H7 | 1.0965 | 2.1598 | 2.8374 | 4.2575 | 3.1112 | 1.7882 | | 1.7591 | 4.9313 | 4.4732 | 4.8068 | 3.1220 | 2.5856 | H8 | 1.0965 | 2.1597 | 2.8378 | 4.2577 | 3.1108 | 1.7882 | 1.7591 | | 4.9317 | 4.8070 | 4.4730 | 2.5860 | 3.1230 | H9 | 4.7426 | 3.5025 | 2.1678 | 1.0942 | 3.9038 | 5.6207 | 4.9313 | 4.9317 | | 1.7752 | 1.7752 | 2.5151 | 2.5151 | H10 | 4.2560 | 2.8289 | 2.1709 | 1.0933 | 2.8003 | 4.9021 | 4.4732 | 4.8070 | 1.7752 | | 1.7607 | 3.0893 | 2.5450 | H11 | 4.2559 | 2.8290 | 2.1709 | 1.0933 | 2.8006 | 4.9023 | 4.8068 | 4.4730 | 1.7752 | 1.7607 | | 2.5450 | 3.0893 | H12 | 2.7755 | 2.1301 | 1.1000 | 2.1801 | 3.1021 | 3.7672 | 3.1220 | 2.5860 | 2.5151 | 3.0893 | 2.5450 | | 1.7417 | H13 | 2.7756 | 2.1301 | 1.1000 | 2.1801 | 3.1019 | 3.7670 | 2.5856 | 3.1230 | 2.5151 | 2.5450 | 3.0893 | 1.7417 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
116.362 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
O5 |
121.522 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
110.254 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.183 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H8 |
110.178 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
114.441 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H12 |
107.369 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H13 |
107.370 |
| C3 |
C2 |
O5 |
122.116 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H9 |
110.770 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H10 |
110.900 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H11 |
110.901 |
| C4 |
C3 |
H12 |
111.189 |
|
C4 |
C3 |
H13 |
111.190 |
| H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.673 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H8 |
109.669 |
| H7 |
C1 |
H8 |
106.823 |
|
H9 |
C4 |
H10 |
108.457 |
| H9 |
C4 |
H11 |
108.457 |
|
H10 |
C4 |
H11 |
107.236 |
| H12 |
C3 |
H13 |
104.726 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.281 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.384 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.158 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.296 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.703 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.128 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.143 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.143 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.113 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.126 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.126 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.137 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.137 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.146 |
-2.855 |
0.000 |
2.858 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-30.368 |
1.192 |
-0.000 |
| y |
1.192 |
-35.614 |
0.001 |
| z |
-0.000 |
0.001 |
-30.829 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.853 |
1.192 |
-0.000 |
| y |
1.192 |
-5.015 |
0.001 |
| z |
-0.000 |
0.001 |
2.162 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 4.325 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.245 |
|---|
| xy | 1.192 |
|---|
| xz | -0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.001 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.635 |
0.222 |
-0.000 |
| y |
0.222 |
8.587 |
-0.000 |
| z |
-0.000 |
-0.000 |
6.604 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
138.053 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
11.750 |
